Abstract
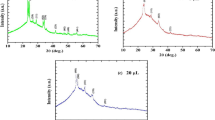
In this study, we use dipping and spinning methods to coat glass slides with sol-gel ZnO thin films, composed of zinc acetate dihydrate, monoethanolamine (MEA), de-ionized water and isopropanol. The effect of the annealing temperature on the structural morphology and optical properties of these films is investigated. These ZnO films were preheated at 275 °C for 10 min and annealed either at 350, 450 or 550 °C for 60 min. As-deposited films, formed by amorphous zinc oxide-acetate submicron particles, are transformed into a highly-oriented ZnO after thermal treatment. The surface morphology, phase structure and optical properties of the thin films were investigated by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and optical transmittance. Both techniques produced nanostructured ZnO thin films with well-defined orientation. The annealed films were transparent in the visible range with an absorption edge at about 375 nm and a transmittance of ca 85–90% with an average diameter of 40 nm. XRD results show the film was composed of polycrystalline wurtzite, with a preferential c-axis orientation of (002) and a single sharp XRD peak at 34.40, corresponding to the hexagonal ZnO. The grain size is increased by the annealing temperature. Both coating techniques create sol-gel ZnO films with the potential for application as transparent electrodes in optic and electronic devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.C. Klein, A.S. Edelstein, R.C. Cammarata (Eds.), Processing of Nanostructured Sol-Gel Materials, Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications, Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol and Philadelphia, 1996, pp. 147–164.
G.M. Chow, Chemical Synthesis and Processing of Nanostructured Powders and Films, NATO Advanced Study Institute on Nanostructured Materials Science and Technology, St. Petersburg, Russia (Aug. 1997), NATO ASI Series 3. High Technology-Vol. 50, Kluwer Publications, Netherlands, 1998.
L.H. Larry, K.W. Jon, Chem. Rev. 90 (1990) 33.
M.J. Alam, D.C. Cameron, Surf. Coat. Technol. 142 (2001) 776.
C. Shaoqiang, Z. Jian, F. Xiao, W. Xiaohua, L. Laiqiang, S. Yanling, X. Qingsong, W. Chang, Z. Jianzhong, Z. Ziqiang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 241 (2005) 384.
K. Keis, C. Bauer, G. Boschloo, A. Hagfeldt, K. Westermark, H. Rensmo, H. Siegbahn, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 148 (2002) 57.
Y.S. Kim, W.P. Tai, S.J. Shu, Thin Solid Films 491 (2005) 153.
F. Peng, H. Wang, H. Yu, S. Chen, Mater. Res. Bull. 41 (2006) 2123.
M. Suchea, S. Christoulakis, K. Moschovis, N. Katsarakis, G. Kiriakidis, Thin Solid Films 515 (2006) 551.
R. Ghosh, G.K. Paul, D. Basak, Mater. Res. Bull. 40 (2005) 1905.
Y.S. Kim, W.P. Tai, S.J. Shu, Thin Solid Films 491 (2005) 153.
M.H. Aslan, A.Y. Oral, E. Men-Sur, A.G. Ula, E. Ba- Saran, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 82 (2004) 543.
A.E. Jimenez Gonzalez, J.A. Soto Urueta, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 52 (1998) 345.
B.S. Li, Y.C. Liu, D.Z. Shen, J.Y. Zhang, Y.M. Lu, X.W. Fan, J. Cryst. Growth 249 (2003) 179.
B.M. Atae, A.M. Bagamadova, A.M. Djabrailov, Thin Solid Films 260 (1995) 19.
V.V. Siva Kumar, F. Singh, A. Kumar, D.K. Avasthi, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 244 (2006) 91.
A. Ashour, M.A. Kaid, N.Z. El-Sayed, A.A. Ibrahim, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252 (2006) 7844.
Y. Natsume, H. Ssakata, T. Hirayama, Phys. Statuse Solidi. 148 (1995) 485.
W. Shena, Y. Zhaoa, T. Zhang, Thin Solid Films 483 (2005) 382.
X. Liu, Z. Jin, Z. Liu, K. Yu, S. Bu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252 (2006) 8668.
S. Fujihara, C. Sasaki, T. Kimura, Appl. Surf. Sci. 180 (2001) 341.
Z. Jiwei, Z. Liangying, Y. Xi, Ceram. Int. 26 (2000) 883.
Y.S. Kim, W.P. Tai, S.J. Shu, Thin Solid Films 491 (2005) 153.
D. Bao, H. Gu, A. Kuang, Thin Solid Films 312 (1998) 37.
B. Houng, C. Huang, Surf. Coat. Technol. 201 (2006) 3188.
U.N. Maiti, P.K. Ghosh, S. Nandy, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Physica. B 387 (2007) 103.
S. Rahimnejad, S. Rahman Setayesh, M.R. Gholami, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 5 (2008) 367.
Q.-Z. Zhai, P. Wang, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 5 (2008) 268.
Z.Y. Ning, S.H. Cheng, S.B. Ge, Y. Chao, Z.Q. Gang, Y.X. Zhang, Z.G. Liu, Thin Solid Films 307 (1997) 50.
V. Lujala, J. Skarp, M. Tammenmaa, T. Suntola, Appl. Surf. Sci. 82/83 (1994) 34.
K. Kaiya, N. Yoshii, N. Takahashi, T. Nakamura, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19 (2000) 2089.
S. Chaisitsak, T. Sugiyama, A. Yamada, M. Konagai, J. Appl. Phys. 38 (1999) 4989.
M.H. Habibi, N. Talebian, Dyes Pigm. 73 (2007) 186.
M.H. Habibi, N. Talebian, J.-H. Choi, Dyes Pigm. 73 (2007) 103.
M.H. Habibi, N. Talebian, J.-H. Choi, Thin Solid Films 515 (2006) 1461.
M.H. Habibi, M. Khaledi Sardashti, J. Nanomater. ID 356765 (2008).
M.G. Lagally, J. Appl. Phys. 32 (1993) 1493. [38]_S. Fujihara, C. Sasaki, T. Kimura, Appl. Surf. Sci. 180 (2001) 341.
H.Y. Bae, G.M. Choi, Sens. Actuators B 55 (1999) 47.
T. Yamamoto, T. Shiosaki, A. Kawabata, J. Appl. Phys. 51 (1980) 3113.
H.Z. Wu, K.M. He, D.J. Qiu, D.M. Huang, J. Cryst. Growth 217 (2000) 131.
Y. Igasaki, J. Cryst. Growth 116 (1992) 357.
S. Amirhaghi, V. Cracium, D. Cracium, J. Elders, W. Boyd, Microelectron. Eng. 25 (1994) 321.
C. Shaoqiang, Z. Jian, F. Xiao, W. Xiaohua, L. Laiqiang, S. Yanling, X. Qingsong, W. Chang, Z. Jianzhong, Z. Ziqiang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 241 (2005) 384.
T. Schuler, M.A. Aegerter, Thin Solid Films 351 (1999) 125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habibi, M.H., Khaledi Sardashti, M. Structure and morphology of nanostructured zinc oxide thin films Prepared by dip-vs. spin-coating methods. JICS 5, 603–609 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03246140
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03246140