Abstract
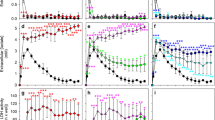
Increased ammonia has been considered a key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. The high concentration of ammonia interferes with oxidative metabolism in the brain through an inhibitory effect on the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA). Inhibition of the TCA cycle may result in depletion of ATP. Due to the involvement of astrocytes in brain detoxification of ammonia, these cells are good candidates for studying ammonia's effect on energy stores in the brain. C6-glioma cells, which have altered glycolytic rates, may show greater sensitivity to the toxicity of ammonium chloride than astrocytes. To study the effect of ammonium chlrode on energy storage of both astrocytes and C6-glioma, we observed the acute and chronic effects of NH4Cl (7.5 or 15 mM) on the metabolism of isolated astrocytes and C6-glioma cells. Primary astrocytes were isolated from the cerebral hemispheres of 1–2 day old Sprague-Dawley rats, and C6-glioma cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). Following treatment of the cells with ammonia, glucose, lactate, glutamate, ATP, and PCr were assayed. Our data showed that at 15 min following treatment with NH4Cl, there were no significant differences in the concentration of metabolites measured in astrocytes. However, following 15 min of treatment with NH4Cl, the concentration of some metabolites, for example. ATP and lactate, changed significantly in C6-glioma cells. We have shown that 24 h of treatment was sufficient time to see significant biochemical changes but not morphological changes in either cell type. Simultaneous biochemical and morphologicla changes were observed 48 h following treatment in C6-glioma cells and at 9–10 days following treatment in primary astrocytes. In primary astrocytes at 24 h following treatment, glucose utilization increased. This high utilization of glucose was in accordance with the increase in lactate and glutamate production and the decrease in ATP and PCr formation. In C6-glioma cells the utilization of glucose increased but this high utilization of glucose was consistent with a significant decrease in the concentration of lactate, glutamate and ATP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin, A.M. (1982). Ammonia. In (A. Lajtha, ed),Handbook of Neurochemistry, Vol. 1, 2nd Ed. Plenum, New York, pp. 117–137.
Berl, S. (1971). Cerebral amino acid metabolism in hepatic coma.Exp. Biol. Med.,40:71–84.
Bessman, S.P., and Bessman, A.N. (1955). The cerebral and peripheral uptake of ammonia in liver disease with an hypothesis for the mechanism of hepatic coma.J. Clin. Invest. 34:622–628.
Bessman, S.P. (1956). In (W.D. McElroy, and B. Glass, ed.)Inorganic Nitrogen Metabolism. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press, pp. 408.
Bessman, S.P., and Pal, N. (1976). In (S. Grisolia, R. Baguena, and F. Major, eds.)The Urea Cycle, Wiley, New York, pp. 83–88.
Clark, G.M., and Eiseman, B.E. (1958),New England J. Med. 259:178.
Conn, H.O., and Lieberthal, M.L. (1979),The Hepatic Coma Syndromes and Lactulose, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore.
Cooper, A.J.L., McDonald, J.M., Gelbard, A.S., Gledhill, R.F., and Duffy, T.E. (1979). The metabolic fate of13N-labeled ammonia in rat brain.J. Biol. Chem. 245:4982–4992.
Cooper, A.J.L., and Lai, J.C.K. (1987). Cerebral ammonia metabolism in normal and hyperammonemic rats.Neurochem. Pathol. 6:67–95.
Cooper, A.J.L., and Plum, F. (1987). Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia.Physiol. Rev. 67:440–519.
Di Chiro, G., DeLapaz, R.L., Brooks R.A., Sokoloff, L., Kornblith, P.L., Smith, B.H.,et al. (1982). Glucose utilization of cerebral gliomas measured by [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography.Neurology 32:1323–1329.
Du Ruisseau, J.P., Greenstein, J.P., Winitz, M., and Birnbaum, S.M. (1957).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 68:161.
Flannery, D.B., Hsia, E., and Wolf, B. (1982). Current status of hyperammonemic syndromes.Hepatology 2:495–506.
Galarraga, J., Loreck, D.J., Graham, J.F., DeLapaz, R.L., Smith, B.H., Hallgren, D., and Cummins, C.J. (1986). Glucose metabolism in human gliomas: Correspondence ofin situ andin vitro metabolic rates and altered energy metabolism.Metab. Brain Dis. 1:279–291.
Haghighat, N., and McCandless, D. (1997). The effect of 6-Aminonicotinamide on metabolism of astrocytes and C6-glioma cells.Metab. Brain Dis. 12:29–45.
Hawkins, R.A., Miller, A.L., Nielsen, R.C., and Veech, R.L. (1973). The acute action of ammonia on rat brain metabolismin vivo.Biochem. J. 134:1001–1008.
Hindfelt, B, and Siesjo, B.K. (1971). Cerebral effects of acute ammonia intoxication. II. The effect upon energy metabolism.Scan. D. Clin. Lab. Invest. 28:365–374.
Hindfelt, B. (1972). The effect of sustained hyperammonia upon the metabolic state of the brain.Scand. J. Clin. Invest. 30:245–255.
Hindfelt, B., Plum, F., and Duffy, T.E. (1977). Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts.J. Clin. Invest. 59:386–396.
Hsia, Y.E. (1974). Inherited hyperammonemic syndromes.Gastroenterol. 67:347–374.
Hoyumpa, A.M., Desmond, P.V., Avant, G.R., Roberts, R.K., and Schenker, S. (1979). Clinical conference Hepatic encephalopathy.Gastroenterol. 76:84–195.
Huttenlocher, P.R., Schwartz, A.D., and Klatskin, G. (1969). Reye's syndrome: ammonia intoxication as a possible factor in the encephalopathy.Pediatrics 43:443–454
Kirsch, W.M. (1965). Substrates in glycolysis in intracranial tumors during complete ischemia.Cancer Res. 25:432–439.
Lai, J.C.K., and Cooper, A.J.L. (1986). Brain alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: kinetic properties, regional distribution, and effects of inhibitors,J. Neurochem. 47:1376–1386.
Lowry, O.H., and Passonneau, J.V. (1972). A flexible system of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, San Francisco, London.
McCandless, D.W., and Schenker, S. (1981). Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on energy stores in the cerebral reticular activating system.Exp. Brain. Res. 44:325–330.
McKhann, G.M., and Tower, D.B. (1961). Ammonia toxicity and cerebral oxidative metabolism.Am. J. Physiol. 200:420–424.
Navazio, F., Gerritsen, T., and Wright, G.J. (1961). Relationship of ammonia intoxication to convulsions and coma in rats.J. Neurochem. 8:146–151.
Norenberg, M.D., and Martinez-Hermandez, A. (1979). Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain.Brain Res. 161:303–310.
Norenberg, M.D. (1981). The astrocyte in liver disease. In (St Fedoroff and L. Hertz, eds.),Advances in Cellular Neurobiology. Vol. 2, Academic: New York, pp. 303–352.
Norenberg, M.D., Neary, J.T., Baker, L., Blicharska, J., and Norenberg, L.O.B. (1990). Protection of ammonia-induced swelling in cultured astrocytes.Trans. Am. Soc. Neurochem. 21:221.
Norenberg, M.D., Baker, L., Norenberg, L.O.B., Blicharska, J., Bruce-Gregorios, J.H., and Neary, J.T. (1991). Ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in primary culture.Neurochem Res. 16: 833–836.
Peters, E.L., and Tower, D.B. (1959). Glutamic acid and glutamine metabolism in cerebral cortex after seizure induced by methionine sulfoximine.J. Neurochem. 5:80–90.
Ratnakumari, L., and Murthy, Ch.R.K. (1992).In vitro andin vivo effects of ammonia on glucose metabolism in the astrocytes of rat cerebral cortex.Neuroscience Letters 148:85–88.
Roberts, E. (1980). Epilensy and antiepileptic drugs: a speculative synthesis. In (G.H. Glaser, J.K. Penry, and D.M. Woodbury, eds.),Antiepileptic, Drugs. Mechanism of Action. Raven, New York, pp. 667–713.
Schenker, S., McCandless, D.W., Brophys, E., and Lewis, M.S. (1967). Studies on the intracerebral toxicity of ammonia.J. Clin. Invest. 46:838–848.
Siegel, S. (1956). Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc.
Smith, P.K., Krohn, R.I., Hermanson, G.T., Mallia, A.K., Gartner, F.H., Provenzano, M.D.,et al. (1985). Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid.Anal. Biochem. 150:76–85.
Strecker, H.J. (1957). In (D. Righter, ed.),Metabolism of the Central Nervous System, London: Pergamon, pp. 459.
Tower, D.B., Wherrett, J.R., and McKhann, G.M. (1961). In (S.S. Kety, ed.)Regional Chemistry of the Nervous System. Oxford: Pergamon, p. 65.
Yu, A.C.H., Schousboe, A., and Hertz, L. (1984). Influence of pathological concentrations of ammonia on metabolic fate of14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures.J. Neurochem. 42: 594–597.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghighat, N., McCandless, D.W. Effect of ammonium chloride on energy metabolism of astrocytes and C6-glioma cellsin vitro . Metab Brain Dis 12, 287–298 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674673
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674673