Abstract
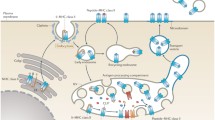
CD4-positive T cells recognize foreign antigens displayed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells as small peptides bound to MHC class II molecules. Thus, the ability of antigen-presenting cells to generate these class II-peptide complexes is central to the initiation and regulation of immune responses. Class II predominantly associates with peptides derived from soluble protein antigens that are internalized and degraded within endosomal compartments. It is within these endosomal compartments that class II encounters and binds antigenic peptides. A number of signals have been implicated in directing the intracellular transport of class II to endosomes. These include sequences within class II itself and within the class II-associated invariant chain (Ii).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pelham H: Recycling of proteins between the ER and Golgi complex. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1991;3:585–591.
Bretscher M, Munro S: Cholesterol and the Golgi apparatus. Science 1993;261:1280–1281.
Ferro-Novick S, Novick P: The role of GTP-binding proteins in transport along the exocytic pathway. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1993;9:575–599.
Mayor S, Presley J, Maxfield F: Sorting of membrane components from endosomes and subsequent recycling to the cell surface occurs by a bulk flow process. J Cell Biol 1993; 121:1257–1269.
Davis C, Goldstein J, Sudhof T, Anderson R, Russell D, Brown M: Acid-dependent ligand dissociation and recycling of LDL receptor mediated by growth factor homology region. Nature 1987;326:760–765.
Tabas I, Myers J, Innerarity T, Xu X, Arnold K, Boyles J, Maxfield F: The influence of particle size and multiple appprotein-receptor interactions on the endocytic targeting of β-VLDL in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Cell Biol 1991;115: 1547–1560.
Molloy S, Thomas L, VanSlyke J, Stenberg P, Thomas G: Intracellular trafficking and activation of the furin proprotein convertase: Localization to the TGN and recycling from the cell surface. EMBO J 1994;13: 18–33.
Humphrey J, Peters P, Yuan L, Bonifacino J: Localization of TGN38 to the trans-Golgi network: Involvement of a cytoplasmic tyrosine-containing sequence. J Cell Biol 1993; 120:1123–1135.
Neefjes J, Stollorz V, Peters P, Geuze H, Ploegh H: The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell 1990;61:171–183.
Guagliardi L, Koppelmann B, Blum J, Marks M, Cresswell P, Brodsky F: Colocalization of molecules involved in antigen processing and presentation in an early endocytic compartment. Nature 1990;343: 133–139.
Pieters J, Horstmann H, Bakke O, Griffiths G, Lipp J: Intracellular transport and localization of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules and associated invariant chain. J Cell Biol 1991;115:1213–1223.
Romagnoli P, Layet C, Yewdell J, Bakke O, Germain R: Relationship between invariant chain expression and major histocompatibility complex class II transport into early and late endocytic compartments. J Exp Med 1993;177:583–596.
Harding C, Geuze H: Class II MHC molecules are present in macrophage lysosomes and phagolysosomes that function in the phagocytic processing ofListeria monocytogenes for presentation to T cells. J Cell Biol 1992;119:531–542.
Peters P, Neefjes J, Oorschot V, Ploegh H, Geuze H: Segregation of MHC class II molecules from MHC class I molecules in the Golgi complex for transport to lysosomal compartments. Nature 1991;349:669–676.
Amigorena S, Drake J, Webster P, Mellman I: Transient accumulation of new class II MHC molecules in a novel endocytic compartment in B lymphocytes. Nature 1994;369: 113–120.
Qiu Y, Xu X, Wandinger-Ness W, Calke D, Pierce S: Separation of subcellular compartments containing distinct functional forms of MHC class II. J Cell Biol 1994;125: 595–605.
Tulp A, Verwoerd D, Dobberstein B, Ploegh H, Pieters J: Isolation and characterization of the intracellular MHC class II compartment. Nature 1994;369:120–126.
West M, Lucocq J, Watts C: Antigen processing and class II MHC peptide-loading compartments in human B-lymphoblastoid lines. Nature 1994;369:147–151.
Calafat J, Nijenhuis M, Janssen H, Tulp A, Dusseljee S, Wubbolts R, Neefjes J: Major histocompatibility complex class II molecules induce the formation of endocytic MIIC-like structures. J Cell Biol 1994;126: 967–977.
Arunachalam B, Lamb C, Cresswell P: Transport properties of free and MHC class II-associated oligomers containing different isoforms of human invariant chain. Int Immunol 1994;6:439–451.
Riberdy J, Avva R, Geuze H, Cresswell P: Transport and intracellular distribution of MHC class II molecules and associated invariant chain in normal and antigen-processing mutant cell lines. J Cell Biol 1994; 126:1225–1237.
Fling S, Arp B, Pious D: HLA-DMA and HLA-DMB genes are both required for MHC class II/peptide complex formation in antigen presenting cells. Nature 1994;368:554–558.
Morris P, Shaman J, Attaya M, Amaya M, Goodman S, Bergman C, Monaco J, Mellins E: An essential role for HLA-DM in antigen presentation by class II MHC molecules. Nature 1994;368:551–554.
Roche P, Teletski C, Stang E, Bakke O, Long E: Cell surface HLA-DR-invariant chain complexes are targeted to endosomes by rapid internalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993;90:8581–8585.
Harter C, Mellman I: Transport of the lysosomal membrane glycoprotein lgp120 (lgp-A) to lysosomes does not require appearance on the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 1992; 117:311–325.
Lamb C, Yewdell P, Bennink J, Cresswell P: Invariant chain targets HLA class II molecules to acidic endosomes containing internalized influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991;88:5998–6002.
Chervonsky A, Gordon L, Sant A: A segment of the MHC class II β chain plays a critical role in targeting class II molecules to the endocytic pathway. Int Immunol 1994;6:973–982.
Simonsen A, Momburg F, Drexler J, Hammerling G, Bakke O: Intracellular distribution of the MHC class II molecules and the associated invariant chain in different cell lines. Int Immunol 1993;5:903–917.
Bikoff E, Huang L, Episkopou V, Meerwijk J, Germain R, Robertson E: Defective major histocompatibility complex class II assembly, transport, peptide acquisition, and CD4+T cell selection in mice lacking invariant chain. J Exp Med 1993;177: 1699–1712.
Elliott E, Drake J, Amigorena S, Elsemore J, Webster P, Mellman I, Flavell R: The invariant chain is required for intracellular transport and function of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. J Exp Med 1994;179:681–694.
Viville S, Neefjes J, Lotteau V, Dierich A, Lemeur M, Ploegh H, Benoist C, Mathis D: Mice lacking the MHC class II-associated invariant chain. Cell 1993;72:635–648.
Anderson M, Miller J: Invariant chain can function as a chaperone protein for class II major histocompatibility complex molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89:2282–2286.
Layet C, Germain R: Invariant chain promotes egress of poorly expressed, haplotype-mismatched class II major histocompatibility complex AαAβ dimers from the endoplasmic reticulum/cis-Golgi compartment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991;88:2346–2350.
Schaiff W, Hruska K, Bono C, Shuman S, Schwartz B: Invariant chain influences post-translational processing of HLA-DR molecules. J Immunol 1991;147:603–608.
Loss G, Sant A: Invariant chain retains MHC class II molecules in the endocytic pathway. J Immunol 1993;150:3187–3197.
Neefjes JJ, Ploegh HL: Inhibition of endosomal proteolytic activity by leupeptin blocks surface expression of MHC class II molecules and their conversion to SDS resistant αβ heterodimers in endosomes. EMBO J 1992;11:411–416.
Bakke O, Dobberstein B: MHC class II-associated invariant chains contains a sorting signal for endosomal compartments. Cell 1990;63:707–716.
Lotteau V, Teyton L, Peleraux A, Nilsson T, Karlsson L, Schmid S, Quaranta V, Peterson P: Intracellular transport of class II MHC molecules directed by invariant chain. Nature 1990;348:600–605.
Anderson M, Swier K, Arneson L, Miller J: Enhanced antigen presentation in the absence of the invariant chain endosomal localization signal. J Exp Med 1993;178:1959–1969.
Roche P, Teletski C, Karp D, Pinet V, Bakke O, Long E: Stable surface expression of invariant chain prevents peptide presentation by HLA-DR. EMBO J 1992;11:2841–2847.
Odorizzi C, Trowbridge I, Xue L, Hopkins C, Davis C, Collawn J: Sorting signals in the MHC class II invariant chain cytoplasmic tail and transmembrane region determine trafficking to an endocytic processing compartment. J Cell Biol 1994; 126:317–330.
Pieters J, Bakke O, Dobberstein B: The MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains two endosomal targeting signals within its cytoplasmic tail. J Cell Sci 1993;106:831–846.
Letourneur F, Klausner R: A novel di-leucine motif and a tyrosinebased motif independently mediate lysosomal targeting and endocytosis of CD3 chains. Cell 1992;69:1143–1157.
Arneson L, Miller J: Invariant chain multimerization is necessary for efficient endosomal localization of class-invariant chain complexes. Submitted 1994.
Roche P, Marks M, Cresswell P: Formation of a nine subunit complex by HLA class II glycoproteins and the invariant chain. Nature 1991;354:392–394.
Lamb C, Cresswell P: Assembly and transport properties of invariant chain trimers and HLA-DR-invariant chain complexes. J Immunol 1992;148:3478–3482.
Nadimi F, Moreno J, Momburg F, Heuser A, Fuchs S, Adorini L, Hammerling G: Antigen presentation of hen egg lysozyme but not ribonuclease A is augmented by the MHC class II associated invariant chain. Eur J Immunol 1991;21:1255–1263.
Peterson M, Miller J: Invariant chain influences the immunological recognition of MHC class II molecules. Nature 1990;345:172–174.
Peterson M, Miller J: Antigen presentation enhanced by the alternatively spliced invariant chain gene product p41. Nature 1992;357: 596–598.
Salamero J, Humbert M, Cosson P, Davoust J: Mouse B lymphocyte specific endocytosis and recycling of MHC class II molecules. EMBO J 1990;9:3489–3496.
Stockinger B, Pessara U, Lin R, Habicht J, Grez M, Koch N: A role of Ia-associated invariant chains in antigen processing and presentation. Cell 1989;56:683–689.
Romagnoli P, Germain R: The CLIP region of invariant chain plays a critical role in regulating major histocompatibility complex class II folding, transport, and peptide occupancy. J Exp Med 1994; 180:1107–1113.
Freisewinkel I, Schneck K, Koch N: The segment of invariant chain that is critical for association with major histocompatibility complex class II molecules contains the sequence of peptide eluted from class II polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993;90:9703–9706.
Fineschi B, Arneson L, Naujokas M, Miller J: Differential proteolysis of invariant chain trimers containing a single p41 invariant chain component. Submitted 1994.
Klausner R, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Bonifacino J: The T cell antigen receptor: Insights into organelle biology. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1990;6: 403–431.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, J. Endosomal localization of MHC class II-invariant chain complexes. Immunol Res 13, 244–252 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935616
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935616