Abstract
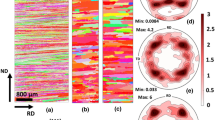
In high purity aluminium two different types of hot band textures were produced by changing the final hot rolling temperatures. The texture of the hot bands was found to be inhnmogeneous through thickness. The strong preferred orientation of {001}<110> developed in the surface layer of the hot band which had been rolled at the higher finishing temperature. For the lower finishing temperature sample, the cold rolling type of texture was formed in the hot band. The cold rolling texture was dependent on the initial hot rolling texture. The hot band which had strong {001}<110> at the surface layer led to the maximum orientation density at {44 11}<11 11 8> after the subsequent cold rolling. Preferred orientations near {123}<634> in the hot band caused the maximum at {123}<634> in the cold rolling texture. The experimental results were discussed based on the simulation test of deformation texture in which the rotation of orientations was calculated from the Taylor model. In this calculation, the strain state of the deformation zone in the rolling gap is assumed to vary with shears induced from the geometry and the friction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Hirsch and K. Lücke,Acta metall.,36, 2863 (1988).
J. Hirsch and K. Lücke,Acta metall.,36, 2883 (1988).
Y. Zhou, K. W. Neale and L. S. Toth,Acta metall,39, 2921 (1991).
M. Y. Huh, J. Hirsch and K. Lücke: inProc. 7th Int. Conf. on Textures of Materials (eds., C. M. Brakman, P. Jongenburger, E. J. Mittemeijer), p. 601, Netherland Soc. of Mat. Sci., Noordwijkerhout (1984).
J. Hirsch, E. Nes and K. Lücke:Acta metall. 35, 427 (1987).
I. L. Dillamore and H. Katoh,Met. Sci.,8, 21 (1974).
G. I. Taylor,J. Inst. Metall.,62, 307 (1938).
P. Van Houtte, Proc. inProc. 7th Int. Conf. on Textures of Materials (eds., CM. Brakman, P. Jongenburger, E. J. Mittemeijer), p.7, Netherland Soc. of Mat. Sci, Noordwijkerhout (1984).
M. Y. Huh, J. H. Lee, K. Y. Ha and S. Lee, Proc.ICAA 4, to be published (1996).
J. Hansen and H. Mecking: inProc. 4th Int. Conf. on Textures of Materials (eds., G.J. Davie, I.L. Dillamore, R.C. Hudd, J.S. Kallend), p. 147, Chameleon Press, London (1975).
W. Truszkowski, J. Kr and B. Major,Metall. Trans. 11A, 749 (1980).
W. Truszkowski, J. Kr and B. Major,Metall. Trans. 13A, 665 (1982).
C. S. Lee and B. J. Duggan,Metall. Trans 22A, 2637 (1991).
C. S. Lee and B. J. Duggan,Acta metall. mater.,41, 2691 (1993).
J. Hirsch, M. Loeck, L. Loof and K. Lücke, inProc. 7th Int. Conf. on Textures of Materials (eds., C. M. Brak-man, P. Jongenburger, E. J. Mittemeijer), p. 765, Netherland Soc. of Mat, Sci., Noodwijkerhout (1984).
H. J. Bunge,Mathematische Methoden der Texturanalyse, Akademie-Verlag, Berlin (1969)
J. M. Capus and M. G. Cockcrofs,J. Inst Metals,90, 289 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huh, MY., Park, JC. & Lee, S. Interpretation of hot rolling and cold rolling texture in high purity aluminium. Metals and Materials 2, 141–149 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026088
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026088