Abstract
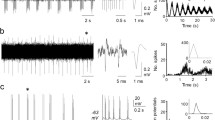
Aperiodic firing independent of extraneous stimuli at rates varying between 3–8 and 65–100 Hz (spontaneous firing activity, or SFA) was recorded at ventral root filaments of isolated, sagitally hemisected frog spinal cord. Lowest activity level was observed at temperatures of 7–11°C and an increased rate at either higher or lower temperatures. Some consistent short-lasting changes in SFA were noted straight away during the course of thermal changes: heating and cooling the preparation increased and reduced discharge rate, respectively. Characteristic activity rate for a given temperature level would set in 1–3 min after this level had stabilized. Microwave radiation of the spinal cord (6.45 GHz; specific absorption rates: 0.1, 0.4, and 2.0 W/g; duration 5 min) brought about no significant alteration in SFA at a steady temperature level. Microwave heating of the preparation and raised temperature both produced the same effects in all trials. Results would indicate that a thermal mechanism underlies the microwave effects on SFA at the ventral roots of frog spinal cord.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
B. I. Davydov, V. S. Tikhonchuk, and V. V. Antipov, Biological Action, Evaluation, and Protection from Electromagnetic Irradiation [in Russian], Énergoatomizdat (1984).
N. A. Levitina, “Research into athermal microwave action on heartbeat in the frog”, Byul. Éxp. Biol. Med.,79, No. 12, 64–66 (1966).
T. Yu. Ruchinskaya, Yu. S. Sverdlov, and Ts. V. Serbenyuk, “Organization of motoneuronal rhythmic activity in spinal centers of lymphatic hearts inRana temporaria”, Zh. Évol. Biokhim. Fiziol.,12, No. 4, 314–421 (1976).
K. V. Sudakov and G. D. Antimonii, “Central mechanisms of EMP action”, Usp. Fiziol., Nauk,4, No. 2, 101–135 (1973).
A. M. Chernushenko, N. E. Melanchenko, L. G. Maloratskii, and B. V. Petrov, Setting up VHF Assemblies and Screens [in Russian], Radio and Communications, Moscow (1983).
S. Baranski and Z. Edelwejn, “Studies on the combined effect of microwaves and some drugs on bioelectrical activity of the rabbit central nervous system”, Acta Physiol. Polon.,19, No. 1, 31–41 (1968).
W. Bise, “Low-power radio-frequency microwave effects on human electroencephalogram and behavior”, Physiol. Chem. Phys. Med., NMR,10, No. 5, 387–398 (1977).
P. B. Dunscombe, J. McLellan, and K. Malaker, “Heat production in microwave irradiated thermocouples”, Med. Phys.,13, No. 4, 457–461 (1986).
Y. Kudo and H. Fukuda, “Spontaneous electrical activity of the bullfrog spinal cord and susceptibility to some centrally acting drugs and amino acids”, Jpn. J. Pharmacol.,22, No. 5, 731–734 (1972).
Y. Kudo, “The pharmacology of the amphibian spinal cord”, Prog. Neurobiol.,11, No. 1, 1–76 (1978).
H. Okada, “On the action potentials of the lymph-cardiac spinal centers”, Jpn. J. Physiol.,6, No. 3, 249–258 (1956).
B. Servantie, A. M. Servantie, and J. Etienne, “Synchronization of cortical neurones by a pulsed microwave field as evidenced by spectral analysis of electrocorticograms from the white rat”, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.,247, 82–86 (1975).
B. Servantie, J. Gillard, A. M. Servantie, et al., “Comparative study of the action of three types of microwave fields upon the behaviour of the white rat”, J. Microwave Power,11, No. 2, 145–146 (1976).
H. Wachtel, R. Seaman, and W. Joines, “Effects of low-intensity microwaves on isolated neurones”, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.,247, 47–62 (1975).
Additional information
Institute of Medical Radiology, Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR, Obninsk. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 20, No. 6, pp. 723–728, November-December, 1988.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pakhomov, A.G. Effects of microwave irradiation and temperature on spontaneous ventral root discharges in prog spinal cord. Neurophysiology 20, 521–525 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02150252
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02150252