Summary
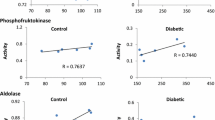
Several lysosomal enzymes (β-N-D-acetylglucosaminidase, β-D-glucoronidase, α-D-galactosidase, β-D-galactosidase, α-L-fucosidase, α-D-glucosidase, α-D-mannosidase, β-D-glucosidase), glycated albumin and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were determined in the serum of 81 insulin-dependent diabetics with different degrees of metabolic control (optimal, 21 patients; good, 39 patients; poor, 21 patients) and without signs of complications, and in 42 control subjects. All parameters examined increased in serum in inverse proportion to the degree of metabolic control. A highly significant correlation (p<0.01) was found between lysosomal enzymes and both glycated albumin and HbA1c. All parameters correlated with hyperglycemia, glycated albumin having the highest γ-value (0.586) and lysosomal enzymes the lowest one. Unlike glycated albumin and HbA1c, serum levels of lysosomal enzymes in patients with optimal metabolic control were undistinguishable or even lower than those of controls. A 2-month longitudinal monitoring of a patient who was hospitalized in conditions of poor metabolic control and adequately treated, proved that lysosomal enzymes diminished in serum parallel to glycated albumin and HbA1c in relation to improvement of the metabolic situation. The conclusion is drawn that serum lysosomal enzymes are good indicators of the metabolic control of diabetic patients probably reflecting the overall metabolic state connected with insulin action rather than hyperglycemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E. C., Huff T. A., Cope N. D., Wilson J. B., Bransome E. D., Huisman T. H. J.: Determination of the glycosylated hemoglobins (HbA1) with a new microcolumn procedure — Diabetes27, 931, 1978.
Belfiore F., Lo Vecchio L., Napoli E., Borzi V.: Increased β-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity in diabetes mellitus — Clin. Chem.20, 1229, 1974.
Deming W. E.: Statistical adjustment of data — J. Wiley and Sons, New York, 1943; p. 184.
Dolhofer R., Siess E. A., Wieland O. H.: Inactivation of bovine kidney β-N-acetylgucosaminidase by non enzymatic glucosylation — Hoppe-Seyler’s Z. physiol. Chem.363, 1427, 1982.
Dolhofer R., Wieland O. H.: Increased glycosylation of serum albumin in diabetes mellitus — Diabetes29, 417, 1980.
Gabbay K. A., Hasty K., Breslow J. L., Ellison R. C., Bunn H. F., Gallop P. M.: Glycosylated hemoglobins and long-term blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus — J. clin. Endocrinol.44, 859, 1977.
Kennedy L., Mehl T. D., Riley W. J., Merimee T. J.: Non-enzymatically glycosylated serum protein in diabetes mellitus: an index of short-term glycaemia — Diabetologia21, 94, 1981.
Kirschenbaum D. M.: Glycosylation of proteins: its implications in diabetic control and complications — Pediat. Clin. N. Amer.31, 611, 1984.
Kohler E., Sheth K. J., Good T. A.: Plasma acidic glycohydrolases in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Acta diabetol. lat.18, 243, 1981.
Lombardo A., Caimi L., Marchesini S., Goi G., Tettamanti G.: Enzymes of lysosomal origin in human plasma and serum: assay conditions and parameters influencing the assay — Clin. chim. Acta108, 337, 1980.
Mallia A. K., Hermanson G. T., Krohn R. I., Fujimoto E. K., Smith P. K.: Preparation and use of a boronic acid affinity support for separation and quantitation of glycosylated hemoglobins — Anal. Letters14, 649, 1981.
Miralles J. M., Corrales J. J., Garcia-Diez L. C., Cabezas J. A., Reglero A.: N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase and α-L-fucosidase activities in relation to the glycosylated hemoglobin levels and to retinopathy in diabetes — Clin. chim. Acta121, 373, 1982.
Niebes P.: Determination of enzymes and degradation products of glycosaminoglycans metabolism in the serum of healthy and varicose subjects — Clin. chim. Acta42, 399, 1972.
Perdichizzi G., Cucinotta D., Saitta A., Cavalieri A., Squadrito G.: Serum and urinary activities of β-N-acetylglucosaminidase and β-glucuronidase in diabetic patients — Acta diabetol. lat.20, 257, 1983.
Shin Y. S., Stern C., Rucker A. V., Endres W.: Glycated haemoglobin and glycated albumin: evaluation of different methods in diabetic control — J. clin. Chem. clin. Biochem.22, 47, 1984.
Snedecor G. W., Cochran W. G.: Statistical methods — The Iowa State University Press, Ames, 1967.
Trivelli L. A., Ranney H. M., Lai H. T.: Hemoglobin components in patients with diabetes mellitus — New Engl. J. Med.284, 353, 1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goi, G., Fabi, A., Lorenzi, R. et al. Serum enzymes of lysosomal origin as indicators of the metabolic control in diabetes: Comparison with glycated hemoglobin and albumin. Acta diabet. lat 23, 117–125 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624671
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624671