Abstract
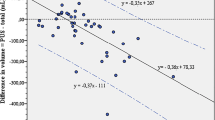
A portable ultrasound unit (BladderScan BVI 2000) has been developed which offers a non-invasive procedure to determine urine volume. This study was undertaken to evaluate the accuracy of measurements by this method. A high correlation was demonstrated between the catheterized volume and ultrasound estimation (r=0.98, p<0.0001). In patients with residual urine of >50 ml, the unit could correctly identify 93%. This instrument is useful in estimating the residual urine volume, and its application is recommended as an alternative to catheterization for the determination of residual urine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardenas, D. D., Kelly, E., Krieger, J. N., Chapman, W. H.: Residual urine volumes in patients with spinal cord injury: Measurement with a portable ultrasound instrument.Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil., 69, 514 (1988).
Roehrborn, C. G., Peters, P. C.: Can transabdominal ultrasound estimation of postvoiding residual (PVR) replace catheterization?Urology, 31, 445 (1988).
Harrison, N. W., Parks, C., Sherwood, T.: Ultrasound assessment of residual urine in children.Br. J. Urol., 47, 805 (1976).
Hakenberg, O. W., Ryall, R. L., Langlois, S. L., Marshall, V. R.: The estimation of bladder volume by sonocystography.J. Urol., 130, 249 (1983).
Alfthan, O., Mattsson, T.: Ultrasonic method of measuring residual urine.Ann. Chir. Gyn. Fenniae, 58, 300 (1969).
Henriksson, L., Marsal, K.: Bedside ultrasound diagnosis of residual urine volume.Arch. Gynecol., 231, 129 (1982).
Ravichandran, G., Fellows, G. J.: Accuracy of a hand-held real time ultrasound scanner for estimating bladder volume.J. Urol., 55, 25 (1983).
Widder, B., Kornhuber, H. H., Renner, A.: Restharnmessung in der ambulanten Versorgung mit einem Klein-Ultraschall-Gerät.Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr., 2, 1552 (1983).
Ireton, R. C., Krieger, J. N., Cardenas, D. D., Williams-Burden, B., Kelly, E., Souci, T., Chapman, W. H.: Bladder volume determination using a dedicated, portable ultrasound scanner.J. Urol., 143, 909 (1990).
Massagli, T. L., Cardenas, D. D., Kelly, E. W.: Experience with portable ultrasound equipment and measurement of urine volumes: Inter-user reliability and factors of patient position.J. Urol., 142, 969 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuse, H., Yokoyama, T., Muraishi, Y. et al. Measurement of residual urine volume using a portable ultrasound instrument. International Urology and Nephrology 28, 633–637 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02552157
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02552157