Summary
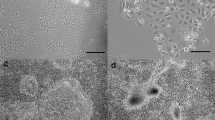
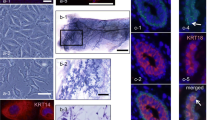
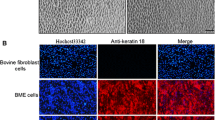
One bovine mammary epithelial cell clone, designated PS-BME-C1, and two bovine mammary epithelial cell lines, designated PS-BME-L6 and PS-BME-L7, were derived from mammary tissue of a pregnant (270 day) Holstein cow. The cells exhibit the distinctive morphologic characteristics of mammary epithelial cells and express the milk fat globule membrane protein, PAS-III. They form domes when cultured on plastic substrata and acinilike aggregates when cultured on a collagen matrix. These cells are capable of synthesizing and secretingα-lactalbumin andα-s1-casein when cultured on a collagen matrix in the presence of insulin, cortisol, and prolactin. The cells have a near-normal diploid number and do not grow in suspension culture. When transplanted to the cleared mammary fat pads of female athymic nude mice, the cells readily proliferate forming noninvasive palpable spherical cellular masses within 8 wk after inoculation. The cells may become a useful tool to study the regulation of ruminant mammary epithelial cell growth and differentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akers, R. M.; McFadden, T. B.; Beal, W. E., et al. Radioimmunoassay for measurement of bovineα-lactalbumin in serum, milk and tissue culture media. J. Dairy Res. 53:419–429; 1986.
Barcellos-Hoff, M. H.; Aggeler, J.; Ram, T. G., et al. Functional differentiation and alveolar morphogenesis of primary mammary cultures on reconstituted basement membrane. Development 105:223–235; 1989.
Baumrucker, C. R.; Deemer, K. P.; Walsh, R., et al. Primary culture of bovine mammary acini on a collagen matrix. Tissue & Cell 20:541–554; 1988.
Chen, L.-H.; Bissell, M. J. A novel regulatory mechanism for whey acidic protein genes of the rat and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1:45–54; 1989.
Collier, R. J.; Bauman, D. E.; Hays, R. L. Lactogenesis in explant cultures of mammary tissue from pregnant cows. Endocrinology 100:1192–1200; 1977.
Collier, R. J. Nutritional, metabolic, and environmental aspects of lactation. In: Larson, B. L., ed. Lactation. Ames: The Iowa State University Press; 1985:91–104.
Danielson, K. G.; Oborn, C. J.; Durban, E. M., et al. Epithelial mouse mammary cell line exhibiting normal morphogenesis in vivo and function differentiation in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:3756–3760; 1984.
Ethier, S. P. Serum-free culture conditions for the growth of normal rat mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 22:485–490; 1986.
Freshney, R. I. Introduction: Principles of sterile technique and cell propagation. In: Freshney, R. I., ed. Animal cell culture, a practical approach. New York:Academic Press; 1986:1–11.
Gertler, A.; Weil, A.; Cohen, N. Hormonal control of casein synthesis in organ culture of the bovine lactating mammary gland. J. Dairy Res. 49:387–398; 1982.
Goodman, G. T.; Akers, R. M.; Friderici, K. H., et al. Hormonal regulation ofα-lactalbumin secretion from bovine mammary tissue cultured in vitro. Endocrinology 112:1324–1330; 1983.
Hadsell, D. L.; Vega, J. R.; Skaar, T. C., et al. Regulation of type I insulin-like growth factor receptors in a clonal population of bovine mammary epithelial cells. American Dairy Science Association, 1990 Annual Meeting, Raleigh, NC. 24–27, June 1990:P285.
Hay, R. J. Preservation and characterization. In: Freshney, R. I., ed. Animal cell culture, a practical approach. New York: Academic Press; 1986:71–112.
Hurley, D.; Hwang, S.-I.; Rocha, V. Casein accumulation in distended rough endoplasmic reticulum of collagen gel-cultivated mouse mammary epithelia. J. Cell. Physiol. 141:135–141; 1989.
Hsu, T. C. Karytology of cells in culture. In: Kruse, P. F.; Patterson, M. K., Jr., ed. Tissue culture methods and applications. New York: Academic Press; 1973:764–773.
Imagawa, W.; Tomooka, Y.; Nandi, S. Serum-free growth of normal and tumor mouse mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:4074–4077; 1982.
Kaetzel, C. S.; Banghart, L. R.; Jackson, D. Y., et al. Expression of a 95 kDa glycoprotein on the apical surfaces of bovine mammary epithelial cells during lactation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 15:117–118; 1987.
Laemmli, U. K. Cleavage of protein during assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685; 1970.
Mackenzie, D. D. S.; Forsyth, I. A.; Brooker, B. E., et al. Culture of bovine mammary epithelial cells on collagen gels. Tissue & Cell 14:231–244; 1982.
MacPherson, I. Soft agar techniques. In: Kruse, P. F.; Patterson, M. K., Jr., ed. Tissue culture methods and applications. New York: Academic Press; 1973:276–280.
McGrath, M. F. A novel system for mammary epithelial cell culture. J. Dairy Sci. 70:1967–1980; 1987.
Nicholas, K. R.; Sankaran, L.; Kulski, J. K., et al. Comparison of some biological effects of epidermal growth factor and commercial serum albumin on the induction ofα-lactalbumin in rat and rabbit mammary explants. J. Endocrinol. 119:133–139; 1988.
O’Brien, T.; Riss, T. L.; Baumrucker, C. R. Ultrastructure of collagenaseisolated acini (alveoli) from lactating mammary tissue. Trans. Am. Micros. Soc. 100:306–315; 1981.
Park, C. S.; Smithe, J. J.; Sasaki, M., et al. Isolation of functionally active acini from bovine mammary gland. J. Dairy Sci. 62:537–545; 1978.
Parry, G.; Cullen, B.; Kaetzel, C. S., et al. Regulation of differentiation and polarized secretion in mammary epithelial cells maintained in culture: extracellular matrix and membrane polarity influences. J. Cell Biol. 105:2043–2051; 1987.
Rosen, J. M.; Bayna, E. Analysis of milk protein gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol. Biol. Med. 6:501–509; 1989.
Schmid, E.; Schiller, D. L.; Grund, C., et al. Tissue type-specific expression of intermediate filament proteins in cultured epithelial cell line from bovine mammary gland. J. Cell Biol. 95:38–50; 1982.
Shamay, A.; Gertler, A. A model for in vitro proliferation of undifferentiated bovine mammary epithelial cells. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 10:923–929; 1986.
Sheffield, L. G.; Welsch, C. W. Transplantation of bovine mammary tissue to athymic nude mice: growth subcutaneously and in mammary gland-free fat pads. J. Dairy Sci. 69:1141–1147; 1986.
Skaar, T. C.; Gibson, C. A.; Vega, J. R., et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins are hormonally regulated in a bovine mammary epithelial cell line. The Endocrine Society, 72nd Annual Meeting, Atlanta, GA. 20–23, June 1990:307.
Spyratos, F.; Le Doussal, V.; Zangerle, P. F., et al. Immunohistochemical detection of alpha-lactalbumin and gross cyst fluid protein in human breast carcinoma. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 464:571–572; 1986.
Stemberger, B. H.; Patton, S. Relationship of size, intracellular location, and time required for secretion of milk fat droplets. J. Dairy Sci. 64:422–426; 1981.
Tannenbaum, E.; Cassidy, M.; Alabaster, O., et al. Measurement of cellular DNA mass by flow microfluorometry with use of a biological internal standard. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 26:145–148; 1978.
Towbin, H.; Stachelin, R.; Gordon, J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedures and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:4350–4354; 1979.
Turner, J. D.; Hung, H. T. Establishment of hormone responsive bovine mammary epithelial cell lines. American Dairy Science Association and American Society of Animal Science Combined Annual Meeting, Lexington, KY. 31, July-4, Aug 1989:317.
Watson, J. V. Quantitation of molecular and cellular probes in population of single cells using fluorescence. In: Hales, C. N.; Yolken, R. H., eds. Molecular and cellular probes, vol. 1. New York: Academic Press; 1987:121–136.
Welsch, C. W.; McManus, M. J.; DeHoog, J. V., et al. Hormone-induced growth and lactogenesis of grafts of bovine mammary gland maintained in the athymic “nude” mouse. Cancer Res. 39:2046–2050; 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Pennsylvania State University Experiment Station.
The PS-BME cells are the property of The Pennsylvania Research Corporation. Scientists interested in obtaining the PS-BME clone or cell lines for their research may request them from the corresponding author.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02634376.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gibson, C.A., Vega, J.R., Baumrucker, C.R. et al. Establishment and characterization of bovine mammary epithelial cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal 27, 585–594 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02631290
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02631290