Summary
The somatomedins, multitargit growth-promoting peptide hormones, were measured with radio receptor assay in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) after subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) in 21 patients and after head injury in 2 patients.
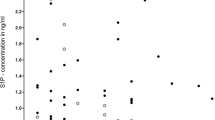
In the first group of 10 patients, lumbar (n=8) or central (n=2) CSF was collected on days three, six and nine after SAH. 6 of the 8 patients with SAH showed an increase in somatomedin concentrations ranging between 0.52–1.26 U/ml while 2 patients fell within the normal range between 0.19–0.48 U/ml. In the 2 patients with head injury, the somatomedin concentrations were scarcely detectable.
In the second group of 13 patients with SAH, CSF was collected peroperatively during surgical clipping of an aneurysm. These patients fell into two groups: 6 patients who had CSF somatomedin levels within the normal range and 7 patients with pathologically increased somatomedin concentrations ranging between 0.38–1.26 U/ml. Neither the neurological condition nor the cerebral vascular diameter correlated with the somatomedin concentrations. It is suggested that the increased somatomedin levels in CSF after SAH could be a compensatory response in order to stimulate cerebral anabolism after injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäckström, M., Hall, K., Sara, V. R., Somatomedin levels in cerebrospinal fluid from adult with pituitary disorders. Acta Endocrin.107 (1984), 171–178.
Ekbom, K., Greitz, T., Carotid angiography in cluster headache. Acta Radiol. Diagn. (1979), 1–10.
Fein, J. M., Cerebral energy metabolism after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Stroke6 (1975), 1–8.
Fein, J. M., Brain energetics and circulatory control after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg.45 (1976), 498–507.
Gabrielson, G., Greitz, T., Normal size of internal carotid, middle and anterior cerebral arteries. Acta Radiol.10 (1970), 1–10.
Grubb, R. L., Raichle, M. E., Phelps, M. E., Effects of increased intracranial pressure on blood volume, blood flow and oxygen utilisation in monkeys. J. Neurosurg.43 (1975), 385–398.
Grubb, R. L., Cerebral hemodynamics and metabolism in subarachnoid hemorrhage. In: Clinical Management of Intracranial Aneurysms (Hopkins and Long, eds.), pp. 163–176. New York: Raven Press. 1982.
Hall, K., Sara, V. R., Growth and somatomedins. Vitamins and Hormones40 (1983), 175–230.
Hall, K., Sara, V. R., Somatomedin levels in childhood adolescence and adult life. Clinics in Endocrinology. J. Metabolism.13, No. 1 (1984), 91–112.
Hunt, W. E., Hess, R. M., Surgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J. Neurosurg.28 (1976), 14–19.
Jennet, B., Bond, M., Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet (1975), 480.
Sara, V. R., Hall, K., Wetterberg, L., Fetal brain growth: Proposed model for regulation by embryonic somatomedin. In: Biology of Normal Human Growth (Ritzén, M., Apeira, A.,et al, eds.), pp. 241–254. New York: Raven Press. 1981.
Sara, V. R., Hall, K., von Holst, H., Humbel, R., Sjögren, B., Wetterberg, L., Evidence for the presence of specific receptors for insulinike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and 2 (IGF-2) and insulin throughout the adult human brain. Neuroscience Letters34 (1982), 39–44.
Sara, V. R., Hall, K., Enzell, K., Gardner, A., Morawski, R., Wetterberg, L., Somatomedins in aging and dementia disorders of the Alzheimers type. Neurobiology of aging3 (1982), 117–120.
Sara, V. R., Uvnäs-Moberg, K., Uvnäs, B., Hall, K., Wetterberg, L., Posloncec, B., Goiny, M., The distribution of somatomedins in the nervous system of cat and their release on neural stimulation. Acta Physiol. Scand.115 (1982), 467–470.
Siesjö, B., Brain energy metabolism. John Wiley and Sons Ltd. 1978.
Von Holst, H., Hagenfeldt, L., Increased concentrations of amino acids in cerebrospinal fluid after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. In press.
Wilkins, R., Cerebral arteria spasm. Proceedings of the second international workshop, Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Ltd. 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from Karolinska Institutet, the Swedish Medical Research Council, Sävstaholmsföreningen, and Loo and Hans Osterman Research Fund.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Holst, H., Sara, V. Increased levels of somatomedins in human lumbar and central cerebrospinal fluid after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta neurochir 78, 157–160 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808696
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808696