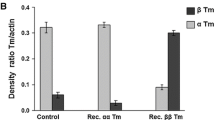
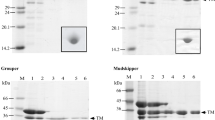
Summary
In a search for an invertebrate muscle from which the muscle regulatory proteins could be obtained in a great quantity and at high homogeneity, the regulatory proteins, tropomyosin (Tm) and three subunits of troponin (Tn), have been isolated from the lobster tail muscle, purified and partially characterized. The calcium-sensitive ATPase of lobster myofibril was restored when purified lobster Tm and lobster Tn were added to actin. Quantitative SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed that the lobster muscle contains actin, Tm, Tn with a molar ratio 7∶1∶1 and that lobster Tn consists of three subunits, one of each I, C and T. Each subunit was identified according to its effect on the acto-S1 ATPase rate. The isomer composition in each fraction of purified Tn subunit and in Tm are different from the rabbit skeletal muscle proteins; Tm consists of a single species of polypeptide of Mr 38 000; the TnT fraction appears to be homogeneous with Mr 43 000; the TnI fraction contains five isomers, all showing similar isoelectric pH, differing in Mr in the range from 28 000 to 31 000; two TnC fractions contain three isomers in total with a range of Mr from 18 500 to 19 000.
Further study of the lobster Tm elucidated that digestion by carboxypeptidase A gave rise to a homogeneous preparation of truncated and non-polymerizable Tm which is devoid of 11 residues at the C-terminus of the molecule. The C-terminal amino acid sequence of 11 residues is homologous to the thoracic isomer generated fromDrosophila melanogaster Tm-I gene.
The present study indicated that, despite heterogeneities owing to the occurrence of isomers, the lobster regulatory proteins serve as an invertebrate source of the proteins for structural and biophysical studies, alternative to vertebrate counterparts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, D. G., Blinks, J. R. &Prendergast, F. G. (1976) Aequorin luminescence: relation of light emission to calcium concentration—a calcium-independent component.Science 195, 996–8.
Basi, G. S. &Storti, R. V. (1986) Structure and DNA sequence of the tropomyosin I gene fromDrosophila melanogaster.J. Biol. Chem. 261, 817–27.
Benzonana, G., Kohler, L. &Stein, E. A. (1974) Regulatory proteins of crayfish tail muscle.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 368, 247–58.
Breitbart, R. E. &Nadal-Ginard, B. (1986) Complete nucleotide sequence of the fast skeletal troponin T gene. Alternative spliced exons exhibit unusual interspecies divergence.J. Mol. Biol. 188, 313–24.
Briggs, M. M., Klevit, R. E. &Schachat, F. H. (1984) Heterogeneity of contractile proteins. Purification and characterization of two species of troponin T from rabbit fast skeletal muscle.J. Biol. Chem. 259, 10369–75.
Bronson, D. D. &Schacht, F. H. (1982) Heterogeneity of contractile proteins. Differences in tropomyosin in fast, mixed, and slow skeletal muscles of the rabbit.J. Biol. Chem. 257, 3937–44.
Ebashi, S. &Endo, M. (1968) Calcium ions and muscle contraction.Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 18, 125–83.
Ebashi, S., Wakabayashi, T. &Ebashi, F. (1971) Troponin and its components.J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 69, 441–5.
Fujita, S., Maeda, K. &Maéda, Y. (1991) Complete coding sequences of cDNAs of four variants of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin-T.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 12, 560–5.
Garone, L., Theibert, J. L., Miegel, A., Maéda, Y., Murphy, C. &Collins, J. H. (1991) Lobster troponin C: amino acid sequences of three isomers.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 291, 89–91.
Haselgrove, J. C. (1973) X-ray evidence for a conformational change in the actin-containing filaments of vertebrate striated muscle.Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 37, 341–52.
Huxley, H. E. (1973) Structural changes in the actin- and myosin-containing filaments during contraction.Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 37, 361–76.
Imamura, K., Tada, M. &Tonomura, Y. (1966) The pre-steady state of the myosin—adenosine triphosphate system, IV. Liberation of ADP from the myosin-ATP system and effects of modifiers on the phosphorylation of myosin.J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 59, 280–9.
Jahromi, S. S. &Atwood, H. L. (1969) Correlation of structure, speed of contraction, and total tension in fast and slow abdominal muscle fibres of the lobster (Homarus americanus).J. Exp. Zool. 171, 25–38.
Johnson, P. &Smillie, L. (1977) Polymerizability of rabbit skeletal tropomyosin: effects of enzyme and chemical modifications.Biochemistry 16, 2264–9.
Kobayashi, T., Takagi, T., Konishi, K. &Cox, J. A. (1989a) Amino acid sequences of crayfish troponin I.J. Biol. Chem. 264, 1551–7.
Kobayashi, T., Takagi, T., Konishi, K. &Wnuk, W. (1989b) Amino acid sequences of the two major isoforms of troponin C from crayfish.J. Biol. Chem. 264, 18247–59.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature (London) 227, 680–5.
Leavis, P. C. &Gergely, J. (1984) Thin filament proteins and thin filament-linked regulation of vertebrate muscle contraction.CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 16, 235–305.
Lehman, W. &Szent-Györgyi, A. G. (1975) Regulation of muscular contraction: distribution of actin control and myosin control in the animal kingdom.J. Gen. Physiol. 66, 1–30.
Lehman, W., Kendrick-Jones, J. &Szent-Györgyi, A. G. (1973) Myosin-linked regulatory systems: comparative studies.Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 37, 319–30.
Lehman, W., Regenstein, R. M. &Ransom, A. L. (1976) The stoichiometry of the components of arthropod thin filaments.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 434, 215–22.
Lehrer, S. S. &Morris, E. P. (1982) Dual effects of tropomyosin and troponin-tropomyosin on actomyosin subfragment 1 ATPase.J. Biol. Chem. 257, 8073–80.
Mak, A. &Smillie, L. B. (1981) Non-polymerizable tropomyosin: preparation, some properties and F-actin binding.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 101, 208–14.
Mak, A., Smillie, L. B. &Bárány, M. (1978) Specific phosphorylation at serine-283 of α-tropomyosin from frog skeletal and rabbit skeletal and cardiac muscle.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 75, 3588–92.
Miegel, A. &Maéda, Y. (1990) Regulation of lobster tail muscle.Biophys. J. 57, 150a.
Miegel, A., Lee, L., Dauter, Z. &Maéda, Y. (1992) A new crystal form of tropomyosin. InMechanism of Myofilament Sliding in Muscle Contraction (edited bySugi, H. &Pollack, G. H.) New York: Plenum Press (in press).
Miyazaki, J., Hosoya, M., Ishimoda-Takagi, T. &Hirabayashi, T. (1990) Tissue specificity of tropomyosin from the crayfish,Cambarus clarki.J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 108, 59–65.
Murakami, U. &Uchida, K. (1984) Two-dimenmsional electrophoresis of troponin complex with non-equilibrium pH gradient-sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide slab gel.J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 95, 1577–84.
Mykles, D. (1985) Heterogeneity of myofibrillar proteins in lobster fast and slow muscles: variants of troponin, paramyosin and myosin light chains comprise four distinct protein assemblages.J. Exp. Zool. 234, 23–32.
Nishita, K. &Ojiima, T. (1990) American lobster troponin.J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 108, 677–83.
O'farrell, P. H. (1975) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins.J. Biol. Chem. 250, 4007–21.
O'farrell, P. Z., Goodman, H. M. &O'farrell, P. H. (1977) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins.Cell 12, 1133–42.
Ohtsuki, I., Maruyama, K. &Ebashi, S. (1986) Regulatory and cytoskeletal proteins of vertebrate skeletal muscle.Adv. Protein Chem. 38, 1–67.
Ojima, T. &Nishita, K. (1986a) Isolation of troponins from striated and smooth adductor muscles of Akazara scallop.J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 100, 821–4.
Ojima, T. &Nishita, K. (1986b) Troponin fromAkazara scallop striated adductor muscles.J. Biol. Chem. 261, 16749–54.
Pan, B-S., Gordon, A. M. &Luo, Z. (1989) Removal of tropomyosin overlap modifies cooperative binding of myosin S-1 to reconstituted thin filaments of rabbit striated muscle.J. Biol. Chem. 264, 8495–8.
Parry, D. A. D. &Squire, J. M. (1973) Structural role of tropomyosin in muscle regulation: analysis of the X-ray diffraction patterns from relaxed and contracting muscles.J. Mol. Biol. 75, 33–55.
Potter, J. D. (1974) The content of troponin, tropomyosin, actin and myosin in rabbit skeletal muscle myofibrils.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 162, 436–41.
Regenstein, J. M. &Szent-Györgyi, A. G. (1975) Regulatory proteins of lobster striated muscle.Biochemistry 14, 917–25.
Shinoda, Y., Yamada, A. &Yagi, K. (1988) Identification of troponin-I of crayfish myofibrils.J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 103, 636–40.
Stone, D. &Smillie, L. B. (1978) The amino acid sequence of rabbit skeletal α-tropomyosin.J. Biol. Chem. 253, 1137–48.
Tawada, Y., Ohara, H., Ooi, T. &Tawada, K. (1975) Non-polymerizable tropomyosin and control of the superprecipitation of actomyosin.J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 78, 65–72.
Vibert, P. J., Haselgrove, J. C., Lowy, J. &Poulsen, F. R. (1972) Structural changes in actin-containing filaments of muscle.J. Mol. Biol. 71, 757–67.
Walsh, T. P., Trueblood, C. E., Evans, R. &Weber, A. (1984) Removal of tropomyosin overlap and the co-operative response to increasing calcium concentrations of the acto-subfragment-1 ATPase.J. Mol. Biol. 182, 265–9.
White, H. D. (1982) Special instrumentation and techniques for kinetic studies of contractile systems. InMethods in Enzymology, Vol. 85 (edited byFrederiksen, D. W. &Cunningham, L. W.) pp. 698–708. New York: Academic Press.
Wnuk, W. (1989) Resolution and calcium-binding properties of the two major isoforms of troponin C from crayfish.J. Biol. Chem. 264, 18240–6.
Wnuk, W., Schoechlin, M. &Stein, E. A. (1984) Regulation of actomyosin ATPase by a single calcium-binding site on troponin C from crayfish.J. Biol. Chem. 14, 9017–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miegel, A., Kobayashi, T. & Maéda, Y. Isolation, purification and partial characterization of tropomyosin and troponin subunits from the lobster tail muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 13, 608–618 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738250
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738250