Abstract
Drug dependence refers to a process in which an increasing proportion of an individual’s behavior is controlled by drug use vs. other maintaining events. Stimulus-control research is critical for an understanding of drug dependence because discriminative and conditioned stimuli are recognized as playing an important role in maintenance of drug use. Historically, the idea that stimuli can exert control over drug use has been conceptualized in terms of classical conditioning. Research employing the classical-conditioning model has demonstrated several interesting phenomena, but has not led to the development of effective treatment strategies. Consequently, this paper discusses the need to broaden our understanding of the role that environmental stimuli can play in the genesis, maintenance, and treatment of drug dependence. To do this, two recent experiments are reviewed that may facilitate this broadening. One experiment tested for the transfer of stimulus control over drug taking to stimuli in an equivalence class never paired with drug taking, and the other experiment examined the question of whether interoceptive (drug) stimuli can enter into equivalence relations with exteroceptive (visual) stimuli. Using the results of these two experiments as examples, the remaining discussion focuses on the role of stimulus control in the etiology and treatment of drug dependence and drug relapse. In concluding, a model is presented-based partly on the behavioral treatment of cocaine dependence-that may be more effective in eliminating stimulus control over drug use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANDREWS, J. S., & STEPHENS, D. N. (1990). Drug discrimination models in anxiety and depression. Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 47, 276–280.
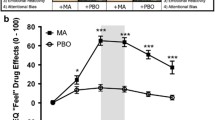
BICKEL, W. K., DEGRANDPRE, R. J., MORTENSEN, A., & HIGGINS, S. T. (1993). Emergent stimulus control over drug taking via equivalence. Manuscript submitted for publication.
BICKEL, W. K., & KELLY, T. H. (1988). The relationship of stimulus control to the treatment of substance abuse. In B. A. Ray (Ed.), Learning factors in substance abuse (pp.122–140). (National Institute on Drug Abuse Monograph, 84). Washington, DC: U. S. Government Printing Office.
BICKEL, W. K., OLIVETO, A. H., KAMIEN, J. B., HIGGINS, S. T., & HUGHES, J. R. (1993). A novel-response procedure enhances the selectivity and sensitivity of a triazolam discrimination in humans. The Journal of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 264, 360–367.
BUSH, K. M. (1993: this issue). Stimulus equivalence and cross-modal transfer. The Psychological Record, 43, 567–584.
CARROLL, M. E. (in press). The economic context of drug and nondrug reinforcers affects acquisition and maintenance of drug-reinforced behavior and withdrawal effects. Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
CHILDRESS, A. R., MCLELLAN, A. T., EHRMAN, R., & O’BRIEN, C. P. (1988). Classically conditioned responses in opioid and cocaine dependence: A role for relapse. In B. A. Ray (Ed.), Learning factors in substance abuse (pp. 122–140). (National Institute on Drug Abuse Monograph, 84). Washington, DC: U. S. Government Printing Office.
DeGRANDPRE, R. J., BICKEL, W. K., & HIGGINS, S. T. (1992). Emergent equivalence relations between interoceptive (drug) stimuli and exteroceptive (visual) stimuli. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 58, 9–18.
DeGRANDPRE, R. J., & BICKEL, W. K. (in press). Drug dependence as consumer demand. In L. Green & J. Kagel (Eds.), Advances in behavioral economics (Vol. 3).
DE WIT, H., & STEWART, J. (1981). Reinstatement of cocaine reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology, 75, 134–143.
DRUMMOND, D. C., COOPER, T., & GLAUTIER, S. P. (1990). Conditioned learning in alcohol dependence: Implications for cue exposure treatment. British Journal of Addictions, 85, 725–743.
EDWARDS, E. F., ARIF, A., & HODGSON, R. (1981). Nomenclature and classification of drug-and alcohol-related problems: A Who memorandum. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 59, 225–242.
EMMETT-OGLESBY, M. W., MATHIS, D. A., MOON, R. T. Y., & LAL, H. (1990). Animal models of drug withdrawal symptoms. Psychopharmacology, 101, 292–309.
FIELDS, L., ADAMS, B. J., VERHAVE, T., & NEWMAN, S. (1993). Are stimuli in equivalence classes equally related to each other? The Psychological Record, 43, 85–105.
FIELDS, L., ADAMS, B., BROWN, J. L., & VERHAVE, T. (1993). The generalization of emergent relations in equivalence classes: Stimulus substitutability. The Psychological Record, 43, 235–254.
HARRISON, R. J., & GREEN, G. (1990). Development of conditional and equivalence relations without differential reinforcement. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 54, 225–237.
HAYES, L. J., TILLEY, K., & HAYES, S. C. (1988). Extending stimulus equivalence class membership to gustatory stimuli. The Psychological Record, 38, 473–482.
HAYES, S. C., KOHLENBERG, B. S., & HAYES, L. J. (1991). The transfer of specific and general consequential functions through simple conditional equivalence relations. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 56, 119–137.
HIGGINS, S. T., BUDNEY, A. J., & BICKEL, W. K. (in press). Applying behavioral concepts and principles to the treatment of cocaine dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
HIGGINS, S. T., BUDNEY, A. J., BICKEL, W. K., HUGHES, J. R., Foerg. F., & Badger, G. (1993). Achieving cocaine abstinence with a behavioral approach. American Journal of Psychiatry, 150, 763–769.
HIGGINS, S. T., DELANEY, D. D., BUDNEY, A. J., BICKEL, W. K., HUGHES, J. R., FOERG, F., & FENWICK, J. W. (1991). A behavioral approach to achieving initial cocaine abstinence. American Journal of Psychiatry, 148, 1218–1224.
HUNT, G. H., & ODEROFF, M. E. (1962). Follow-up study of narcotic drug addict after hospitalization. Public Health Reports, 77, 41–54.
JAFFE, J. H. (1990). Drug addiction and drug abuse. In A. G. Goodman, T. W. Rail, A. S. Nies, & P. Taylor (Eds.), The pharmacological basis of therapeutics (8th ed., pp. 522–573). New York: Pergamon Press.
KATZ, J. L., & GOLDBERG, S. R. (1991). Second-order schedules of drug injection: Implications for understanding reinforcing effects of abused drugs. In N. Mello (Ed.), Advances in substance abuse: Behavioral and biological research (Vol. 4, pp. 522–573). London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers.
LUDWIG, A. M., WIKLER, A., & STARK, L. H. (1974). The first drink: Psychobiological aspects of craving. Archives of General Psychiatry, 30, 539–547.
O’BRIEN, C. P., CHILDRESS, A. R., MCLELLAN, A. T., EHRMAN, R., & TERNES, W. J. (1988). Types of conditioning found in drug-dependent humans. In B. A. Ray (Ed.), Learning factors in substance abuse (pp. 44-61). (National Institute on Drug Abuse Monograph, 84). Washington, DC: U. S. Government Printing Office.
OVERTON, D. A. (1984). State dependent learning and drug discrimination. In L. L. Iverson, S. D. Iverson, & S. H. Snyder (Eds.), Handbook of psychopharmacology (pp. 59–69). New York: Plenum Press.
PRESTON, K. L., & BIGELOW, G. E. (1991). Subjective and discriminative effects of drugs. Behavioural Pharmacology, 2, 293–313.
ROBINS, L. N., HELZER, J. E., HESSELBROCK, M., & WISH, E. D. (1977). Vietnam veterans three years after Vietnam: How our study changed our view of heroin. In L. Harris (Ed.), Problems of drug dependence. Richmond, VA: Committee on Problems of Drug Dependence.
SAUNDERS, R. R., SAUNDERS, K. J., KIRBY, K. C., & SPRADLIN, J. E. (1988). The merger and development of equivalence classes by unreinforced conditional selection of comparison stimuli. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 50, 145–162.
SAUNDERS, R. R., WÄCHTER, J., & SPRADLIN, J. E. (1988). Establishing auditory stimulus control over an eight member equivalence class via conditional discrimination procedures. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 49, 95–116.
SEIGEL, S. (1988). Drug anticipation and the treatment of dependence. In B. A. Ray (Ed.), Learning factors in substance abuse (pp. 1–28) (National Institute on Drug Abuse Monograph, 84). Washington, D. C.: U. S. Government Printing Office.
SIDMAN, M. (1990). Equivalence relations: Where do they come from? In D. E. Blackman & H. Lejeune (Eds.), Behavior analysis in theory and practice. Hove, UK: Lawrence Erlbaum Ltd.
SIDMAN, M., & TAILBY, W. (1982). Conditional discrimination vs. matching to sample: An expansion of the testing paradigm. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 7, 5–22.
SISSON, R. W., & AZRIN, N. H. (1989). The community reinforcement approach. In R. K. Hester & W. R. Miller (Eds.), Handbook of alcoholism treatment approaches: Effective alternatives (pp. 242–258). New York: Pergamon Press.
SKINNER, B. F. (1945). The operational analysis of psychological terms. Psychological Review, 52, 270–277.
SKINNER, B. F. (1953). Science and human behavior. New York: Macmillan.
SKINNER, B. F. (1974). About behaviorism. New York: Knopf.
STRETCH, R., GERBER, G. J., & WOOD, S. M. (1971). Factors affecting behavior maintained by response-contingent intravenous infusions of amphetamine by squirrel monkeys. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 49, 581–589.
WIKLER, A. (1965). Conditioning factors in opiate addiction and relapse. In D. I. Wiher & G. Kassebaum (Eds.), Narcotics. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was funded by a National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Training Grant T32 DA-07242; NIDA Grant RO1 06205.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DeGrandpre, R.J., Bickel, W.K. Stimulus Control And Drug Dependence. Psychol Rec 43, 651–666 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395905
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395905