Abstract
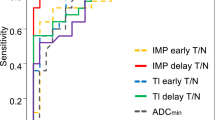
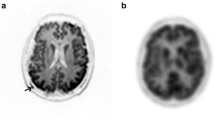
Although201Tl chloride (Tl) SPECT has been used in the differential diagnosis between recurrence of malignant brain tumor and necrosis after treatment, it is not generally recognized as a definite modality to distinguish them. We conducted a preliminary study using Tl SPECT and99mTc-MDP or99mTc-HMDP (Tc) SPECT because it has been said that extraosseous accumulation was caused by calcium deposits in necrotic tissues. In our study, for the purposes of clarifying the mechanism of extraosseous uptake and the correlation between extraosseous accumulation of bone-scanning agent and tumor viability in malignant brain tumors, we compared whether Tc uptake was correlated with the histopathological findings and further performed semi-quantitative evaluation between Tc SPECT and Tl SPECT. The correlation coefficients between the ratio of tumor to normal skull count obtained from Tc SPECT (Tc-T/N) and those of tumor to normal brain count (T/N) and to normal scalp count (T/S) both obtained from Tl SPECT were calculated. Using contrast enhanced CT (CECT) or contrast enhanced MRI (CE-MRI), 8 of 10 cases showed intensely ring-enhanced tumor with necrotic lesion. Histopathologically, 7 of 8 cases whose tumor had been resected before treatment had necrosis with increased vascularity or bleeding. Of the remaining 2 cases one case, malignant lymphoma had only hypervascularity by biopsy, while the other one was excluded for resection after treatment. Three of these 8 cases whose CE-CT or CE-MRI showed necrotic lesions exhibited Tc and Tl accumulations in the area corresponding to necrosis. In contrast, 2 showed no Tc nor Tl uptake. Tc-T/N had no significant correlation with any of early-, delayed-T/N or T/S. In conclusion, there was no significant correlation between Tc and Tl uptakes by malignant brain tumors in semiquantitative evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yasuda E, Yoshida H, Ichikawa H, Matsuo S, Kimura T, Kanamori I, et al. Extraosseous accumulation of99mTc-MDP — with special reference to intratumor accumulation.Rinsho Hoshasen 1983; 28: 851–857. (in Japanese)
Sty JR, Starshak RJ, Casper JT. Extraosseous accumulation of99mTc-MDP. Metastatic intracranial neuroblastoma.Clin Nucl Med 1983; 8: 26–27.
Ozarda AT, Legaspi JR, Haynie TP. Detection of a brain metastasis from osteosarcoma with99mTc-methylene diphosphonate bone scanning.Eur J Nucl Med 1983; 8: 552–554.
Grames GM, Jansen C, Carlsen EN, Davidson TR. The abnormal bone scan in intracranial lesions.Radiology 1975; 115: 129–134.
Chaudhuri TK, Chaudhuri TK, Gulesserian HP, Christie JH, Tonami N. Extraosseous noncalcified soft-tissue uptake of99mTc-polyphosphate.J Nucl Med 1974; 15: 1054–1056.
Suzuki A, Togawa T, Kuyama J, Nakahara T, Yui N, Iuchi T, et al. Extraosseous accumulation of99mTc phosphonate complexes in primary brain tumor evaluated with SPECT.Ann Nucl Med 2002; 16: 495–498.
Shiomi S, Kuroki T, Hasegawa I, Nishio H, Azuma K, Ochi H. Accumulation of99mTc-HMDP in hepatic metastasis from colon carcinoma without detectable calcification.Ann Nucl Med 1996; 10: 347–349.
Rengachary SS, Batnitzky S, Arjunan K. Diagnosis of intracranial meningioma with radionuclide bone scan.Surg Neurol 1980; 14: 337–341.
Buja LM, Tofe AJ, Kulkarni PV, Mukherjee A, Parke RW, Franci MD, et al. Sites and mechanisms of localization of technetium-99m phosphorus radiopharmaceuticals in acute myocardial infarcts and other tissues.J Clin Invest 1977; 60: 724–740.
Yoshida S, Fukumoto M, Yoshimura N, Oobayashi K, Takada Y. Ectopic accumulation of99mTc-HMDP in primary lung cancer in comparison with CT findings.Ann Nucl Med 1996; 10: 329–333.
Togawa T, Hoshi K, Kimura K, Sato T, Matsuda S, Uchida T, et al. A case of adult T-cell leukemia with metastatic calcification.Eur J Nucl Med 1985; 10: 90–92.
Rosenthall L.99mTc-methylene diphosphonate concentration in soft tissue malignant fibrous histiocytoma.Clin Nucl Med 1978; 3: 58–61.
Parkey RW, Bonte FJ, Meyer SL, Atkins JM, Curry GL, Stokely EM, et al. A new method for radionuclide imaging of acute myocardial infarction in humans.Circulation 1974; 50: 540–546.
Corbett JR, Lewis M, Willerson JT, Nicod PH, Huxley RL, Simon T, et al.99mTc-pyrophosphate imaging in patients with acute myocardial infarction: comparison of planar imaging with single-photon tomography with and without blood pool overlay.Circulation 1984; 69: 1120–1128.
Fujiwara Y, Itoh T, Douiuchi J, Ochi T, Kokubu T, Murase K, et al. Quantitative analysis of acute myocardial infarction using single photon emission computed tomography using technetium-99m pyrophosphate.J Cardiogr 1986; 16: 555–562.
Krause T, Hohnloser SH, Kasper W, Schumichen C, Reinhardt M, Moser E. Assessment of acute myocardial necrosis after cardiopulmonary resuscitation and cardioversion by means of combined thallium-201/technetium-99m pyrophosphate tomography.Eur J Nucl Med 1995; 22: 1286–1291.
Kawano M, Taki J, Kinuya S, Higuchi T, Nakajima K, Miyazaki Y, et al. Improvement of99mTc-pyrophosphate scintigraphy in detection of acute myocardial infarction: combined with99mTc-tetrofosmin.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 2001; 38: 707–713. (in Japanese)
Dewanjee MK, Kahn PC. Mechanism of localization of99mTc-labeled pyrophosphate and tetracycline in infarcted myocardium.J Nucl Med 1976; 17: 639–646.
Slizofski WJ, Krishna L, Kasetos CD, Black P, Miyamoto C, Brown SJ, et al. Thallium imaging for brain tumors with results measured by semiquantitative index and correlated with histopathology.Cancer 1994; 74: 3190–3197.
Igase K, Oka Y, Ohta S, Murakami Y, Kumo Y, Sasaki S. Usefulness of thallium-201 single photon emission computed tomography to quantify the malignancy grade of brain tumors.Neurol Med Clir (Tokyo) 1996; 36: 434–439.
Kallen K, Heiling M, Andersson AM, Brun A, Holtas S, Ryding E, et al. Evaluation of malignancy in ring enhancing brain lesions on CT by thallium-201 SPECT.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1997; 63: 569–574.
Higa T, Maetani S, Kobayashi Y, Nabeshima S.201Tl SPECT compared with histopathologic grade in the prognostic assessment of cerebral gliomas.Clin Nucl Med 2001; 26: 119–124.
Kosuda S, Shinoyama Y, Kamata N, Suzuki K, Tanaka Y, Nakamura O, et al. Differential diagnosis between recurrence of brain tumor and radiation necrosis by201Tl SPECT.Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 1991; 51 (4): 415–421. (in Japanese)
Serizawa T, Ono J, Odaki M, Hirai S, Sato M, matsuda S, et al. Differentiation between tumor recurrence and radiation injury after gamma knife radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors: value of serial thallium-201 chloride SPECT.Jpn J Neurosurg (Tokyo) 2001; 10: 726–732. (in Japanese)
Yoshii Y, Satou M, Yamamoto T, Yamada Y, Hyodo A, Nose T, et al. The role of thallium-201 single photon emission tomography in the investigation and characterization of brain tumors in man and their response to treatment.Eur J Nucl Med 1993; 20: 39–45.
Seo H, Sato K, Fujita T, Yamada K, Nakai O, Komatani A. Sequential changes in SPECT using201Tl chloride during the treatment of intracranial gliomas.No To Shinkei 1993; 45: 537–543. (in Japanese)
Tomura N, Kobayashi M, Seino Y, Ishikawa H, Watarai J, Kato T, et al. Usefulness of201TlCl-SPECT in the evaluation of radiation and chemotherapy for brain tumors.Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 1993; 53: 484–486. (in Japanese)
Kojima Y, Kuwana N, Noji M, Tosa J. Differentiation of malignant glioma and metastatic brain tumor by thallium-201 single photon emission computed tomography.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1994; 34 (9): 588–592.
Kaplan WD, Takvorian T, Morris JH, Rumbaugh CL, Connolly BT, Atkins HL. Thallium-201 brain tumor imaging: comparative study with pathologic correlation.J Nucl Med 1987; 28: 47–52.
Lorberboym M, Baram J, Feibel M, Hercberg A, Lieberman L. A prospective evaluation of thallium-201 single photon emission computerized tomography for brain tumor burden.Int Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1995; 32: 249–254.
Ohnishi H, Koizumi K, Uchiyama G, Yamaguchi M, Okada J, Ogata H, et al. Evaluation of malignancy and viability of brain tumors by201Tl SPECT: the correlation between201Tl SPECT and pathology, clinical progress and the intensity of enhancement on CT images.Nippon Igakun Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 1994; 54: 1388–1398. (in Japanese)
Front D. Scintigraphic assessment of vascularity and bloodtissue barrier of human brain tumors.J Neural Neurosurg Psychiatry 1978; 41: 18–23.
Nakagawara J, Fukuoka S, Takahashi S, Takahashi M, Satoh K, Suematsu K, et al. Assessment of vascularity and permeability in brain tumor using SPECT and99mTc-DTPA-human albumin in relation to201Tl SPECT.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1993; 31: 117–124. (in Japanese)
Sehweil AM, Mckillop JH, Milroy R, Wilson R, Abdel-Dayem HM, Omar YT. Mechanism of201Tl uptake in tumors.Eur J Nucl Med 1989; 15: 376–379
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, A., Togawa, T., Kuyama, J. et al. Extraosseous accumulation of bone scanning agents in malignant brain tumors: Comparison to semi-quantitative evaluation with99mTc SPECT/201Tl SPECT and histological findings. Ann Nucl Med 17, 387–392 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03006606
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03006606