Abstract
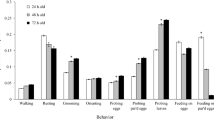
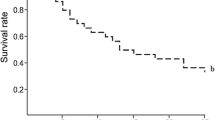
The effect of various diets on nymphal development and survival of two predaceous anthocorid bugs,Orius albidipennis (Reuter) andO. laevigatus (Fieber) was investigated in the laboratory. Five different diets were compared: eggs ofEphestia kuehniella Zeller; eggs ofE. kuehniella plus mixed flower pollen; only mixed flower pollen; pollen from sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv. Mazurka) flowers; and sweet pepper plants. A high percentage of predators successfully completed nymphal development on those diets containing lepidopterous eggs. When fed on sweet pepper pollen, the survival percentages were 65% forO. laevigatus and 38% forO. albidipennis. No nymphs of either species completed the nymphal stage on mixed flower pollen or on sweet pepper plants. Development was significantly faster on diets containing eggs ofE. kuehniella. Results are discussed in relation to the capability of the bugs to survive periods of prey scarcity and to the optimization of release strategies for these predators in the greenhouse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askari, A. &Stern, V. M. — 1972. Biology and feeding habits ofOrius tristicolor (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). —Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 65, 96–100.
Carayon, J. &Steffan, J. R. — 1959. Observations sur le régime alimentaire desOrius particulièrement d’Orius pallidicornis Reuter (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae). —Cahiers Natur. Bull. N.P., n.s., 15, 53–63.
Chambers, R. J., Long, S. &Helyer, N. L. — 1993. Effectiveness ofOrius laevigatus (Hem.: Anthocoridae) for the control ofFrankliniella occidentalis on cucumber and pepper in the UK. —Biocontrol Sci. Technol., 3, 295–307.
Chyzik, R., Klein, M. &Ben-Dov, Y. — 1995. Overwintering biology of the predatory bugOrius albidipennis (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) in Israel. —Biocontrol Sci. Technol., 5, 287–296.
Cocuzza, G. E., De Clercq, P., Van de Veire, M., De Cock, A., Degheele, D. &Vacante, V. — 1997. Reproduction ofOrius laevigatus andOrius albidipennis on pollen andEphestia kuehniella eggs. —Entomol Exp. Appl., 82, 101–104.
DataMost — 1995. StatMost for Windows: Statistical Analysis and Graphics. User’s handbook. DataMost Corporation, Salt Lake City, UT.
Fauvel, G. — 1974. Sur l’alimentation pollinique d’un anthocoridae prédateurOrius (Heterorius) vicinus Rib. (Hémiptère). —Ann. Zool. Ecol. Anim., 6, 245–258.
Funao, T. &Yoshiyasu, Y. — 1995. Development and fecundity ofOrius sauteri (Poppius) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) reared onAphis gossypii Glover and corn pollen. —Jap. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool., 39, 84–85.
Kiman, Z. B. &Yeargan, K. V. — 1985. Development and reproduction of the predatorOrius insidiosus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) reared on diets of selected plant material and arthropod prey. —Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 78, 464–467.
Péricart, J. — 1972. Hémiptères. Anthocoridae, Cimicidae et Microphysidae de l’Ouest Paléarctique. —Masson & Cie, Paris, 402 pp.
Richards, P. C. &Schmidt, J. M. — 1996. The effect of selected dietary supplements on survival and reproduction ofOrius insidiosus (Say) (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae). —Can. Entomol., 128, 171–176.
Riudavets, J., Gabarra, R. &Castañe, C. — 1993.Frankliniella occidentalis predation by native natural enemies. —IOBC/WPRS Bull., 16(2), 137–140.
Salas-Aguilar, J. &Ehler, E. — 1977. Feeding habits ofOrius tristicolor. —Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 70, 60–62.
Stanley, R. G. &Liskens, H. F. — 1974. Pollen: biology, biochemistry, management.Springer Verlag, New York, 307 p.
Vacante, V. & Tropea Garzia, G. — 1993. Prime osservazioni sulla risposta funzionale diOrius laevigatus (Fieber) nel controllo diFrankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) su peperone in serra fredda. —Colture Protette, suppl. no. 1, 33–36.
Van de Veire, M. — 1995. Integrated pest management in glasshouse tomatoes, sweet peppers and cucumbers in Belgium. —Doctoral dissertation, University of Ghent, 133 p.
Villevieille, M. &Millot P. — 1991. Lutte biologique contreFrankliniella occidentalis avecOrius laevigatus sur fraisier. —IOBC/WPRS Bull., 14(5), 57–64.
Zhou, W. &Wang, R. — 1989. Rearing ofOrius sauteri (Hem.: Anthocoridae) with natural and artificial diets. —Chin. J. Biol. Control, 5, 9–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vacante, V., Cocuzza, G.E., De Clercq, P. et al. Development and survival ofOrius albidipennis andO. levigatus (Het.: Anthocoridae) on various diets. BioControl 42, 493–498 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02769809
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02769809