Summary
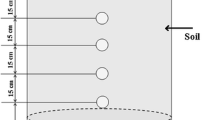
The effect of sulfur (S) placement and S rate on the efficiency of urea (U) relative to ammonium sulfate (AS) and ammonium nitrate (AN) for cotton were examined in a pot experiment using sandy clay loam soil (pH 7.9). The results showed that AS and AN application in the absence of S increased the yield than U partly because U-induced damage to plants. The combined application of the N sources with S increased the yields and that, the placement of S in the seed horizon in contact with N was more effective than mixing throughout the soil especially with U. These effects were observed with three cotton cultivars. The addition of S to a maximum of 1.5 g/pot gave further increases in yields or the N content of leaves for U, AS or AN. Using the least squares method, it was found that the presence of S significantly increased the efficiency of U than AS or AN. Incubation of S and the N sources with S in the soil was carried out to understand the growth conditions of cotton fertilized by U in alkalin soil. In the case of U-soil system, the pH increased. NO2−N accumulated and considerable loss of N took place. The pH, NO2−N accumulation and the loss of N decreased with S increments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, F. E. 1963 Losses of gaseous N forms by chemical mechanisms involving nitrose acid and nitrite. Soil Sci.96, 404–409.
Amer, F. and Abuamin, H. 1969 Evaluation of cotton responce to rates, sources and timing of nitrogen application by petiole analysis. Agron. J.61, 635–637.
Black, C. A. (Ed.) 1965 Methods of Soil Analysis part 2. Am. Soc. Agron. Inc., Madison, USA.
Bremner, J. M. 1965 Total nitrogen, Inorganic and Organic forms of nitrogen.In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Ed. C. A. Black. Agron.9, 1149–1255.
Cook, I. J. 1962 Damage to plant roots caused by urea and anhydrous ammonia. Nature London194, 1262–1263.
Court, M. N., Stephen, R. C. and Waid, J. S. 1964 Toxicity as a cause of the inefficiency of urea as a fertilizer. J. Soil Sci.15, 42–48.
Court, M. N., Dickins, J. C., Stephen, R. C. and Waid, J. S. 1963 The influence of soil type on the response of maize to urea in glasshouse experiments. J. Soil Sci.14, 247–255.
Chapman, H. D. and Pratt, P. F. 1961 Methods of Analysis for Soils, Plant and Water. Univ. of California, Agric. Pub., Berkeley.
Devine, J. R. and Holmes, M. R. J. 1963 Field experiments comparing ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate and urea applied respectively to grassland. J. Agric. Sci.60, 297–304.
Douglas, L. A. and Bremner, J. M. 1970 Extraction and colorimetric determination of urea in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.34, 859–862.
Ernst, J. W. and Massey, H. F. 1960 The effects of several factors on volatilization of ammonia formed from urea in the soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.24, 87–90.
Johnson, C. M. and Nishite, H. 1952. Microestimation of sulfur in plant materials, soils and irrigation waters. Anal. Chem.24, 736–742.
Khadr, A. and Rehab, F. 1974 Influence of nitrogen form on cotton growth and yield. Egypt. Cotton Gaz.62, 97–103.
Low, A. J. and Piper, F. J. 1961 Urea as a fertilizer. Laboratory and pot culture studies. J. Agric. Sci.57, 249–255.
Stephen, R. C. and Waid, J. S. 1963 A study of fertilizer urea in pot experiments. II. The influence of other fertilizer constituents on the responce of maize to urea. Plant and Soil19, 97–105.
Tisdale, S. and Nelson, W. 1966 Soil fertility and fertilizers. Sulfur and Microelements in Soils and Fertilizer. Collier Mac. Publ. (3 Ed.), London.
Wilkinson, S. R. and Ohlrogge, A. J. 1960 Influence of biuret and urea fertilizers containing biuret on corn plant growth and development. Agron. J.52, 560–562.
Volk, G. M. 1961 Gaseous loss of ammonia from surface applied nitrogenous fertilizers. J. Agric. Food Chem.9, 280–283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasseem, M.G., Nasrallah, A.K. The effect of sulfur on the response of cotton to urea under alkali soil conditions in pot experiments. Plant Soil 62, 255–263 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374089
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374089