Abstract
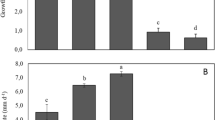
Uptake of phosphate ions by 1 mm segments of isolated maize root cortex layers was studied. Cortex segments (from roots of 8 days old maize plants) absorb phosphate ions from 1 mM KH2PO4 in 0.2 mM CaSCO4 at the average rate of 34.3 ±3.2 μg Pi g−1 (fr. m.) h−1,i.e. 0.35± 0.02 μmol Pi g−1 (fr. m.) h−1. Phosphate uptake considerably increases after a certain period of “augmentation”,i.e. washing in aerated 0.2 mM CaSO4. This increase is completely blocked by the presence of 10 μg ml−1 cycloheximide.
The relation of uptake rate to phosphate concentration in the medium was shown to have 3 phases in the concentration range of 0.02 - 40 mM. Transition points were found between 0.8–1 mM and 10–20 mM. Following Km and Vmax values were found: Km[mM] : 0.37 - 3.82 - 27.67 Vmax[μg Pi g−1 (fr. m.) h−1] : 3.33 - 39.40 - 66.67
We have found no sharp pH optimum for phosphate uptake. It proceeds at almost constant rate till pH 6.0 and then the uptake rate drops with increasing pH. At low phosphate concentrations (1 mM) the lowest uptake rate was found at 5 and 13 °C, while the uptake is higher at 5 °C than at 13 °C at phosphate concentrations higher than 1 mM. At these concentrations uptake rate at 35 °C is lower than at 25 °C.
Phosphate uptake considerably decreased in anaerobic conditions. DNP and iodoacetate (0.1 mM) completely blocked phosphate uptake from 1 mM KH2PO4, while uptake from 5 and 10 mM KH2PO4 was left unaffected by these substances. The inhibitors of active - SH groups NEM and PCMB inhibited phosphate uptake: 10−3 M NEM by 81.6%, 104 M NEM by 42% and 10−4 M PCMB by 42%.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Pi :
-
inorganic phosphate
- DNP:
-
2,4-dinitrophenol
- NEM:
-
N-ethyl maleiimide
- PCMB(S):
-
p-chloromercuribenzoate (benzene-sulfonic acid)
References
Borstlap, A. C.: Invalidity of multiphasic concept of ion absorption in plants. - Plant Cell Environ.4 : 189–195, 1981.
Borst-Pauwels, G. W. F. H., Dobbleman, J.: The mechanism of inhibition of anaerobic phosphate uptake by fatty acids in yeast. - Biochim. biophys. Acta290: 348–354, 1972.
Bowling, D. J. F., Graham, R. D., Dunlop, J.: The relationship between the cell electrical potential difference and salt uptake in the roots ofHelianthus annuus. - J. exp. Bot.108: 135–140, 1978.
Cram, W. J.: Chloride fluxes in cells of the isolated root cortex ofZea mays. - Aust. J. biol. Sci.26 : 757–779, 1973.
Harrison, S. J., Nicholas, W. L., Phipps, D. A.: Calculation of kinetic constants for ion uptake studies. A comparison of methods in relation to their effects on data interpretation. - J. Plant Nutr.3: 181–192, 1981.
Laštůvka, Z., Minář, J.: [Water culture of higher plants.] In Czech. - Fol. Fac. Sci. nat. Univ. Purk. brunensis8 [Biol. 16(2)]: 1–83, 1967.
Laties, G. G., Budd, K.: The development of differential permeability in isolated steles of corn roots. - Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA52: 462–469, 1964.
Leonard, R. T., Hanson, J. B.: Induction and development of increased ion absorption in corn root tissue. -Plant Physiol.49: 430–435, 1972.
Lichtner, F. T., Lucas, W. J., Spanswick, R. M.: Effect of sulfhydryl reagents on the biophysical properties of the plasmalemma ofChara corallina. - Plant Physiol.68: 899–904, 1981.
Lin, W.: Potassium and phosphate uptake in corn roots. Further evidence for an electrogenic Hcc/K+ exchanger and an OH−/Pi antiporter. - Plant Physiol.63: 952–955, 1979.
Lin, W.: Corn root protoplasts. Isolation and general characterization of ion transport. - Plant Physiol.66: 550–554, 1980.
Lin, W.: Inhibition of anion transport in corn root protoplasts. - Plant Physiol.68: 435–438, 1981.
Metler, I. J., Leonard, R. T.: Ion transport in isolated protoplasts from tobacco suspension cells. 1. General characteristics. - Plant Physiol.63: 183–190, 1979.
Michalík, 1.: The influence of phosphate concentration on the kinetics of uptake by maize roots. - Biol. Plant.24: 161–169, 1982.
Murphy, J., Riley, J. P.: A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters.- Anal. ehim. Acta27: 31–36, 1962.
Nissen, P.: Multiphasic uptake in plants. I. Phosphate and sulphate. - Physiol. Plant.28: 304–316, 1973.
Nissen, P.: Ion uptake in higher plants and KC1 stimulation of plasmalemma adenosine triphosphatase: comparison of models. -Physiol. Plant.40: 205–214, 1977.
Pedro-Bravo, F., Uribe, E. G.: Temperature dependence of the concentration kinetics of absorption of phosphate and potassium in corn roots. - Plant Physiol.67: 815–819, 1981.
Polley, L. D., Hopkins, J. W.: Rubidium (potassium) uptake byArabidopsis. A comparison of uptake in suspension culture and by roots of intact seedlings. - Plant Physiol.64: 374 to 378, 1979.
Raven, J. A.: Phosphate transport inHydrodictyon africanum. - New Phytol.73: 421–432, 1974.
Smith, F. A., Raven, J. A.: Energy-dependent processes inChara corallina: absence of light stimulation when only photosystem I is operative. - New Phytol.73: 1–12, 1974.
Ullrich-Eberius, C. I.: Die pH-Abhängigkeit der Aufnahme von H2PO4 −, SO4 −2, Na+ and K+ und ihre gegenseitige Beeinflussung beiAnkistrodesmus braunii. - Planta109: 161–176, 1973.
Ullrich-Eberius, C. I., Novacky, A., Fischer, E., Lüttge, U.: Relationship between energydependent phosphate uptake and the electrical membrane potential inLemma gibba G 1. - Plant Physiol.67: 791–801, 1981.
van Iren, F., Boers-van der Sluijs, P.: Symplasmic and apoplasmic radial ion transport in plant roots. Cortical plasmalemmas lose absorption capacity during differentiation. - Planta148: 130–137, 1980.
van Iren, F., Loulou Joolen, M., Gerritsen, A. F. C., Noordervliet, M. A. W., Boers-van der Sluijs, F. P.: The lag-phase of potassium translocation from the root to the shoot of low-salt barley plants. -Kinetic and localization studies. - Physiol. Plant.52: 15–22, 1981.
van Steveninck, R. F. M.: The “washing” or “ageing” phenomenon in plant tissues. - Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.26: 237–258, 1975.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macháčková, I., Král, J. & Zmrhal, Z. Characterization of phosphate absorption in maize root cortex segments. Biol Plant 25, 366–372 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878282
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878282