Summary
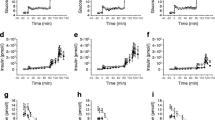
Insulin-like growth factor I (65 μg/kg) or insulin (0.1 IU/kg) were injected i.v. on two separate occasions in random order in normal and in Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic subjects. Insulin-like growth factor I and insulin injection resulted in identical decrements of plasma glucose concentrations after 30 min but in delayed recovery after insulin-like growth factor I as compared to insulin in both groups (p<0.05 insulin-like growth factor I vs insulin). Counterregulatory increases in plasma glucagon, adrenaline, cortisol and growth hormone concentrations after hypoglycaemia (1.9±0.2 mmol/l) in normal subjects were blunted after insulin-like growth factor I administration compared to insulin (p<0.05). Plasma glucose in Type 2 diabetic subjects did not reach hypoglycaemic levels but the acute glucose decrease to 4.5±0.8 mmol/l was associated with significantly lower responses of plasma glucagon and adrenaline but higher cortisol levels after insulin-like growth factor I compared to insulin (p<0.003). Plasma concentrations of non-esterified fatty acids and leucine decreased similarly after insulin-like growth factor I and insulin in both groups. The present results demonstrate that insulin-like growth factor I is capable of mimicking the acute effects of insulin on metabolic substrates (plasma glucose, non-esterified fatty acids, leucine). The decreases of plasma glucose were similar after both peptides in normal and in diabetic subjects who were presumably insulin resistant. Counterregulatory hormone responses to plasma glucose decrements differed, however, between insulin-like growth factor I and insulin and in the diabetic and the control subjects. After insulin-like growth factor I the increases in adrenaline, cortisol, growth hormone and glucagon were blunted in normal subjects despite slightly lower plasma glucose concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moxley RT, Arner P, Moss A et al. (1990) Acute effects of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin on glucose metabolism in vivo. Am J Physiol 59: 561–567
Rossetti L, Frontoni S, Dimarchi R, DeFronzo RA, Giaccari A (1991) Metabolic effects of IGF-I in diabetic rats. Diabetes 40: 444–448
Jacob R, Barrett E, Plewe G, Fagin KD, Sherwin RS (1989) Acute effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose and amino acid metabolism in the awake fasted rat. J Clin Invest 83: 1717–1723
Boulware SD, Tamborlane WV, Matthews LS, Sherwin RS (1992) Diverse effects of insulin-like growth factor 1 on glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism. Am J Physiol 262: E130-E133
Turkalj I, Keller U, Ninnis R, Vosmeer S, Stauffacher W (1992) Effects of increasing doses of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor 1 on glucose, lipid and leucine metabolism in man. J Clin Endocr Metab 75: 1186–1191
Zenobi PD, Graf S, Ursprung H, Froesch ER (1992) Effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose tolerance, insulin levels and insulin secretion. J Clin Invest 89: 1908–1913
Laager R, Ninnis R, Vosmeer S, Dembinsky K, Keller U (1992) Comparison of the metabolic effects of rh-insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and of insulin in man. Diabetologia 35 [Suppl 1]: A 65 (Abstract)
Jacob JJ, Sherwin RS, Bowen L et al. (1991) Metabolic effects of IGF-I and insulin in spontaneously diabetic BB/w rats. Am J Physiol 260:E262-E268
Guler H, Zapf J, Froesch ER (1987) Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med 317: 137–140
Holst JJ, Aasted B (1974) Production and evaluation of glucagon antibodies for radioimmunoassay. Acta Endocrinol 77: 715–726
Da Prada M, Zürcher G (1976) Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci 19: 1161–1174
Girard J, Erb T, Pampalone A, Eberle AN, Baumann JB (1987) Growth hormone in urine: development of an ultrasensitive assay applicable to plasma and urine. Horm Res 28: 71–80
Zapf J, Walter H, Froesch ER (1981) Radioimmunological determination of insulin-like growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest 68: 1321–1330
Herbert V, Kam-Seng L, Gottlieb CW, Bleicher SJ (1965) Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocr 25: 1375–1384
Miles J, Glasscock R, Aikens J, Gerich J, Haymond M (1983) A microfluorometric method for the determination of free fatty acids in plasma. J Lipid Res 24: 96–99
Schwenk WF, Berg PF, Beaufrère B, Miles JM, Haymond MW (1984) Use of T-butyldimethylsilylation in the gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of physiologic compounds found in plasma using electron-impact ionization. Anal Biochem 141: 101–109
Moller DE, Flier JS (1991) Insulin resistance: mechanisms, syndromes and implications. New Engl J Med 325: 938–943
Bodkin NL, Sportsman R, DiMarchi RD, Hansen BC (1991) Insulin-like growth factor-1 in non-insulin dependent diabetic monkeys: basal plasma concentrations and metabolic effects of exogenously administered biosynthetic hormone. Metabolism 40: 1131–1137
Jacob R, Sherwin S, Greenawalt K, Shulman GI (1992) Simultaneous insulin-like growth factor I and insulin resistance in obese Zucker rats. Diabetes 41: 691–697
Quin JD, Miles Fisher B, Paterson RK (1990) Acute responses to recombinant insulin-like growth factor I in a patient with Mendenhall's syndrome. New Engl J Med 323: 1425–1426
Schoenle EJ, Zenobi PD, Torresani T et al. (1991) Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I (rhIGF 1) reduces hyperglycaemia in patients with extreme insulin resistance. Diabetologia 34: 675–679
Usala AL, Madigan T, Burguera B et al. (1992) Brief report: treatment of insulin resistant diabetic ketoacidosis with insulinlike growth factor I in an adolescent with insulin-dependent diabetes. New Engl J Med 327: 853–857
Liu D, Moberg E, Kollind M, Lins PE (1991) A high concentration of circulating insulin suppresses the glucagon response to hypoglycemia in normal man. J Clin Endocr Metab 73: 1123–1128
Diamond MP, Hallarman L, Starick-Zych K et al. (1991) Suppression of counterregulatory hormone response to hypoglycemia by insulin per se. J Clin Endocr Metab 72: 1388–1390
Mauras N, Horber FF, Haymond MW (1992) Low dose recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I fails to affect protein anabolism but inhibits islet cell secretion in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75: 1192–1197
Gerich J, Davis J, Lorenzi M et al. (1979) Hormonal mechanisms of recovery from insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. Am J Physiol 236:E380-E385
De Feo P, Perriello G, Torlone E et al. (1989) Contribution of cortisol to glucose counterregulation in humans. Am J Physiol 257:E35-E42
Kerr D, Tamborlane W, Frances R, Sherwin R (1993) Effect of Insulin-like growth factor 1 on the response to and recognition of hypoglycemia in humans. J Clin Invest 91: 141–147
De Fronzo RA, Hendler R, Christensen N (1980) Stimulation of counterregulatory hormonal responses in diabetic man by a fall in glucose concentration. Diabetes 29: 125–131
Guler HP, Zapf J, Schmid C, Froesch ER (1989) Insulin-like growth factor I and II in healthy man. Estimation of half lives and production rates. Acta Endocrinol 121: 753–758
Zapf J, Hauri C, Waldvogel M, Froesch ER (1986) Acute metabolic effects and half-lives of intravenously administered insulin-like growth factors I and II in normal and hypophysectomized rats. J Clin Invest 77: 1768–1775
Zapf J, Schmid C, Guler HP et al. (1990) Regulation of binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors (IGF-1) in humans. J Clin Invest 86: 952–961
Guler HP, Schmid C, Zapf J, Froesch E (1989) Effects of recombinant insulin-like growth factor-I on insulin secretion and renal function in normal human subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 2868–2872
Bolinder J, Lindblad A, Engfeldt P, Arner P (1987) Studies of acute effects of insulin-like growth factors I and II in human fat cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65: 732–737
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laager, R., Keller, U. Effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I and insulin on counterregulation during acute plasma glucose decrements in normal and Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic subjects. Diabetologia 36, 966–971 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374481
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374481