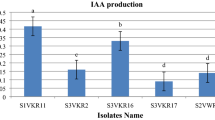
Abstract
Impact of four chromium resistant bacterial strains (S3, S4, S6, and S7) was studied on the different growth parameters of sunflower (Helianthus annuus var SF-187) in chromium free or under chromium stress. Strains used exhibited very high-level resistance to chromate (up to 50 mg ml-1 on nutrient agar and 1-2 mg ml-1 in minimal medium). Application of Cr(VI) salt adversely affected the seed germination, root and shoot length, and fresh weight of seedlings. Bacterial inoculations improved the growth parameters. The effects of Cr(VI) on the different biochemical parameters were also very severe but seedlings inoculated with bacteria showed much improvements as compared to non-inoculated controls. Uptake of Cr(VI) was higher than Cr(III) by the seedlings. Inoculated seedlings contained less chromium than non-inoculated seedlings. Much improvement in the internal region of root and shoot was observed in inoculated plants especially in guard cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Afrasayab S, Zeb A, Hasnain S (2001) Variable effects of mono and mixed culture bacterial inoculations onTriticum aestivum grown under salt stress. Pak J Microbiol 1: 29–41
Ben-Effraim I, Gadd AE, Cohen P, Reymond P, Pilet PE (1990) The effect of 4-chlororesorcinol on the endogenous level of IAA, ABA and oxidative enzymes in cutting. Plant Reg 9: 97–106
Benova D, Hadjidekova V, Hristova R, Nikolova T, Boulanova M, Georgieva I, Grigorova M, Popov T, Panev T, Georgieva R, Natarajan AT, Darroudi F, Nilsson R (2002) Cytogenetic effects of hexavalent chromium in Bulgarian chromium platers. Mutat Res 514: 29–38
Burd Gl, Dixon G, Glick BR (1998) A plant growth-promoting bacterium that decreases nickel toxicity in seedlings. Appl Environ Microbiol 64: 3663–3668
Burd Gl, Dixon G, Glick BR (2000) Plant growth-promoting bacteria that decrease heavy metal toxicity in plants. Can J Microbiol 46: 237–245
Camargo FAO, Bento FM, Okeke BC, Frankenberger WT (2004) Hexavalent chromium reduction by an actinomycete, arthrobacter crystalopoietes ES 32. Biol Trace Elem Res 97: 183–194
Clesceri SL, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, Ed 20, American Public Health Association. Washington D.C., pp 3–66
Dushenkov V, Kumar R Motto H, Raskin I (1995) Rhizofil-teration, the use of plants to remove heavy metals from aqueous streams. Environ Sci Technol 29: 1239–1245
Ehrlich HL (1997) Microbes and metals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48: 687–692
Hasnain S, Sabri AN (1997) Growth stimulation ofTriticum aestivum seedlings under Cr-stresses by Non-Rhizo-sphericPseudomonas strains. Environ Pollut 97: 265–273
Hewitt EJ (1963) Minerals nutrition of plants in culture media,In FC Steward, ed, Plant Physiology. Academic Press, New York, pp 99–137
Hoflich G, Metz R (1997) Interaction of plant microorganism-association in heavy metal containing soils from sewage farms. Bodenkultur 48: 238–247
Humphries EC (1958) Mineral component and ash analysis,In K Paech, MY Traley, eds, Modern Methods of Plant Analysis. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Iqbal J, Rafique N (1986) Toxic effect of BaCI2 on germination, early seedling growth, soluble proteins and acid phosphatase inZea mays L. Pak J Bot 19: 1–8
Kapulnik Y (1996) Plant growth promotion by rhizobacteria,In Y Waisel, A Eshel, U Kafkazi, eds, Plant Roots: The Hidden Half. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 769–781
Kastori RM, Petrovic M, Petrovic N (1992) Effect of excess lead, cadmium, copper and zinc on water relation in sunflower. J Plant Nutr 15: 2427–2439
Mabbett AN, Lloyd JR, Macaskie LE (2002) Effect of complexing agents on reduction of Cr(VI) byDesulfovibrio vulgaris ATCC 29579. Biotechnol Bioeng 79: 389–397
Macaskie LE (1995) Use of biological processes for the removal of heavy metal andorganophosphorous compounds from aqueous solution,In N Ahmad, M Ishfaq, OB Khan, F Sarwar, eds, Biotechnology for Environment and Agriculture. BCC and T Press, University of Karachi, Karachi, pp 127–142
Mehmood U, Sabri AN, Hasnain S (1998) Involvement of plasmid associated with chromium resistant pseudomonas strains in stimulation ofTriticum aestivum seedlings grown under cr-stresses. Biologia 1: 204–217
Montgomery DM, Dean AC, Macaskie LE (1995) Phosphatase production and activity inCitrobacter freundii and a naturally occurring, heavy-metal-accumulatingCitrobacter sp. Microbiol 141: 2433–2441
Mutaftchier S, Macaya A, Prat R, Deviller R Colberg R (1993) Early effects of plant cell wall fragment on plant cell growth. Plant Physiol Biochem 31: 459–467
Nichols PB, Cough JD, Al-Hamdani SH (2000) Selected physiological responses ofSalvinia minima to different chromium concentrations. Aquatic Bot 68: 313–319
Proctor DM, Otani JM, Finley BL, Paustenbach DJ, Bland JA, Speizer N, Sargent EV (2002) Is hexavalent chromium carcinogenic via ingestion? A weight-of-evi-dence review. J Toxicol Environ Hlth Part A 65: 701–746
Saleh MT, Belisle JT (2000) Secreation of acid phosphatase (Sap M) byMycobacterium tuberclosis that is similar to eukaryotic acid phosphatase. J Bacteriol 182: 6850–6853
Sanderson JB (1994) Biological Microtechnique. RMS Handbook 28, BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford
Stoychev D, Stefanov P, Nicolova D, Valov I, Marinova T (2002) Chemical composition and corrosion resistance of passive chromate films formed on stainless steels 316 L and 1.4301. Mat Chem Phys 73: 252–258
Wyss M, Pasamontes L, Remy R, Kohler J, Kusznir E, Gadient M, Miiller F, van Loon APGM (1998) Comparison of the thermostability properties of three acid phosphatases from molds:Aspergillus fumigatus phytase,A niger phytase, andA. niger pH 2.5 acid phosphatase. Appl Environ Microbiol 64: 4446–4451
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faisal, M., Hasnain, S. Chromate resistantBacillus cereus augments sunflower growth by reducing toxicity of Cr (VI). J. Plant Biol. 48, 187–194 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030407
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030407