Abstract
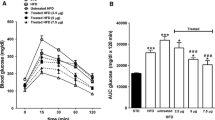
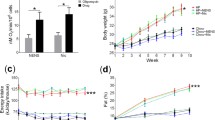
The combination of vanadate plus benzylamine has been reported to stimulate glucose transport in rodent adipocytes and to mimic other insulin actions in diverse studies. However, benzylamine alone activates glucose uptake in human fat cells and increases glucose tolerance in rabbits. The aim of this work was to unravel the benzylamine antihyperglycemic action and to test whether its chronic oral administration could restore the defective glucose handling of mice rendered slightly obese and diabetic by very high-fat diet (VHFD). When VHFD mice were i.p. injected with benzylamine at 0.7 to 700 μmol/kg before glucose tolerance test, they exhibited reduced hyperglycemic response without alteration of insulin secretion. Whole body glucose turnover, as assessed by the glucose isotopic dilution technique, was unchanged in mice perfused with benzylamine (total dose of 75 μmol/kg). However, their in vivo glycogen synthesis rate was increased. Benzylamine appeared therefore to directly facilitate glucose utilisation in peripheral tissues. When given chronically at 2000 or 4000 μmol/kg/d in drinking water, benzylamine elicited a slight reduction of water consumption but did not change body weight or adiposity and did not modify oxidative stress markers. Benzylamine treatment improved glucose tolerance but failed to normalize the elevated glucose fasting plasma levels of VHFD mice. There was no influence of benzylamine ingestion on lipolytic activity, basal and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, and on inflammatory adipokine expression in adipocytes. The improvement of glucose tolerance and the lack of adverse effects on adipocyte metabolism, reported here in VHFD mice allow to consider orally given benzylamine as a potential antidiabetic strategy which deserves to be further studied in other diabetic models.
Resumen
Se ha descrito que la combinación de vanadato y benzilamina estimula el transporte de glucosa en los adipocitos de roedor y que promueve otros efectos de tipo insulina. La benzilamina sola activa la captación de glucosa en adipocitos humanos e incrementa la tolerancia a la glucosa en el conejo. En este trabajo, se ha tratado de profundizar en la acción antihiperglucemiante de la benzilamina y a probar si su administración oral crónica podía normalizar la glucemia en ratones ligeramente obesos y diabéticos tras una dieta muy rica en grasa (VHFD). Cuando la benzilamina se administraba (i.p.; de 0,7 a 700 μmoles/kg) a ratones VHFD antes de realizar el test de tolerancia a la glucosa, la respuesta hiperglucémica se reducía sin alterar la secreción de insulina. Cuando los ratones VHFD se perfundían con glucosa radiactiva, la benzilamina (dosis total de 75 μmoles/kg) no cambió el turnover de glucosa pero aumentó la síntesis de glucógeno, facilitando la utilización de glucosa en los tejidos periféricos. Cuando se administró crónicamente a 2000 ó a 4000 μmoles/kg/día en el agua del bebedero, la benzilamina produjo una ligera reducción del consumo de agua pero no cambió el peso corporal o la adiposidad y no modificó los marcadores de estrés oxidativo. Este tratamiento mejoró la tolerancia a la glucosa pero no fue capaz de normalizar los niveles plasmáticos en ayunas de glucosa en los ratones VHFD. Asimismo, no hubo influencia de la ingestión de benzilamina sobre la actividad lipolítica o la captación de glucosa ni sobre la expresión de adipoquinas inflamatorias en adipocitos. En suma, la mejora de la tolerancia a la glucosa y la falta de efectos adversos, observados en ratones VHFD, permite considerar a la benzilamina administrada oralmente como una estrategia antidiabética potencial que requiere ser estudiada en profundidad en otros modelos diabéticos.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abella, A., Marti, L., Camps, M., Claret, M., Fernandez-Álvarez, J., Gomis, R., Gumà, A., Viguerie, N., Carpéné, C., Palacin, M., Testar, X., Zorzano, A. (2003): Diabetes, 52, 1004–1013.
Abella, A., Marti, L., Carpéné, C., Palacin, M., Testar, X., Zorzano, A. (2003): J. Physiol. Biochem., 59, 153–160.
Anwar, F., Latif, S., Ashraf, M., Gilani, A.H. (2007): Phytother. Res., 21, 17–25.
Bour, S., Daviaud, D., Gres, S., Lefort, C., Prévot, D., Zorzano, A., Wabitsch, M., Saulnier-Blache, J.-S., Valet, P., Carpéné, C. (2007): Biochimie, 89, 916–925.
Bour, S., Visentin, V., Prévot, D., Daviaud, D., Saulnier-Blache, J.-S., Guigné, C., Valet, P., Carpéné, C. (2005): J. Physiol. Biochem., 61, 371–379.
Burcelin, R., Crivelli, V., Dacosta, A., Roy-Tirelli, A., Thorens, B. (2002): Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 282, E834-E842.
Carpéné, C., Daviaud, D., Boucher, J., Bour, S., Visentin, V., Grès, S., Duffaut, C., Fontana, E., Testar, X., Saulnier-Blache, J.-S., Valet, P. (2006): Metabolism, 55, 1397–1405.
Enrique-Tarancón, G., Marti, L., Morin, N., Liczano, J., Unzeta, M., Sevilla, L., Camps, M., Palacin, M., Testar, X., Carpéné, C., Zorzano, A. (1998): J. Biol. Chem., 273, 8025–8032.
García-Vicente, S., Yraola, F., Marti, L., Gonzalez-Munoz, E., García-Barrado, M.J., Canto, C., Abella, A., Bour, S., Artuch, R., Sierra, C., Brandi, N., Carpéné, C., Moratinos, J., Camps, M., Palacin, M., Testar, X., Guma, A., Albericio, F., Royo, M., Mian, A., Zorzano, A. (2007): Diabetes, 56, 486–493.
Goldstein, B. J., Mahadev, K., Wu, X., Zhu, L., Motoshima, H. (2005): Antioxid. Redox Signal., 7, 1021–1031.
Iglesias-Osma, M.C., Bour, S., García-Barrado, M. J., Visentin, V., Pastor, M. F., Testar, X., Marti, L., Enrique-Tarancon, G., Valet, P., Moratinos, J., Carpéné, C. (2005): Pharmacol. Res., 52, 475–484.
Iglesias-Osma, M. C., García-Barrado, M. J., Visentin, V., Pastor-Mansilla, M. F., Bour, S., Prévot, D., Valet, P., Moratinos, J., Carpéné, C. (2004): J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 309, 1020–1028.
Morin, N., Lizcano, J. M., Fontana, E., Marti, L., Smih, F., Rouet, P., Prévot, D., Zorzano, A., Unzeta, M., Carpéné, C. (2001): J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 297, 563–572.
Morin, N., Visentin, V., Calise, D., Marti, L., Zorzano, A., Testar, X., Valet, P., Fischer, Y., Carpéné, C. (2002): J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 303, 1238–1247.
Soltesz, Z., Tabi, T., Halasz, A. S., Palfi, M., Kocsis, E., Magyar, K., Toth, M., Szökö, E. (2007): J. Neural Transm., 114, 851–855.
Soolen, C. M., Madanat, R., Marti, L., Kari, S., Yegutkin, G. G., Sariola, H., Zorzano, A., Jalkanen, S. (2004): FASEB J., 18, 702–704.
Subra, C., Fontana, E., Visentin, V., Testar, X., Carpéné, C. (2003): J. Physiol. Biochem., 59, 209–216.
Szökö, E., Tabi, T., Halasz, A. S., Palfi, M., Magyar, K. (2004): J. Chromatogr. A., 1051, 177–183.
Visentin, V., Prévot, D., Marti, L., Carpéné, C. (2003): Eur. J. Pharmacol., 466, 235–243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iffiú-Soltész, Z., Prévot, D., Grès, S. et al. Influence of acute and chronic administration of benzylamine on glucose tolerance in diabetic and obese mice fed on very high-fat diet. J. Physiol. Biochem. 63, 305–315 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165762
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165762