Abstract
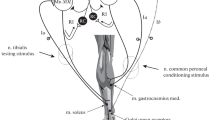
In testing of healthy subjects, we studied the influence of conditioning stimulation of then.peroneus communis on the H-reflex EMG discharge recorded from them. soleus. Two waves of inhibition separated by a period of relative facilitation of the reflex were observed. The first wave,D 1, was not longer than 50 msec. The intensity of later inhibition (D 2 wave) within a 500 to 4000 msec time segment linearly depended on the logarithm of the interval between the conditioning and test stimuli. Extrapolation showed that the duration of this wave could be evaluated as equal to 6.3 msec, on average. We also studied the temporal course of H-reflex inhibition after conditioning vibrational stimulation of the receptors of them. tibialis ant. andm. biceps femori. Within a 500 to 4000 msec test interval, it could also be fitted with a logarithmic dependence similar to that observed after electrical stimulation of then. peroneus comm. The duration of inhibition after vibrational stimulation of them. tibialis ant. andm. biceps femori was 6.2 and 8.9 sec, respectively. Inhibition evoked by both conditioning influences was not removed after a voluntary plantar flexion of the foot. Our observations support the statement that in humans stimulation of the afferent fibers from the antagonist muscles, as well of the muscle receptors, evokes in two-neuron reflex arcs presynaptic inhibition, whose duration reaches several seconds; this phenomenon can play a significant role in the control of muscle tone in the course of muscle performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Mizuno, R. Tanaka, and N. Yanagisawa, “Reciprocal group I inhibition ontriceps surae motoneurons in man,”J. Neurophysiol.,34, No. 6, 1010–1017 (1971).
A. El-Tohamy and E. M. Sedgwick, “Spinal inhibition in man: depression of the soleus H-reflex by stimulation of the nerve to the antagonist muscle,”J. Physiol.,337, 497–508 (1983).
B. L. Day, C. D. Marsden, J. A. Obeso, and J. C. Rothwell, “Long-lasting inhibition of the flexor monosynaptic reflex from extensor muscles in the human forearm,”J. Physiol.,326, 31P (1982).
C. Crone and J. Nielsen, “Methodological implications of the post activation depression of the soleus H-reflex in man”,Exp. Brain Res.,78, No. 1, 28–32 (1989).
H. Hultborn, B. Meunier, C. Morin, and E. Pierrot-Deseilligny, “Assessing changes in presynaptic inhibition of la fibers: a study in man and in the cat,”J. Physiol.,389, 729–756 (1987).
J. Cheng, J. D. Brooke, W. R. Staines, et al., “Long-lasting conditioning of the human soleus H reflex following quadriceps tendon tap,”Brain Res.,681, Nos. 1/2, 197–200 (1995).
P. Ashby and M. Verrier, “Human motoneuron responses to group I volleys blocked presynaptically by vibration,”Brain Res.,184, No. 2, 511–516 (1980).
J. E. Misiaszek, J. D. Brooke, K. B. Lafferty, et al., “Long-lasting inhibition of the human soleus H-reflex pathway after passive movement,”Brain Res.,677, No. 1, 69–81 (1995).
J. F. Iles and R. C. Roberts, “Inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes in the human lower limb,”J. Physiol.,385, 69–87 (1987).
P. J. Delwaide, P. Crenna, and M. N. Fleron, “Cutaneous nerve stimulation and motoneuronal excitability: I. Soleus and tibialis anterior excitability after ipsilateral sural nerve stimulation,”J. Neurol., Neurosurg., Psychiat.,44, No. 8, 699–707 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rudneva, V.N., Slivko, É.I. Long-lasting H-reflex inhibition evoked by stimulation of a nerve to the antagonist muscles and vibrational stimulation of the muscle receptors in humans. Neurophysiology 32, 34–37 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02515166
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02515166