Abstract
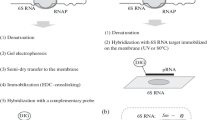
A reverse Northern analysis that effectively eliminates the false positives isolated from differential display of mRNAs (DD) is demonstrated. Preparation of probe by one-step labeling in reverse transcription reaction is found to be more effective and specific as compared to the preparation of probe by random priming of reverse transcribed cDNA pool. Reverse Northern assay of DNA fragments isolated from DD prior to their cloning into plasmid, analysis of multiple fragments on single slot blot, and requirement of RNA only in small amounts as compared to conventional Northern makes the protocol quick, effective, and economic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang, P. and Pardee, A. B. (1992) Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction.Science 257, 967–971.
Zhao, S., Ooi, S. L., and Pardee, A. B. (1995) New primer strategy improves precision of differential display.BioTechniques 18, 842–850.
Tokuyama, Y. and Takeda, J. (1995) Use of33P-labeled primer increases the sensitivity and specificity of mRNA differential display.BioTechniques 18, 424, 425.
Reeves, S. A., Rubio, M-P., and Louis, D. N. (1995) General method for PCR amplification and direct sequencing of mRNA differential display products.BioTechniques 18, 18–20.
McClelland, M., Francoise M-D., and Welsh, J. (1995) RNA fingerprinting and differential display using arbitrarily primed PCR.Trends Genetics 11, 242–246.
Callard, D., Lescure, B., and Mazzolini, L. (1994) A method for the elimination of false positives generated by the mRNA differential display technique.BioTechniques 16, 1906–1103.
Mou, L., Miller, H., Li, J., Wing, E., and Chalifour, L. (1994) Improvements to the differential display method for gene analysis.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199, 564–569.
Chang, A. C.-M., Janosi, J., Hulsbeek, M., Jong, D. de, Jeffrey, K. J., Noble, J. R., and Reddel, R. R. (1995) A novel human cDNA highly homologous to the fish hormone stanniocalcin.Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 112, 241–247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wadhwa, R., Duncan, E., Kaul, S.C. et al. An effective elimination of false positives isolated from differential display of mRNAs. Mol Biotechnol 6, 213–217 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740775
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740775