Summary
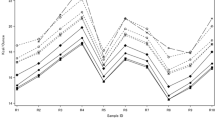
Microwave effects on free amino acid concentrations in milkversus a water bath heating were investigated in view of their importance for infant growth. Concentrations of few amino acids, such as aspartate, serine or lysine, are unchanged whatever the way and the temperature of heating. In contrast, tryptophan concentrations decreased similarly whatever the way of heating (110 ± 3µmol/l before heatingvs 84 ± 4µmol/l after 30°C microwave heating, p < 0.05). On the contrary, concentrations of glutamate and glycine increased more after water bath heating at 90°C (325 ± 4 and 101 ± 1µmol/l, respectively) than after microwave heating (312 ± 4 and 95 ± 1µmol/l, respectively, p < 0.05) suggesting milk proteolysis. Moreover, the accumulation of ammonia observed at 90°C with the water bath together with increase Glu levels might reflect a degradation of glutamine. An ornithine enrichment, more evident with microwave heating, was shown and could be of interest as it is a polyamine precursor. Also, considering few variations of free amino acid concentrations and the time saved, microwave heating appears to be an appropriate method to heat milk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper AJL, Mora SN, Cruz NF, et al (1985) Cerebral ammonia metabolism in hyperammonemic rats. J Neurochem 44: 1716–1723
Finot PA (1996) Effets du traitement par les micro-ondes sur la qualite nutritionnelle des aliments. Cah Nutr Diét 31:4: 239–246
Grimble G (1992) Glutamine glutamate and pyroglutamate facts and fantaisies. Clin Nutr 11: 66–69
Lubec G, Wolf C, Bartosch B (1989) Amino-acid isomerisation and microwave exposure. Lancet ii (8676): 1392–1393
Marchelli R, Dossena A, Palla G, et al (1992) D-amino-acids in reconstituted infant formula: a comparison between conventional and microwave heating. J Sci Food Agric 59: 217–226
Munro HN (1964) An introduction to biochemical aspects of protein metabolism. In: Munro HN, Allison JB (eds) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 31–34
Pegg A (1986) Recent advances in the biochemistry of polyamines in eukaryotes. Biochem J 234: 249–262
Petrucelli L, Fisher GH (1994) D-aspartate and D-glutamate in microwaved versus conventionally heated milk. J Am Coll Nutr 13: 209–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasson, MP., Farges, M.C., Sarret, A. et al. Free amino acid concentrations in milk: Effects of microwaveversus conventional heating. Amino Acids 15, 385–388 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01320902
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01320902