Abstract
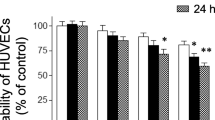
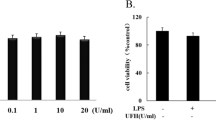
Tissue factor (TF) is an important regulator and effector molecule of coagulation in various inflammatory states. In sepsis, expression of TF by activated endothelial cells leads to disseminated intravascular coagulation. Scoparone is extracted from the traditional Chinese herbArtemisia scoparia and is known to have potent antiinflammatory properties. In the current studies, we examined the effects of scoparone on inhibiting lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced TF expression in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Flowcytometric analysis revealed LPS (10 µg/ml)-activated surface TF induction was concentration-dependently inhibited by scoparone (10–400 µM). The concentrations of scoparone used in this study did not affect cell viability. The elevation of the procoagulant activity of TF by LPS was suppressed by scoparone. The LPS-induced superoxide formation was markedly decreased by scoparone. Messenger RNA expression of TF in LPS-activated HUVECs was also reduced by scoparone. Furthermore, scoparone did not significantly affect the IκBα degradation. Our results demonstrate that the inhibition of scoparone on LPS-induced TF expression in HUVECs may mediate by the mechanisms suppressing superoxide anion formation and TF transcription.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E. NF-kappaB activation. Crit Care Med 28:N100-N104;2000.
Adcock IM, Brown CR, Kwon O, Barnes PJ. Oxidative stress induces NF kappa B DNA binding and inducible NOS mRNA in human epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 199:1518–1524;1994.
Bevilacqua MP, Pober JS, Majeau GR, Fiers W, Cotran RS, Gimbrone MA Jr. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor induces procoagulant activity in cultured human vascular endothelium: Characterization and comparison with the actions of interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4533–4537;1986.
Blackwell TS, Blackwell TR, Holden EP, Christman BW, Christman JW. In vivo antioxidant treatment suppresses nuclear factor-kappa B activation and neutrophilic lung inflammation. J Immunol 157:1630–1637;1996.
Brand K, Fowler BJ, Edgington TS, Mackman N. Tissue factor mRNA in THP-1 monocytic cells is regulated at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels in response to lipopolysaccharide. Mol Cell Biol 11:4732–4738;1991.
Cadroy Y, Dupouy D, Boneu B, Plaisancie H. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes modulate tissue factor production by mononuclear cells: Role of reactive oxygen species. J Immunol 164:3822–3828;2000.
Colucci M, Balconi G, Lorenzet R, Pietra A, Locati D, Donati MB, Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest 71:1893–1896;1983.
Gimbrone MA Jr. Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb 3:1–28;1976.
Gorlach A, Brandes RP, Bassus S, Kronemann N, Kirchmaier CM, Busse R, Schini-Kerth VB. Oxidative stress and expression of p22phox are involved in the up-regulation of tissue factor in vascular smooth muscle cells in response to activated platelets. FASEB J 14:1518–1528;2000.
Gregory SA, Morrissey JH, Edgington TS. Regulation of tissue factor gene expression in the monocyte procoagulant response to endotoxin. Mol Cell Biol 9:2752–2755;1989.
Gyllenhammer H. Lucigenin chemiluminescence in the assessment of neutrophil superoxide production. J Immunol Methods 97:209–213;1987.
Horn KD. Evolving strategies in the treatment of sepsis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). Q J Med 91:265–277;1998.
Huang HC, Chu SH, Chao Lee PD. Vasorelaxants from Chinese herbs, emodin and scoparone, possess immunosuppressive properties. Eur J Pharmacol 198:211–213;1991.
Huang HC, Huang YL, Chang JH, Chen CC, Lee YT. Possible mechanism of immunosuppressive effect of scoparone (6,7-dimethoxy-coumarin). Eur J Pharmacol 217:143–148;1992.
Huang HC, Lee CR, Weng YI, Lee MC, Lee YT. Vasodilator effect of scoparone (6,7-dimethoxycoumarin) from a Chinese herb. Eur J Pharmacol 218:123–128;1992.
Kagawa H, Komiyama Y, Nakamura S, Miyake T, Miyazaki Y, Hamamoto K, Masuda M, Takahashi H, Nomura S, Fukuhara S. Expression of functional tissue factor on small vesicles of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human vascular endothelial cells. Thromb Res 91:297–304;1998.
Levi M, ten Cate H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. N Engl J Med 341:586–592;1999.
Levi M, ten Cate H, Bauer KA, van der Poll T, Edgington TS, Buller HR, van Deventer SJ, Hack CE, ten Cate JW, Rosenberg RD. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis by pentoxifylline or by a monoclonal anti-tissue factor antibody in chimpanzees. J Clin Invest 93:114–120;1994.
Mackman N, Brand K, Edgington TS. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated transcriptional activation of the human tissue factor gene in THP-1 monocytic cells requires both activator protein 1 and nuclear factor kappa B binding sites. J Exp Med 174:1517–2615;1991.
Michie HR, Manogue KR, Spriggs DR, Revhaug A, O'Dwyer S, Dinarello CA, Cerami A, Wolff SM, Wilmore DW. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med 318:1481–1486;1988.
Moll T, Czyz M, Holzmuller H, Hofer-Warbinek R, Wagner E, Winkler H, Bach FH, Hofer E. Regulation of the tissue factor promoter in endothelial cells. Binding of NF kappa B-, AP-1-, and Sp1-like transcription factors. J Biol Chem 270:3849–3857;1995.
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63;1983.
Muller-Berghaus G. Pathophysiologic and biochemical events in disseminated intravascular coagulation: Dysregulation of procoagulant and anticoagulant pathways. Semin Thromb Hemost 15:58–87;1989.
Nawroth PP, Handley DA, Esmon CT, Stern DM. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell procoagulant while suppressing cell-surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3460–3464;1986.
Parry GCN, Mackman N. Transcriptional regulation of tissue factor expression in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Biol 15:612–621;1995.
Polack B, Pernod G, Barro C, Doussiere J. Role of oxygen radicals in tissue factor induction by endotoxin in blood monocytes. Haemostasis 27:193–200;1997.
Schreck R, Rieber P, Baeuerle PA. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J 10:2247–2258;1991.
Semeraro N, Biondi A, Lorenzet R, Locati D, Mantovani A, Donati MB. Direct induction of tissue factor synthesis by endotoxin in human macrophages from diverse anatomical sites. Immunology 50:529–535;1983.
Shenkar R, Schwartz MD, Terada LS, Repine JE, McCord J, Abraham E. Hemorrhage activates NF-kappa B in murine lung mononuclear cells in vivo. Am J Physiol 270:L729-L735;1996.
Taylor FB Jr, Chang A, Ruf W, Morrissey JH, Hinshaw L, Catlett R, Blick K, Edgington TS. LethalE. coli septic shock is prevented by blocking tissue factor with monoclonal antibody. Circ Shock 33:127–134;1991.
Thornton SC, Mueller SN, Levine EM. Human endothelial cells: Use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science 222:623–625;1983.
van der Poll T, Levi M, Buller HR, van Deventer SJ, de Boer JP, Hack CE, ten Cate JW. Fibrinolytic response to tumor necrosis factor in healthy subjects. J Exp Med 174:729–732;1991.
van der Poll T, Buller HR, ten Cate H, Wortel CH, Bauer KA, van Deventer SJ, Hack CE, Sauerwein HP, Rosenberg RD, ten Cate JW. Activation of coagulation and administration of tumor necrosis factor to normal subjects. N Engl J Med 322:1622–1627;1990.
van Deventer SJH, Buller HR, ten Cate JW, Aarder A, Hack CE, Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: Analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic and complement pathways. Blood 76:2520–2526;1990.
Vervloet MG, Thijs LG, Hack CE. Derangements of coagulation and fibrinolysis in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock. Semin Thromb Hemost 24:33–44;1998.
Warr TA, Rao LV, Rapaport SI. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in rabbits induced by administration of endotoxin or tissue factor: Effect of anti-tissue factor antibodies and measurement of plasma extrinsic pathway inhibitor activity. Blood 1990;75:1481–1489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YM., Hsiao, G., Chang, JW. et al. Scoparone inhibits tissue factor expression in lipopolysaccharide-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biomed Sci 10, 518–525 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256113
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256113