Abstract
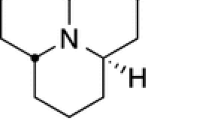
A wide range of alkaloids, many of which are unknown elsewhere in nature, occur in skin of frogs. Major classes of such alkaloids in dendrobatid frogs are the batrachotoxins, pumiliotoxins, histrionicotoxins, gephyrotoxins, and decahydroquinolines. Such alkaloids are absent in skin of frogs (Dendrobates auratus) raised in Panama on wingless fruit flies in indoor terraria. Raised on leaf-litter arthropods that were collected in a mainland site, such terraria-raised frogs contain tricyclic alkaloids including the beetle alkaloid precoccinelline, 1,4-disubstituted quinolizidines, pyrrolizidine oximes, the millipede alkaloid nitropolyzonamine, a decahydroquinoline, a gephyrotoxin, and histrionicotoxins. The profiles of these alkaloids in the captive-raised frogs are closer to the mainland population ofDendrobates auratus at the leaf-litter site than to the parent population ofDendrobates auratus from a nearby island site. Extracts of a seven-month sampling of leaf-litter insects contained precoccinelline, pyrrolizidine oxime236 (major), and nitropolyzonamine (238). The results indicate a dietary origin for at least some “dendrobatid alkaloids,” in particular the pyrrolizidine oximes, the tricyclic coccinellines, and perhaps the histrionicotoxins and gephyrotoxins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayer, W.A., Bennett, J.J., Browne, L.M., andPurdham, J.T. 1976. Defensive substances inCoccinella transversoguttata andHippodamia caseyi, lady bugs indigenous to western Canada.Can. J. Chem. 54:1807–1813.
Daly, J.W., andMyers, C.W. 1967. Toxicity of Panamanian poison frogs (Dendrobates): Some biological and chemical aspects.Science 156:970–973.
Daly, J.W., Myers, C.W., Warnick, J.E., andAlbuquerque, E.X. 1980. Levels of batrachotoxin and lack of sensitivity to its action in poison-dart frogs (Phyllobates).Science 208:1383–1385.
Daly, J.W., Myers, C.W., andWhittaker, N. 1987. Further classification of skin alkaloids from neotropical poison frogs (Dendrobatidae), with a general survey of toxic/noxious substances in the amphibians.Toxicon 25:1023–1095.
Daly, J.W., Secunda, S.I., Garraffo, H.M., Spande, T.F., Wisnieski, A., Nishihira, C., andCover, J.F., Jr. 1992. Variability in alkaloid profiles in neotropical poison frogs (Dendrobatidae): Genetic versus environmental determinants.Toxicon 30:887–898.
Daly, J.W., Secunda, S.I., Garraffo, H.M., Spande, T.F., Wisnieski, A., andCover, J.F., Jr. 1994. An uptake system for dietary alkaloids in poison frogs (Dendrobatidae).Toxicon In press.
Daly, J.W., Garraffo, H.M., andSpande, T.F. 1993. Amphibian alkaloids, pp. 185–288,in G.A. Cordell (ed.). The Alkaloids, Vol. 43. Academic Press, San Diego.
Jones, T.H., andBlum, M.S. 1983. Arthropod alkaloids: Distribution, functions, and chemistry, pp. 33–84,in S.W. Pelletier (ed.). Alkaloids, Chemical and Biological Perspectives, Vol. 1, Chapter 2. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Jones, T.H., Blum, M.S., Fales, H.M., Brandāo, C.R.F., andLattke, J. 1991. Chemistry of venom alkaloids in the ant genusMegalomyrmex.J. Chem. Ecol. 17:1897–1908.
Meinwald, J., Smolanoff, J., Mcphail, A.T., Miller, R.W., Eisner, T., andHicks, K. 1975. Nitropolyzonamine: A spirocyclic nitro compound from the defensive glands of a milliped (Polyzonium rosalbum).Tetrahedron Lett. 1975:2367–2370.
Neuwirth, M., Daly, J.W., Myers, C.W., andTice, L.W. 1979. Morphology of the granular secretory glands in skin of poison-dart frogs (Dendrobatidae).Tissue Cell 11:755–771.
Tokuyama, T., Daly, J.W., Garraffo, H.M., andSpande, T.F. 1992. Pyrrolizidine Oximes: A novel new class of dendrobatid alkaloids.Tetrahedron 48:4247–4258.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daly, J.W., Martin Garraffo, H., Spande, T.F. et al. Dietary source for skin alkaloids of poison frogs (Dendrobatidae)?. J Chem Ecol 20, 943–955 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02059589
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02059589