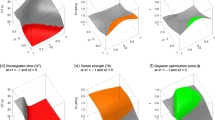
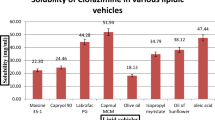
Abstract
The composition of pharmaceutical formulations is often subject to trial and error. This approach is time consuming and unreliable in finding the best formulation. Optimization by means of an experimental design might be helpful in shortening experimenting time. Such a design with the concomitant mathematical models, reveals effects and interactions of the variables. The independent variables are the different compositions of the mixtures of the chosen ingredients [drug(s) and excipients]. The dependent variables are the properties (responses) of the formulation. When all responses of interest have been expressed in models that describe the response as a function of the composition of the mixture, the models can be combined graphically or mathematically to find a composition satisfying all demands. In this paper an introduction to the use of mixture designs will be given by means of a theoretical part and an example: optimizing a tablet formulation consisting of excipients only.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fonner DE, Buck JR, Banker GS. Mathematical Optimization Techniques in Drug Product Design and Process Analysis. J Pharm Sci 1970;59:1587–96.
Doornbos DA. Optimisation in pharmaceutical sciences. Pharm Weekbl [Sci] 1981;3:33–61.
Schwartz JB, Flamholz JR, Press RH. Computer Optimization of Pharmaceutical Formulations 1. J Pharm Sci 1973;62:1165–70.
Jontscher C, Welikowa E. Optimierung der Zusammensetzung einer Mehrkomponenten-Arzneiform durch mathematische Versuchsplanung und experimentelle Prüfung. Pharmazie 1981;36:32–4.
Leuenberger H, Guitard P, Sucker H. Mathematische Modellierung und Optimierung Pharmazeutisch-technologischer Qualitätsmerkmale fester Arzneiformen. Pharm Unserer Zeit 1976;5:65–76.
Anik ST, Sukumar L. Extreme Vertexes Design in Formulation Development: Solubility of Butoconazole Nitrate in a Multicomponent System. J Pharm Sci 1981;70:897–900.
Scheffé H. Experiments with mixtures. J R Stat Soc 1958;B20:344–60.
Snee RD. Design and Analysis of Mixture Experiments. J Qual Technol 1971;3:159–69.
Box GEP. The exploration and exploitation of response surfaces. Biometrics 1954;10:16.
Davies OL, ed. The determination of optimum conditions. In: The design and analysis of industrial experiments. 2nd ed. London-New York: Longman, 1978:495.
Cornell JA. Experiments with mixtures, a review. Technometrics 1973;15:437–55.
Gorman JW, Hinman JE. Simplex lattice designs for multicomponent systems. Technometrics 1962;4:463–87.
Draper NR, Smith H. Applied regression analysis. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1966:128–62.
Marquardt DW, Snee RD. Test statistics for mixture models. Technometrics 1974;16:533–7.
Box GEP, Cox DR. An analysis of transformations. J R Stat Soc 1964;B26:211–52.
Chatterjee S, Price B. Regression Analysis by Example. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1977:117–20.
Becker NG. Models for the response of a mixture. J R Stat Soc 1968;B30:349–58.
Snee RD. Techniques for the analysis of mixture data. Technometrics 1973;15:517–28.
Draper NR, St John RC. A mixture model with inverse terms. Technometrics 1977;19:37–46.
Cornell JA. Experiments with mixtures: An update and bibliography. Technometrics 1979;21:95–106.
Kurotori IS. Experiments with mixtures of components having lower bounds. Indust Qual Cont 1966;22:592–6.
Murty JS, Das MN. Design and analysis of experiments with mixtures. Ann Mathemat Stat 1968;39:1517–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huisman, R., Van Kamp, H.V., Weyland, J.W. et al. Development and optimization of pharmaceutical formulations using a simplex lattice design. Pharmaceutisch Weekblad Scientific Edition 6, 185–194 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01999941
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01999941