Abstract
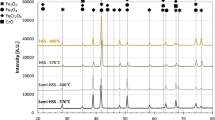
The SW7M high-speed tool steel of composition Fe (80%), Mo (5%), Cr (4%), V (2%) and C (1%) was studied by conversion electron Mössbauer spectroscopy at 293 K. The specimen consists mainly of α-Fe, martensite and austenite grains. The unwanted fraction of austenite was reduced by polishing the sample in an external magnetic field. At elevated temperatures, the SW7M steel exhibits a selective oxidation of its fraction. The corrosion rate is sigificantly reduced by N and Ti low-energy ion bombardment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Wantuch and J. Harasymowicz, Zeszyty Naukowe AGH 5M(1986).
G. Marest, in:Ion Impantation 1988, ed. F.E. Wohlbier (Trans. Tech. Publ.); Defects and Diffusion Forum 57/58(1988)273.
T. Barbaszewski, M. Dabrowski, M. Drwiega and J. Gawlik, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 112(1989)347.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fornal, P., Stanek, J., Gawlik, J. et al. Surface modifications of upgraded high-speed tool steel. Hyperfine Interact 92, 1355–1360 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02065778
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02065778