Abstract
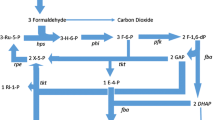
Growth ofEubacterium limosum B2 on methanol-CO2 was dependent upon the pH; optimum growth rates were obtained at pH 7.3–7.4. Carbon dioxide, a necessary cosubstrate for methylotrophic growth on methanol, was a determining factor for both growth and the nature of the organic acid produced. The coefficient of affinity for CO2 was not affected by variations in pH if calculated relative to the concentration of hydrogen carbonate (16 mM). Similarly the conversion rate for methanol into acetic acid and butyric acid remained constant regardless of the level of pH with a fixed concentration of hydrogen carbonate. The metabolism ofE. limosum B2 grown on methanol-CO2 was regulated by the HCO -3 concentration in the medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Adamse AD, Velzeboer CTM (1982). Features ofClostridium, strain CV-AA1, an obligatory anaerobic bacterium producing acetic acid from methanol. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 48:305–313
Bache R, Pfennig N (1981) Selective isolation ofAcetobacterium woodii on methyoxylated aromatic acids and determination of growth yields. Arch Microbiol 130:255–261
Genthner BR, Bryant MP (1982) Growth ofEubacterium limosum with carbon monoxide as the energy source. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:70–72
Genthner BR, Davis CL, Bryant MP (1981) Features of rumen and sewage sludge strains ofEubacterium limosum, a methanol- and H2/CO2-utilizing species. Appl Environ Microbiol 42:12–19
Kerby R, Niemczura W, Zeikus JG (1983) Single carbon catabolism in acetogens: analysis of carbon flow inAcetobacterium woodii andButyribacterium methylotrophicum by fermentation and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance measurement. J Bacteriol 155:1208–1218
Latham, MJ, Wolin MJ (1978) Use of serum bottle technique to study interactions between strict anaerobes in mixed culture. In: Lovellock DW, Davies R (eds) Techniques for the study of mixed populations. New York: Academic Press, pp 113–122
Lynd L, Kerby R, Zeikus JG (1982) Carbon monoxide metabolism ofButyribacterium methylotrophicum. J Bacteriol 149:255–263
Lynd LH, Zeikus JG (1983) Metabolism of H2/CO2, methanol and glucose byButyribacterium methylotrophicum. J Bacteriol 153:1415–1422
Miller TL, Wolin MJ (1974) A serum bottle modification of the Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Appl Microbiol 27:985–987
Moench TT, Zeikus JG (1983) Nutritional growth requirement forButyribacterium methylotrophicum on single carbon substrates and glucose. Curr Microbiol 9:151–154
Samain E (1983) Thèse Docteur 3è Cycle. Metabolisme descomposés intermédiaires de la fermentation méthanique. Lille, France: University des Sciences et Techniques de Lille
Wiegel J, Braun M, Gottschalk G (1981)Clostridium thermoautotrophicum species novum, a thermophile producing acetate from molecular hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Curr Microbiol 5:255–260
Zeikus JG (1983) Metabolism of one carbon compounds by chemotrophic anaerobes. Adv Microb Physiol 24:215–299
Zeikus JG, Lynd LH, Thompson TE, Krzycki JA, Weimer PJ, Hegge PW (1980) Isolation and characterization of a new, methylotrophic, acidogenic anaerobe, the Marburg strain. Curr Microbiol 3:381–386
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pacaud, S., Loubiere, P. & Goma, G. Methanol metabolism byEubacterium limosum B2: Effects of pH and carbon dioxide on growth and organic acid production. Current Microbiology 12, 245–250 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567972
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567972