Abstract
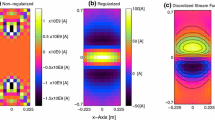
By extending the formalism previously developed for the design of unshielded, biplanar gradient coils, shielded biplanarB 0 coils optimized for homogeneity and either minimum energy or minimum power may be designed. We present results from an integrated approach to shielded biplanar coil design, the results of which are also applicable to gradient coils, enabling the design of shielded coils with a concomitant decrease in total inductance of the coil. Length constraints are also included in the integrated minimization procedure. Results from a preliminary design indicate that high-homogeneity, low-impedance, well-shielded coils result from this design approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowden GJ, Cadogan JM, Khachan J, Starrett RP (1991) Elimination of T2 decay problems in zeeman-perturbed NQR experiments.J Magn Reson 93: 603–608.
Bowden GJ, Prandolini MJ, Pope JM, Separovic F (1993) Zeeman-incremented multiple-quantum NMR.J Magn Reson 103: 307–312.
Martens MA, Petropoulos LS, Brown RW, Andrew JH, Morich MA, Patrick JL (1991) Insertable biplanar gradient coils for magnetic resonance imaging.Rev Sci Instrum 62(11): 2639–2645.
Bowtell R, Mansfield P (1990) Minmum power flat gradient pairs for NMR microscopy.Eighth Annual Meeting Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Berkeley, CA, p. 977.
Bowtell R, Mansfield P (1990) Gradient coil design using active magnetic screening.Magn Reson Med 17: 15–21.
Yoda K (1990) Analytical design method of self-shielded planar coils.J Appl Phys 67: 4349–4353.
Turner R (1986) A target field approach to optimal coil design.J Phys [D] 19: 147–151.
Mansfield P, Chapman B (1986) Active magnetic screening of gradient coils in NMR imaging.J Magn Reson 66: 573–578.
Turner R (1988) Minimum inductance coils.J Phys [E] 21: 948–952.
Roemer PB, Hickey JS (1986) Self-shielded gradient coils for nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. European Patent Application 87, 101, 198.
JD Jackson (1975)Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc.
Turner R (1993) Gradient coil design: a review of methods.Magn Reson Imaging 11: 903–920.
Cho ZH, Yi JH (1991) A novel type of surface gradient coil.J Magn Reson 94: 471–485.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crozier, S., Dodd, S., Luescher, K. et al. The design of biplanar, shielded, minimum energy, or minimum power pulsed B0 coils. MAGMA 3, 49–55 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02426400
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02426400