Abstract
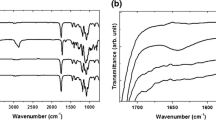
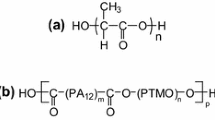
PLA/LPCL/HPCL blends composed of poly(lactic acid) (PLA), low molecular weight poly(ε-caprolactone) (LPCL), and high molecular weight poly(ε-caprolactone) (HPCL) were prepared by melt blending for bioabsorbable filament sutures. The effects of blend composition and blending time on the ester interchange reaction by alcoholysis in the PLA/LPCL/HPCL blends were studied. Their thermal properties and the miscibility due to the ester interchange reaction were investigated by1H-NMR, DSC, X-ray, and UTM analyses. The hydroxyl group contents of LPCL in the blends decreased by the ester interchange reaction due to alcoholysis. Thus, the copolymer was formed by the ester interchange reaction at 220 °C for 30–60 minutes. The thermal properties of PLA/LPCL/HPCL blends such as melting temperature and heat of fusion decreased with increasing ester interchange reaction levels. However, the miscibility among the three polymers was improved greatly by ester interchange reaction. Tensile strength and modulus of PLA/LPCL/HPCL blend fibers increased with increasing HPCL content, while the elongation at break of the blend fibers increased with increasing LPCL content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Yoon, I. J. Chin, M. N. Kim, and C. Kim,Macromolecules,29, 3303 (1996).
P. A. Holmes,Phy. Technol.,16, 32 (1985).
I. Horacek and V. Kalisek,J. Appl. Polym. Sci.,54, 1767 (1994).
R. Gref, Y. Minamike, M. T. Percchia, V. Trubestskoy, V. Torchilin, and R. Langes,Science,263, 1600 (1994).
H. R. Kricheldorf, M. Berl, and N. Scharnagl,Macromolecules,21, 286 (1988).
H. Tsuji and Y. Ikada,Polymer,36, 2709 (1995).
D. W. Grijpma, J. P. Penning, and A. J. Penning,Colloid Polym. Sci.,272, 1068 (1994).
C. W. Lee,J. Korean Fiber Soc.,34, 143 (1997).
S. C. Tjong, Y. Xu, and Y. Z. Meng,Polymer,40, 3703 (1999).
S. H. Kim and S. W. Kang,Fiber. Polym.,1, 83 (2000).
J. H. Youk and W. H. Jo,Fiber. Polym.,2, 81 (2001).
E. J. Choi, J. K. Park, and J. N. Chang,J. Polym. Sci., Part B, Polym. Phys.,32, 2481 (1994).
D. S. Ji and C. S. Yoon,J. Korean Fiber Soc.,36, 25 (1999).
A. M. Kotliar,J. Polym. Sci., Part D, Macromol. Rev.,16, 367 (1981).
P. J. Flory,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,62, 2255 (1940).
W. J. Bae, W. H. Jo, and Y. H. Park,Macromolecular Res.,10, 145 (2002).
R. S. Porter and L. H. Wang,Polymer,33, 2019 (1992).
J. H. Kim and W. S. Ha,J. Korean Fiber Soc.,35, 457 (1998).
J. E. Mark, “Polymer Data Handbook”, pp.627–633, Oxford Univ. Press Inc., New York, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, C.S., Ji, D.S. The effects of blend composition and blending time on the ester interchange reaction and tensile properties of PLA/LPCL/HPCL blends. Fibers Polym 4, 59–65 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02875438
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02875438