Abstract
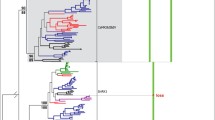
A full-length calmodulin binding protein kinase cDNA,AtCBK1, fromArabidopsis has been isolated by screening of anArabidopsis cDNA library and by 5′-RACE. Northern blot andin situ hybridization indicated that the expression ofAtCBK1 was more abundant in the vascular bundles and the meristems than in other tissues. The phylogenetic analyses reveal thatAtCBK1 is different from animal CaMKs and it falls into CRK subgroup, indicating that they may come from different ancestors. The result suggests thatAtCBK1 encodes a CaM-binding serine/threonine protein kinase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, D. Y., Ma, L. G., Extracellular calmodulin: A polypeptide signal in plants? Science in China, Series C, 2001, 44(5): 449.
Zielinski, R. E., Calmodulin and calmlin-binding proteins in plants, Annu. Rev. Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 1998, 49: 697.
Reddy, A. S. N., Calcium: silver bullet in signaling, Plant Science, 2001, 160(3): 381.
Snedden, W. A., Fromm, H., Calmodulin as a versatile calcium signal transducer in plants, New Phytologist, 2001, 151: 35.
Lee, S. H., Kim, M. C., Cho, M. J. et al., Competitive binding of calmodulin isoforms to calmodulin-binding proteins: implication for the function of calmodulin isoforms in plants, Biochemica et Biophysica Acta, 1999, 1433: 56.
Lee, S. H., Johnson, J. D., Cho, M. J. et al., Differential regulation of Ca2+/ calmodulin-dependent enzymes by plant calmodulin isoforms and free Ca2+ concentration, Biochemical Journal, 2000, 350: 299.
Reddy, V. S., Reddy, A. S. N., Interaction of a Kinesin-like protein with calmodulin isforms from Arabidopsis, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274: 31727.
Liao, B., Zielinski, R. E., Production of recombinant calmodulin and its use to detect calmodulin-binding proteins, Methods in Cell Biology, Vol Plant Cell Biology (eds. D. W. Galbraith, D. Bourque, H. J. Bohnert), San Diego: Academic Press, 1995, 49: 481.
Reddy, V. S., Ali, G. S., Reddy, A. S. N., Genes encoding calmodulin-binding proteins in the Arabidopsis Genome, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 272(12): 9840.
Braun, A. P., Schulman, H., The multifunctional cacium/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: from form to function, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 1995, 57: 417.
Harmon, A. C., Gribskov, M., Gubrium, E. et al., The CDPK superfamily of protein kinases, New Phytologist, 2001, 151: 175.
Harmon, A. C., Gribskov, M., Harper, J. F., CDPK-a kinase for every Ca2+ signal? Trends in Plant Science, 2000, 5(4): 154.
Watillon, B., Kettmenn, R., Boxus, P. et al., Cloning and characterization of an apple (Malus domestica (L.) Brokh) cDNA encoding a calmodulin-binding protein domain similar to the calmodulin-binding domain of type II mammalian calcium/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, Plant Sci., 1992, 81: 227.
Lu, Y. T., Hidaka, H., Feldman, L. J., Characterization of a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase homolog from maize roots showing light-regulated gravitropism, Planta, 1996, 199: 18.
Lu, Y. T., Feldman, L. J., Light-regulated root gravitropism: a role for, and characterization of, a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase homolog, Planta, 1997, 203: 591.
Wang, L., Liang, S. P., Lu, Y. T., Characterization, physical location and expression of the genes encoding calcium/calmodulindependent protein kinase in maize (Zea mays L.), Planta, 2001, 213: 556.
Patil, S., Takezawa, D., Poovaiah, B. W., Chimeric plant calcium/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase gene with a neural visinin-like calcium-binding domain, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 1995, 92: 4897.
Poovaiah, B. W., Xia, M., Liu, Z. H. et al., Developmental regulation of the gene for chimeric calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in anthers, Planta, 1999, 209: 161.
Ramachandiran, S., Takezawa, D., Wang, W. et al., Function domains of plant chimeric calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: regulation by autoinhibitory and visinin-like domains, J. Biochem., 1997, 121: 984.
Sathyanarayanan, P. V., Christine, R. C., Poovaiah, B. W., Plant chimeric Ca2+/Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: role of the neural visinin-like domain in regulating autophosphorylation and calmodulin affinity, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275: 30417.
Takezawa, D., Ramachandiran, S., Paranjape, V. et al., Dual regulation of a chimeric serine/threonine kinase by calcium and calcium/calmodulin, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, 271: 8126.
Wang, W., Poovaiah, B. W., Interaction of plant chimeric calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase with a homolog of eukaryotic elongtion factor-1 alpha, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274: 12001.
Yang, T., Poovaiah, B. W., Molecular and biochemical evidence for the involvement of calcium/calmodulin in auxin action, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275: 3137.
Zielinski, R. E., Production of recombinant plant calmodulin isoforms in bacteria, Methods in Molecular Biology, Calcium-Binding Proteins, Volume 1, Reviews and Case Studies (ed. H. J. Vogel), Totowa: Humana Press Inc., 2001, 172: 143.
Fromm, H., Chua, N. H., Cloning of plant cDNAs encoding calmodulin-binding proteins using35S-labeled recombinant calmodulin as a probe, Plant Mol. Boil. Rep, 1992, 10: 199.
Liu, B. F., Zhang, L., Lu, Y. T., Characterization of phosphorylation of a novel protein kinase in rice cells by capillary electrophoresis, J. Chromatogr., 2001, 918(2): 401.
Chen, S. R., Lu, Y. T., Yang, H. Y.,In situ hybridization of calmodulin mRNA in the development tobacco anthers, Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 44: 142.
O’Neil, K. T., DeGrado, F., How calmodulin binds its targets: sequence independent recognition of amphiphilic α-helices, Trends Biochem. Sci., 1990, 15: 59.
James, P., Vorherr, T., Carafoli, E., Calmodulin-binding domains: just two faced or multi-faceted? Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 1995, 20(1): 38.
Yang, W. N., Liang, S. P., Lu, Y. T., Immunohistochemical localization of Ca2+/calmodulin dependent kinase in tobacco, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(3): 230.
Planas-Silva, M. D., Means, A. R., Expression of a constitutive form of cakcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II leads to arrest of the cell cycle in G2, EMBO J., 1992, 11: 507.
Soderling, T. R., Stull, J. T., Structure and Regulation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases, Chem. Rev., 2001, 101: 2341.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Q., Wang, Y., Liang, S. et al. Characterization of a calmodulin binding protein kinase fromArabidopsis thalian . Chin.Sci.Bull. 48, 57–62 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183335
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183335