Abstract
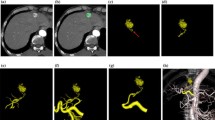
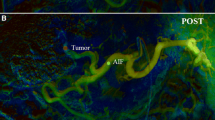
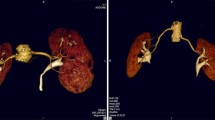
Digital substraction angiography (DSA) with a low injection rate of contrast (0.5 ml/sec) was studied as a means of predicting the regional perfusion of percutaneously placed catheters for hepatic arterial chemotherapy. In 64 hepatic artery catheter placements, conventional injection rate angiography (3–5 ml/sec) and low infusion rate DSA exams were compared to conventional radionuclide perfusion studies performed with Tc-99m-MAA. In 58 of 64 cases (90.6%) the conventional arteriogram correctly predicted the extent of hepatic perfusion, whereas in 63 of 64 cases (98%), the low flow DSA exam correctly predicted hepatic perfusion. The conventional arteriogram correctly predicted the extent of extrahepatic perfusion in 32 cases (50%), with a sensitivity of 100%, but a specificity of only 39.6%. The DSA exam was correct in defining the presence or absence of extrahepatic perfusion in 57 of 64 cases for a sensitivity of 82% and a specificity of 91%. Despite the quantitative difference between the low infusion rate DSA study and the chemotherapy infusion (10 ml/hr), it is a useful tool to assist in the correct positioning of temporary catheters for hepatic arterial chemotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan WD, Ensminger WD, Come SE, Smith EH, D'Orsi CJ, Levin DC, Takvorian RW, Steele GD (1980) Radionuclide angiography to predict patient response to hepatic artery chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Rep 64:1217–1222
Lutz RJ, Miller DL (1988) Mixing studies during hepatic artery infusion in an in vitro model. Cancer 62:1066–1073
Bledin AG, Kantarjian HM, Kim EE, Wallace S, Chuang VP, Patt YZ, Haynie TP (1982) 99m-Tc-Labeled macroaggregated albumin in intrahepatic arterial chemotherapy. AJR 139:711–715
Bledin AG, Kim EE, Chuang VP, Wallace S, Haynie TP (1984) Changes of arterial blood flow patterns during infusion chemotherapy, as monitored by intra-arterially injected Tc-99m macroaggregated albumin. Br J Radiology 57:197–202
Charnsangavej C, Carrasco CH, Wallace S, Richli W, Haynie TP (1987) Hepatic arterial flow distribution with hepatic neoplasms: Significance in infusion chemotherapy. Radiology 165:71–73
Barth KH, Lutz RJ, Kremers PW, Miller DL (1988) Mixing problems of low flow hepatic artery infusion: Improvement with small caliber double-lumen balloon catheters. Invest Radiol 23:519–523
Silbergleit R, Steffey DJ, DeFilipp GJ, Junk L (1988) In vivo evaluation of cerebral perfusion at slow injection rates for intraarterial chemotherapy. 36th Annual Meeting of the Association of University Radiologists, April 17–21, 1988, New Orleans, LA
Ziessman HA, Thrall JH, Yang PJ, Walker SC, Cozzi EA, Neiderhuber JE, Gyves JW, Ensminger WD, Tuscan MC (1984) Hepatic arterial perfusion scintigraphy with Tc-99m-MAA. Radiology 152:167–172
Daly JM, Butler J, Kemeny N, Yeh SDJ, Ridge JA, Botet J, Bading JR, DeCosse JJ, Benua RS (1985) Predicting tumor response in patients with colorectal hepatic metastases. Ann Surg 202:384–393
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrews, J.C., Williams, D.M., Shapiro, B. et al. Low infusion rate digital subtraction angiography to predict regional perfusion in hepatic arterial chemotherapy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 12, 277–280 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02575416
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02575416