Abstract
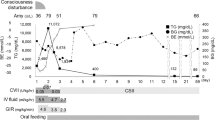
Edema of variable severity is an uncommon complication of insulin treatment. Increased sodium reabsorption, transient proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia are the most frequently reported laboratory disorders at the time of edema formation. This case report describes a 44-yr-old man with a 4-month history of anorexia, polyuria, polydipsia and weight loss of 25 kg who presented with diabetic ketoacidosis. On admission, there were no clinical or laboratory signs of volume depletion. Following insulin treatment he developed marked insulin edema and a cluster of abnormalities, including decreased sodium excretion, hypokalemia, hypouricemia, proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia and anemia. The diagnostic work-up showed the presence of high renin and aldosterone values despite the absence of evident hypovolemia and no evidence of gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, renal, thyroid, hepatic or other endocrine disorder. Complement values were normal; autonomic neuropathy and venoocclusive intraabdominal lesions were excluded and no other drugs except insulin were administered. Initiation of spironolactone was associated with prompt resolution of the edema and gradual correction of the laboratory abnormalities. Our findings show that hyperaldosteronism may occur in patients with insulin edema, even in the absence of volume depletion, contributing to the development of increased sodium reabsorption and of other laboratory disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leifer A. A case of insulin edema. JAMA 1928, 90: 610.
Bronstein HD, Kantrowitz PA, Schaffner F. Marked enlargement of the liver and transient ascites associated with the treatment of diabetic acidosis. N Engl J Med 1959, 261: 1314–8.
Shaper AG. The insulin-oedema syndrome in African diabetic subjects. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1966, 60: 519–25.
Saudeck CD, Boulter PR, Knopp RH, Arky RA. Sodium retention accompanying insulin treatment of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1974, 23: 240–6.
Bleach NR, Dunn PJ, Khalafalla ME, McConkey B. Insulin oedema. Br Med J 1979, 2: 177–8.
Sacerdote A, Bleicher SJ. Congestive heart failure as a complication of improved diabetic control. Diabetes Care 1983, 6: 419–22.
Sheehan JP, Sisam DA, Schumacher OP. Insulin-induced cardiac failure. Am J Med 1985, 79: 147–8.
Wheatley T, Edwards OM. Insulin oedema and its clinical significance: metabolic studies in three cases. Diabet Med 1985, 2: 400–4.
Bosquet F, Grimaldi A, Thervet F, Croisier G. Generalized edematous syndrome: an early and uncommon complication of insulin therapy. Presse Med 1985, 14: 546.
Cosmi F, Bianco C, Mollaioli M, Aimi M, Corbacelli C, Ricca M. Edematogenic syndrome in diabetics treated with insulin: a little-known complication. Minerva Med 1986, 77: 171–4.
Evans DJ, Pritchard-Jones K, Trotman-Dickenson B. Insulin edema. Postgrad Med J 1986, 62: 665–8.
Sharon M, Cassorla FG, Rose SR, Loriaux DL. Edema associated with improved glycemic control in an adolescent with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr 1987, 111: 403–4.
Ravi TS, Nelli P, Rai P, Kundaje GN. Insulin oedema: an uncommon complication of insulin therapy. J Assoc Physicians India 1991, 39: 411–2.
Saule H. Insulin-induced edema in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 1991, 116: 1191–4.
Jobard JM, Cleu D, Terrier S, Alves T, Abriel J, Ory JP. Edema during treatment of first onset diabetes melitus with insulin. Presse Med 1992, 21: 764.
Hopkins DF, Cotton SJ, Williams G. Effective treatment of insulin induced edema using ephedrine. Diabetes Care 1993, 16: 1026–8.
Lwo FS, Lee YJ. Insulin edema in a diabetic child. J Formos Med Assoc 1995, 94: 509–11.
Suzuki Y, Kadowaki H, Taniyama M, et al. Insulin edema in diabetes mellitus associated with the 3243 mitochondrial tRNA [Leu(UUR)] mutation; case reports. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1995, 29: 137–42.
Cotellesa M, Mazzella M, Mulas R, Caratozzolo A, Romano C. Insulin edema in three adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Minerva Pediatr 1995, 47: 245–8.
Hirshberg B, Muszkat M, Marom T, Shalit M. Natural course of insulin edema. J Endocrinol Invest 2000, 23: 187–8.
Juliusson PB, Bjerkens R, Sovik O, Kvistad PH. Generalized edema following insulin treatment of newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 2001, 121: 919–20.
Braunwald E. Edema. In: Petersdorf RG, Adams RD, Braunwald E et al. eds. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 15nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill. 2001, 217–22.
Rosenbloom AL, Giordano B. Chronic overtreatment with insulin in children and adolescents. Am J Dis Child 1977; 131: 881–5.
Lawrence JR, Dunnigan MG. Diabetic (insulin) oedema. Br Med J 1979, 2: 445.
Trevizan R, Fioretto P, Semplicini A, et al. Role of insuline and atrial natriuretic peptide in sodium retention in insulintreated IDDM patients during isotonic volume expansion. Diabetes 1990, 39: 289–98.
Gupta AK, Clark RV, Kirchner KA. Effects of insulin on renal sodium excretion. Hypertension 1992, 19 (Suppl 1): 178–182.
Christlieb AR, Assal JP, Katsilambros N, Williams GH, Kozak GP, Suzuki T. Plasma renin activity and blood volume in uncontrolled diabetes. Ketoacidosis, a state of secondary aldosteronism. Diabetes 1975, 24: 190–3.
Zerbe RL, Vinicor F, Robertson GL. Plasma vasopressin in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1979, 26: 503–8.
MacGregor GA, Markandu ND, Roulstan JE, Jones JC, de Wardener HE. Is ‘idiopathic’ oedema idiopathic? Lancet 1979, 1: 397–400.
Elisaf MS, Tsatsoulis AA, Katopodis KP, Siamopoulos KC. Acid-base and electrolyte disturbances in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1996, 34: 23–7.
Laakso M, Edelman S, Brechtel G, Baron A. Impaired insulin- mediated muscle blood flow in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 1992, 41: 1076–83.
Dela F, Larsen JJ, Mikines KL, Galbo H. Normal effect of insulin to stimulate leg blood flow in NIDDM. Diabetes 1995, 44: 221–6.
Edmonds ME, Archer AG, Watkins PJ. Ephedrine: a new treatment for diabetic neuropathic oedema. Lancet 1983, 1: 548–51.
Quinones-Galvan A, Ferrannini E. Renal effects of insulin in man. J Nephrol 1997, 10: 188–91.
Gonzalez-Sicilia L, Garcia-Estan J, Martinez-Blazquez A, et al. Renal metabolism of uric acid in type I insulin-dependent diabetic patients: relation to metabolic compensation. Horm Metab Res 1997, 29: 520–3.
Namba M, Kikuchi K, Komura H, et al. Study on uric acid metabolism in patients with primary aldosteronism. Nippon Naibunpi Gakkai Zasshi 1992, 68: 51–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalambokis, G., Tsatsoulis, A., Economou, G. et al. A case of insulin edema with inappropriate hyperaldosteronism. J Endocrinol Invest 27, 957–960 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347540
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347540