Abstract
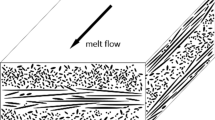
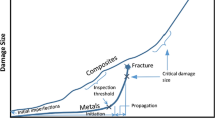
The polymer composites contain numerous internal boundaries and its structural elements have different responses and different resistances under the same service environment. Fatigue phenomenon is much more complex in composites than homogeneous materials. An understanding of the fracture behavior of polymer composite materials subjected to constant and cyclic loading is necessary for predicting the life time of structures fabricated with polymers. There is a need to acquire a better understanding of the fatigue performance and failure mechanisms of composites under such conditions. Therefore, in this study the analyses of fiber orientation and fracture mechanism for low cycle fatigue crack have been studied by SEM and LM for observing the ultrathin sections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attia, O., Kinloch, A. J. and Matthews, F. L., 2001, “Modelling the Fatigue Life of Polymer- Matrix Fibre-Composite Components,”Composites Science and Technology, Vol. 61, No. 15, pp. 2273–2283.
Bell, G. R., Cook, D. C. and Rogers, D. D., 1979, “Microtoming ; An Emerging Tool for Analyzing Polymer Structures,” Plast. Eng.,No. 35, pp. 18.
Harik, V. M., 2000, “Low Cycle Fatigue of Unidirectional Laminates: Stress Ratio Effects,”Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology, Vol. 122, No. 4, pp. 415–419.
Himmel. N., 2002, “Fatigue Life Prediction of Laminated Polymer Matrix Composites,”International Journal of Fatigue, Vol. 24, No. 2, pp. 349–360.
Jack, R. V. and Eyassu Woldesenbet, 2001, “Fiber Orientation Effects on High Strain Rate Properties of Graphite/Epoxy Composites,”Journal of Composite Materials, Vol. 35, No. 6, pp. 509–521.
Karger, K. J. and Friedrich, K., 1988,Advancing with Composites Conf., Milan, pp. 639.
Lim, J. K. and Kim, Y. J., 1993, “A Study on Fatigue Properties of GFRP in Synthetic Sea Water,”Trans, of KSME, Vol. 17, No. 6, pp. 1351–1360.
Lim, J. K. and Kim, Y. J., 2001, “Evaluation of Inhomogeneous Deformation and Stress Concentration in Polymer Composites Injection Weld by means of Thermoelastic Techniques,”KSME International Journal, Vol. 15, No. 12, pp. 1616–1622.
Noda, K., Takahara, A. and Kajiyama, T., 2001, “Fatigue Failure Mechanisms of Short Glass-Fiber Reinforced Nylon 66 Based on Nonlinear Dynamic Viscoelastic Measurement,”Polymer, Vol. 42, pp. 5803–5811.
Song, D. Y. and Otani, N., 1998, “Approximate Estimation of Fatigue Strength of Polymer Matrix Composites by Material Properties,”Materials Science and Engineering A, Vol. 254, No. 1, pp. 200–206.
Young, R. T. and Baird, D. G., 2000, “The Influence of Processing Variables on Injection Molded in Situ Composites Based on Polypheny- lene Sulfide and a Melt Processable Glass,”Composites Part B: Engineering, Vol. 31, pp. 209–221.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J.H., Lim, J.K. Low cycle fatigue of pps polymer injection welds (II) — fiber orientation and fracture mechanism. KSME International Journal 17, 836–843 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983397
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983397