Summary
We present 7 cases of false intracavernous carotid artery aneurysms. Four occurred after trauma and three were caused iatrogenically. Two of the latter occurred in patients with pituitary adenomas, one after transsphenoidal microsurgery and the other after yttrium [YI90] seed implantation into the sella. The third iatrogenic aneurysm was seen shortly after transcavernous tumour surgery.
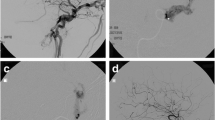
In five of our seven patients massive, delayed, lifethreatening epistaxis was the leading symptom. All traumatic cases were associated with immediate unilateral blindness or blurred vision and with skull base fractures. One of these had a concomitant carotid cavernous fistula. Treatment of choice of our 5 recent cases was permanent balloon occlusion of the intracavernous carotid artery at the level of the lesion. Collateral circulation was evaluated prior to definitive carotid occlusion using a balloon test occlusion. During the balloon test adequate collateral circulation was defined as symmetric angiographic filling of both hemispheres. Awake patients were neurologically examined continuously. In unconscious patients transcranial Doppler sonography, electroencephalographic and somatosensory evoked potential monitoring was used in addition. Intra-operative heparin administration was not reversed with protamin. A postoperative continuous heparin infusion was not found necessary.
In our two early cases this technique was not available: In the first case we accomplished aneurysm occlusion by a surgically introduced Fogarty balloon catheter. Our second patient needed surgical trapping of the involved carotid after early unsuccessful attempts of selective aneurysm occlusion, After treatment no further epistaxis occurred. Follow-up angiography showed persistent aneurysm occlusion. The results were excellent in 5 cases and good in 1 case. One patient with bilateral lesions suffered a stroke after occlusion of the second, remaining carotid artery, despite functioning bilateral extra-intracranial bypasses. Four years later there is a mild dysphasia still present in this patient. The mean follow-up time was 75.6 months.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja A, Gutermann L, Hopkins L (1992) Carotid cavernous fistula and false aneurysm of the cavernous carotid artery: complications of transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery 31: 774–779
Anon V, Aymard A, Gobin Y, Casarco, Rüffenacht D, Khayata M, Abizanda E, Redondo A, Merland J (1992) Balloon occlusion of the internal carotid artery in 40 cases of giant intracavernous aneurysm: technical aspects, cerebral monitoring, and results. Neuroradiology 34: 245–251
Auque J, Bracard S, Dellandrea M, Roland J, Marchal J, Hepner H, Picard L, Lepoire J (1988) Epistaxis grave et immediate par rupture traumatique du siphon carotidien. Neurochirurgie 34: 68–71
Earth G (1924) Tödliche Spätblutung aus der Carotis interna nach Schädeltrauma. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 50: 875–876
Bavinzski G, Asenbaum S, Goerzer H, Killer M, Gruber A, Richling B (1997) Clinical, radiological and hemodynamical long term follow-up of patients after therapeutic carotid artery occlusion (in prep)
Benson P, Sung J (1989) Cerebral aneurysms following radiotherapy for medulloblastoma. J Neurosurg 70: 545–550
Buckingham M, Crone K, Ball W, Tomsick T, Berger T, Tew J (1988) Traumatic intracranial aneurysms in childhood: two cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 22: 398–407
Chambers E, Rosenbaum A, Norman D, Newton T (1981) Traumatic aneurysms of cavernous internal carotid artery with secondary epistaxis. AJNR 2: 405–409
Dellen V (1987) Traumatic carotid aneurysms of the cavernous sinus. In: Dolenc VV (ed) The cavernous sinus. A multidisciplinary approach to vascular and tumorous lesions. Springer, Wien New York
Diaz F, Ohaegbulam S, Dujovny M, Ausmann J (1988) Surgical management of aneurysms in the cavernous sinus. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 91: 25–28
Dolenc V, Clerk M, Sustersic J, Pregelj R, Skrap M (1987) Treatment of intracavernous aneurysms of the ICA and CCFs by direct approach. In: Dolenc VV (ed) The cavernous sinus. A multidisciplinary approach to vascular and tumorous lesions. Springer, Wien New York
Drake C, Peerless S, Ferguson G (1994) Hunterian proximal arterial occlusion for giant aneurysms of the carotid circulation. J Neurosurg 81: 656–665
Evan J (1962) The etiology and treatment of epistaxis based on a review of 200 cases. J Laryngol Otol 76: 185–191
Fox J, Vinuela F, Pelz D, Ferguson G, Peerless S (1985) Comment to Ying Liu. Traumatic intracavernous carotid aneurysm with massive epistaxis. Neurosurgery 17: 573
Gelber B, Thoralf M, Sundt ThM (1980) Treatment of intracavernous and giant carotid aneurysms by combined internal carotid ligation and extra- to intracranial bypass. J Neurosurg 52: 1–10
Higashida R, Halbach V, Dowd C, Barnwell S, Dormandy B, Bell J, Hieshima G (1990) Endovascular detachable balloon embolization therapy of cavernous carotid artery aneurysms: results in 87 cases. J Neurosurg 72: 857–863
Knosp E, Seligo W, Horaczeck A, Czech TH (1986) Carotis-Cavernosus-Fistel durch Messerstich. Unfallchirurg 89: 37–41
Laws E, Kern E (1976) Complications of transsphenoidal surgery. Clin Neurosurg 23: 401–416
Lawton M, Hamilton M, Morcos J, Spetzler R (1996) Revascularization and aneurysm surgery: current techniques, indications, and outcome. Neurosurgery 38: 83–93
Linskey M, Shekhar L, Horton J, Hirsch W, Yonas H (1991) Aneurysms of the intracavernous carotid artery: a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. J Neurosurg 75: 525–534
Liu M, Shih C, Wang Y, Tsai S (1985) Traumatic intracavernous carotid aneurysm with massive epistaxis. Neurosurgery 17: 569–573
McConachie N, Jacobson I (1994) Bilateral aneurysms of the cavernous internal carotid arteries following yttrium-90 implantation. Neuroradiology 36: 611–613
Perneczky A, Knosp E, Vorkapic P, Czech T (1985) Direct surgical approach to infraclinoidal aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 76: 36–44
Richling B, Gruber A, Bavinzski G, Killer M (1995) GDC-system embolization for brain aneurysms — location and follow-up. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 134: 177–183
Richling B (1982) Homologous controlled viscosity fibrin for endovascular embolization. Part 1: experimental development of the medium. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 64: 109–124
Sen C, Shekar L (1992) Direct vein graft reconstruction of the cavernous, petrous, and upper cervical internal carotid artery: lessons learned from 30 cases. Neurosurgery 30: 732–743
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bavinzski, G., Killer, M., Knosp, E. et al. False aneurysms of the intracavernous carotid artery — Report of 7 cases. Acta neurochir 139, 37–43 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01850866
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01850866