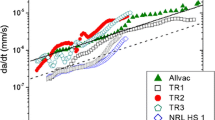
Abstract
Interactions between hydrogen embrittlement and temper embrittlement have been examined in a study of fracture and low growth rate (near-threshold) fatigue crack propagation in 300-M high strength steel, tested in humid air. The steel was investigated in an unembrittled condition (oil quenched after tempering at 650°C) and temper embrittled condition (step-cooled after tempering at 650°C). Step-cooling resulted in a severe loss of toughness (approximately 50 pct reduction), without loss in strength, concurrent with a change in fracture mode from micr ovoid coalescence to inter granular. Using Auger spectroscopy analysis, the embrittlement was attributed to the cosegregation of alloying elements (Ni and Mn) and impurity elements (P and Si) to prior austenite grain boundaries. Prior temper embrittlement gave rise to a substantial reduction in resistance to fatigue crack propagation, particularly at lower stress intensities approaching the threshold for crack growth(x0394;K o). At intermediate growth rates (10-5 to 10-3 mmJcycle), propagation rates in both unembrittled and embrittled material were largely similar, and only weakly dependent on the load ratio, consistent with the striation mechanism of growth observed. At near-threshold growth rates (<10−5 to 10−6 mmJcycle), embrittled material exhibited significantly higher growth rates, 30 pct reduction in threshold ΔKo values and intergranular facets on fatigue fracture surfaces. Near-threshold propagation rates (and ΔKo values) were also found to be strongly dependent on the load ratio. The results are discussed in terms of the combined influence of segregated impurity atoms (temper embrittlement) and hydrogen atoms, evolved from crack tip surface reactions with water vapor in the moist air environment (hydrogen embrittlement). The significance of crack closure concepts on this model is briefly described. ntmis]formerly with the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, University of California in Berkeley.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. R. Low, Jr.: inFracture of Engineering Materials, ASM, 1964, p. 127.
J. R. Low, Jr., D. F. Stein, A. M. Turkalo, and R. P. Laforce:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, p. 14.
H. Ohtani and C. J. McMahon, Jr.:ActaMet., 1975, vol. 23, p. 377.
J. M. Capus:Rev. Met., 1959, vol. 56, p. 181.
E. B. Kula and A. A. Anctil:J. Mater., 1969, vol. 4, p. 817.
J. R. Rellick and C. J. McMahon, Jr.:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 2439.
R. O. Ritchie and J. F Knott.Knott: Acta Met., 1973, vol. 21, p. 639.
R. Bruscato:Weld. J. Suppl., 1970, vol. 49, p. 148-S.
K. Yoshino and C. J. McMahon, Jr.:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 363.
C. J. McMahon, Jr, C. L. Briant, and S. K. Banerji:Proc. Fourth Int. Conf. on Fracture, Waterloo, Canada, June 1977, vol. 2, p. 363.
.U.R. Viswanathan and S. J. Hudak: inEffect of Hydrogen on Behavior of Materials, A.W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein, eds., p. 262, 1975. The Metal-lurgical Society of AIME.
R. M. Latanison and H. Opperhauser, Jr.:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 483.
R. P. Wei and J. D. Landes:Mater. Res. Stand., 1969, vol. 9, p. 25.
F. J. Witt: inPractical Application of Fracture Mechanics to Pressure-Vessel Technology, p. 163, The Institution of Mechanical Engineers, London, 1971.
.J. D. Landes and J. A. Begley: Westinghouse Scientific Paper 76-1E7-JINTF-P3, May 1976, Westinghouse Scientific Laboratories, Pittsburgh, Pa.
R. W. Landgraf, J-D. Morrow, and T. Endo:J. Mater., 1969, vol. 4, p. 176.
R. 0. Ritchie, G. G. Garrett, and J. F. Knott:Int. J. Fract. Mech., 1971, vol. 7, p. 462.
H. Ohtani, H. C. Feng, C. J. McMahon, Jr., and R. A. Mulford:Met. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, p. 87.
M. Guttmann:Surface Sci., 1975, vol. 52, p. 213.
R. A. Mulford, C. J. McMahon, Jr., D. P. Pope, and H. C. Feng:Met. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, p. 1183.
C. J. McMahon, Jr, E. Furubayashi, H. Ohtani, and H. C. Feng:ActaMet., 1976, vol. 24, p. 695.
R. Viswanathan:Met. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, p. 809.
B. J. Schulz and C. J. McMahon, Jr.: inTemper Embrittlement of Alloy Steels, p. 104, ASTM STP 499, ASTM, Philadelphia, Pa., 1972.
G. Clark, R. 0. Ritchie, and J. F. Knott:Nature Phys. Sci., 1972, vol. 239, p. 104.
M. Guttmann and P. Krahe:Scr. Met., 1973, vol. 7, p. 93.
C. L. Smith and J. R. Low, Jr.:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 279.
W. Steven and K. Balajiva:J. Iron SteelInst., 1959, vol. 193, p. 141.
P. C. Paris and F. Erdogan:J. Basic Eng., Trans. ASME Series D, 1963, vol. 85, p. 528.
C. E. Richards and T. C. Lindley:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1972, vol. 4, p. 951.
R. O. Ritchie:J. Eng. Mater. Tech., Trans. ASME Series H, 1977, vol. 99, p. 194. (Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Report No. LBL-5496, Oct. 1976, University of California).
P. C. Paris. R. J. Bucci, E. T. Wessel, W. G. Clark, and T. R. Mager: inStress Analysis and Growth of Cracks, p. 141, ASTM STP 513, ASTM, Philadelphia, Pa., 1972.
R. J. Bucci, W. G. Clark, Jr., and P. C. Paris: itIbid, p. 177.
R. J. Bucci, P. C. Paris, R. W. Hertzberg, R. A. Schmidt, and A. F. Anderson: itIbid, p. 125
34.R. A. Schmidt and P. C. Paris: inProgress in Flaw Growth and Fracture Toughness Testing, p. 79, ASTM STP 536, ASTM, Philadelphia, Pa, 1972.
P. E. Irving and C. J. Beevers:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 391.
R. J. Cooke, P. E. Irving, G. S. Booth, and C. J. Beevers:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1975, vol. 7, p. 69.
J. A. Begley and P. R. Toolin:Int. J. Fract., 1973, vol. 9, p. 243.
R. 0. Ritchie:Metal Sci., 1977, vol. 11, no. 8J9, in press. (Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Report No. LBL-5730, Nov. 1976, University of California.) tory, Report No. LBL-5730, Nov. 1976, University of California.)
V. Weiss and D. N. Lai:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 1946.
T. Misawa:Corros. Sci., 1973, vol. 13, p. 659.
A. R. Troiano:Trans. ASM, 1960, vol. 52, p. 54.
E. D.Hondros:Proc. Roy. Soc. Ser. A, 1965, vol. 286, p. 479.
R. A. Oriani and P. H. Josephic:ActaMet., 1974, vol. 22, p. 1065.
W. W. Gerberich and Y. T. Chen:Met. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, p. 271.
W. Elber: inDamage Tolerance in Aircraft Structures, p. 230, ASTM STP 486, ASTM, Philadelphia, Pa., 1971.
T. C. Lindley and C. E. Richards:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1974, vol. 14, p. 281.
F. J. Pitoniak, A. F. Grandt, L. T. Montulli, and P. F. Packman:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1974, vol. 6, p. 663.
T. T. Shih and R. P. Wei:Ibid, 1974, vol. 6, p. 19.
A. J.McEvily: Metal Sci., 1977, vol.11, no. 8/9, in press.
A. Otsuka, K. Mori, and T. Miyata:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1975, vol. 7, p. 429.
0. Buck, J. D. Frandsen, and H. L. Marcus:Ibid, 1975, vol. 7, p. 167.
P. E. Irving, J. L. Robinson, and C. J. Beevers:Ibid, 1975, vol. 7, p. 619.
P. E. Irving, J. L. Robinson, and C. J. Beevers:Int. J. Fract., 1973, vol. 9, p. 105.
V. Bachmann and D. Munz:Ibid, 1975, vol. 11, p. 713.
C. J. McMahon, Jr.:Mater. Sci. Eng, 1977, vol. 25, p. 233.
R. P. Wei and G. W. Simmons:Scr. Met., 1976, vol. 10, p. 153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly with the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratery, University of California in Berkeley.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ritchie, R.O. Influence of impurity segregation on temper em brittlement and on slow fatigue crack growth and threshold behavior in 300-M high strength steel. Metall Trans A 8, 1131–1140 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02667398
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02667398