Abstract
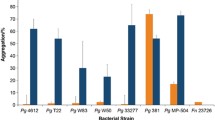
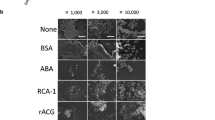
All study strains ofBacteroides gingivalis, B. asaccharolyticus, andB. melaninogenicus subspecies possessed numerous pilus-like fibers and capsule-like outer surface structures. The capsular morphology varied between the different species and subspecies.B. gingivalis strongly agglutinated 16 erythrocyte species studied.B. asaccharolyticus showed variable and weak agglutination of only a few erythrocyte species.B. melaninogenicus subsp.intermedius strains strongly agglutinated rabbit erythrocytes and exhibited variable, often weak agglutination of 8 other erythrocyte species. Preparations of capsular polysaccharide or lipopolysaccharide fromB. gingivalis failed to agglutinate human erythrocytes, while pili preparations from the same organisms possessed marked hemagglutinating activity.B. gingivalis cells adhered in high numbers to human buccal epithelial cells, whereas strains ofB. asaccharolyticus failed to show measurable adherence. Oral strains ofB. melaninogenicus subsp.intermedius feebly adhered to the buccal epithelial cells. Pretreatment ofB. gingivalis cells with serum or saliva prevented the adherence to epithelial cells. Our findings suggest that cell surfaces with distinct properties exist on the various black-pigmentedBacteroides species and subspecies and this may accout for markedly differing ability of these organisms to attach to mammalian cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Buchanan, T. M. 1975. Antigenic heterogeneity of gonococcal pili. Journal of Experimental Medicine141:1470–1475.
Costerton, J. W., Geesey, G. G., Cheng, K.-J. 1978. How bacteria stick. Scientific American238:86–95.
Coykendall, A. L., Kaczmarek, F. S., Slots, J. 1980. Genetic heterogeneity inBacteroides asaccharolyticus. (Holdeman and Moore 1970) Finegold and Barnes 1977 (approved lists, 1980), and proposal ofBacteroides gingivalis sp. nov. andBacteroides macacae (Slots and Genco) comb. nov. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology30:559–564.
Darwish, S., Hyppa, T., Socransky, S. S. 1978. Studies on the predominant cultivable microbiota of early periodontitis. Journal of Periodontal Research13:1–6.
Finegold, S. M. 1977. Anaerobic bacteria in human disease. New York: Academic Press.
Gibbons, R. J. 1977. Adherence of bacteria to host tissue. Position paper. Microbiology—1977:395–496.
Gibbons, R. J., van Houte, J. 1971. Selective bacterial adherence to oral epithelial surfaces and its role as an ecological determinant. Infection and Immunity3:567–573.
Gibbons, R. J., van Houte, J. 1975. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annual Review of Microbiology29:19–44.
Hobson, P. N., MacPherson, M. J. 1954. Some serological and chemical studies on materials extracted from amylolytic streptococcus from the rumen of the sheep. Biochemical Journal57:145–151.
Holdeman, L. V., Moore, W. E. C. 1972. Anaerobic laboratory manual. Blacksburg, Virginia: V. P. I. Anaerobe Laboratory, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
Jann, K., Jann, B., Ørskov, F., Ørskov, I., Westphal, O. 1965. Immunchemische Untersuchungen an K-Antigenen vonEscherichia coli. II. Das K-Antigen vonE. coli O8:K42(A):H−. Biochemische Zeitschrift342:1–22.
Listgarten, M. A., Lai, C. H. 1979. Comparative ultrastructure ofBacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies. Journal of Periodontal Research14:332–340.
Mansheim, B. J., Kasper, D. L. 1977. Purification and immunochemical characterization of the outer membrane complex ofBacteroides melaninogenicus subspeciesasaccharolyticus. Journal of Infectious Diseases135:787–799.
Neter, E. 1956. Bacterial hemagglutination and hemolysis. Bacteriological Reviews20:166–188.
Okuda, K., Takazoe, I. 1974. Hemagglutinating activity ofBacteroides melaninogenicus. Archives of Oral Biology19: 415–416.
Reed, M. J., Slots, J., Mouton, C., Genco, R. J. 1980. Antigenic studies of oral and nonoral black pigmentedBacteroides strains. Infection and Immunity29:564–574.
Sawer, W. D., Rosenthal, R. S. 1978. Pili and bacterial pathogenicity. In: Bradley, D. E., Raizen, E., Fines-Tayler, P., Ou, J. (eds.). Pili. Washington, D. C.: International Conferences on Pili.
Slots, J. 1977. The predominant cultivable microflora of advanced periodontitis. Scandinavian Journal of Dental Research85:114–121.
Slots, J., Gibbons, R. J. 1978. Attachment ofBacteroides melaninogenicus subsp.asaccharolyticus to oral surfaces and its possible role in colonization of mouth and peridontal pockets. Infection and Immunity19:254–264.
Slots, J., Genco, R. J. (1979. Direct hemagglutination technique for differentiatingBacteroides asaccharolyticus oral strains from nonoral strains. Journal of Clinical Microbiology10:371–373.
Smith, H. 1977. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriological Reviews41:475–500.
Westphal, O., Luderitz, O., Bister, F. 1952. Über die Extraktion von Bacterien, mit Phenol/Wasser. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung7B:148–155.
Woo, D.D.L., Holt, S.C., Leadbetter, E.R. 1979. Ultrastructure ofBacteroides species:Bacteroides asaccharolyticus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspeciesmelaninogenicus, andBacteroides melaninogenicus subspeciesintermedius. Journal of Infectious Diseases139:534–546.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okuda, K., Slots, J. & Genco, R.J. Bacteroides gingivalis, Bacteroides asaccharolyticus, andBacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies: Cell surface morphology and adherence to erythrocytes and human buccal epithelial cells. Current Microbiology 6, 7–12 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01566718
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01566718