Summary
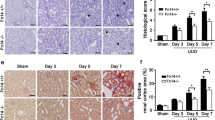
The role of protease activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) in the renal tubulointerstitial lesion induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) was explored. Mice were sacrificed on the day 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14 and 21 after UUO. The expression of PAR-2 mRNA and protein and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) protein in tubulointerstitium was detected by RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry at each time point, respectively. The results showed that the PAR-2 expression in renal tubulointerstitium was increased progressively starting form 24 h to the day 14 post-ligation, and it was significantly associated with the relative volume of interstitium and the positive area of α-SMA. PAR-2 was mainly expressed in renal tubule epithelial cells, especially in proximal tubular cells. It also located in renal capillary ansa, interstitial infiltrate cells and fibroblasts. It was concluded that PAR-2 was active in interstitial and tubular cells in the early phase of fibrotic process and played an important role in mediating the tubulointerstitial lesion after UUO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaneto H, Morrissey J, McCracken Ret al. Enalapril reduces collagen type IV synthesis and expansion of the interstitium in the obstructed rat kidney. Kidney Int, 1994, 45: 1637
Alexopoulos E, Papagianni A, Papadimitriou M. Is membranous nephropathy only a glomerular disease? Renal Failure, 1998, 20: 1
Nystedt S, Emilsson K, Wahlestedt Cet al. Molecular cloning of a potential proteinase activated receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1994, 91: 9208
Pavone-Macaluso M. Tissue mast cells in renal diseases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scant, 1960, 50: 337
Ehara T, Shigematsu H. Contribution of mast cells to the tubulo-interstitial lesions in IgA nephritis. Kidney Int, 1998, 54: 1675
Roberts I S D, Brenchley P E C. Mast cells: the forgotten cells of renal fibrosis. J Clin Pathol, 2000, 53: 858
Hiromura K, Kurosawa M, Yano Set al. Tubulointerstitial mast cell infiltration in glomerulonepritis. Am J Kidney Dis, 1998, 32: 593
Kondo S, Kagami S, Kido Het al. Role of mast cell tryptase in renal interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2001, 12: 1668
Powell D W, Mifflin R C, Valentich J Det al. Myofibroblasts. II. Intestinal subepithelial myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 1999, 277: C183
Cottrell G S, Amadesi S, Schmidlin Fet al. Protease-activated receptor 2: activation, signaling and function. Biochem Soc Trans, 2003, 31(6): 1191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
XIONG Jing, female, born in 1976, M. D., Ph.D.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, X., Zhonghua, Z., Jianshe, L. et al. Role of protease activated receptor-2 expression in renal interstitial fibrosis model in mice. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 25, 523–526 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896006
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896006