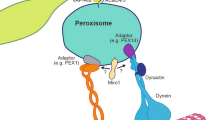
Summary
Chloroplasts and pigment granules are known to be intracellularly translocated upon discrete extracellular stimuli. The machineries transducing these signals inside cells are yet not understood. In studies investigating the motility of peroxisomes, we were able to identify both extracellular and intracellular signaling steps regulating movements of these organelles. Following simultaneous stimulation of CHO cells with both extracellular ATP and lysophosphatidic acid, an arrest of peroxisomes was observed. This block of motility was shown to be dependent on signaling cascades involving heterotrimeric G proteins of the class Gi/Go, phospholipase C, calcium influx, and activation of protein kinase C as well as of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is a point of convergence for these pathways, resulting in the release of arachidonic acid. This signaling pathway is specific for peroxisomes and does not influence motility of mitochondria, lysosomes, or endosomes. However, since the cytoskeleton and its associated proteins including the motor proteins play an important role in mediating motility of all cell organelles, it may well be that variant signaling cascades exist ensuring specific regulation of each distinct compartment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
arachidonic acid
- ATPγS:
-
adenosine-5′-O-(3-thiotriphosphate)
- cAMP:
-
cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- CaM-PK:
-
calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
- CLIP:
-
cytosolic linker protein
- DAG:
-
diacylglycerol
- DiC8 :
-
1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycerol
- GFP:
-
green-fluorescent protein
- GTPγS:
-
guanosine-5′-O-(3-thiotriphosphate)
- IP3 :
-
inositol trisphosphate
- LPA:
-
lysophosphatidic acid
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEK MAPK:
-
kinase
- PKA:
-
protein kinase A
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- cPKC:
-
classical PKC isoforms
- PLA2 :
-
phospholipase A2
- PLAP:
-
PLA2-activating proteinpeptide
- PLC:
-
phospholipase C
- PP2A:
-
protein phosphatase 2A
References
Arnheiter H (1998) Eyes viewed from the skin. Nature 391: 632–633
Axelrod J, Burch RM, Jelsema CL (1988) Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 via GTP-binding proteins: arachidonic acid and its metabolites as second messengers. Trends Neurosci 11: 117–123
Beck KA, Buchanan JA, Nelson WJ (1997) Golgi membrane skeleton: identification, localization and oligomerization of a 195 kDa ankyrin isoform associated with the Golgi complex. J Cell Sci 110: 1239–1249
Berg KA, Clarke WP, Sailstad C, Saltzman A, Maayani S (1994) Signal transduction differences between 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2A and type 2C receptor systems. Mol Pharmacol 46: 477–484
Blangy A, Lane HA, d'Herin P, Harper M, Kress M, Nigg EA (1995) Phosphorylation of p34cdc2 regulates spindle association of human Eg5, a kinesin-related motor essential for bipolar spindle formation in vivo. Cell 83: 1159–1169
Bradley TJ, Satir P (1979) Evidence of microfilament-associated mitochondrial movement. J Supramol Struct 12: 165–175
Bradtke F, Dotti CG (1997) Neuronal polarity: vectorial flow precedes axon formation. Neuron 19: 1175–1186
Burkhardt JK, Echeverri CJ, Nilsson T, Vallee RB (1997) Overexpression of the dynamitin (p50) subunit of the dynactin complex disrupts dynein-dependent maintenance of membrane organelle distribution. J Cell Biol 139: 469–484
Carman CV, Benovic JL (1998) G-protein-coupled receptors: turnons and turn-offs. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8: 335–344
Cavalier-Smith T (1987) The simultaneous symbiotic origin of mitochondria, chloroplasts, and microbodies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 503: 55–71
Cheng H, Lederer MR, Xiao RP, Gomez AM, Zhou YY, Ziman B, Spurgeon H, Lakatta EG, Lederer WJ (1996) Excitationcontraction coupling in heart: new insights from Ca2+ sparks. Cell Calcium 20: 129–140
Clark JD, Lin LL, Kriz RW, Ramesha CS, Sultzman LA, Lin AY, Milona N, Knopf JL (1991) A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca2+-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell 65: 1043–1051
—, Schievella AR, Nalefski EA, Lin LL (1995) Cytosolic phospholipase A2. J Lipid Med Cell Signal 12: 83–117
Cole NB, Sciaky N, Marotta A, Song J, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1996) Golgi dispersal during microtubule disruption: regeneration of Golgi stacks at peripheral endoplasmic reticulum exit sites. Mol Biol Cell 7: 631–650
Devarajan P, Stabach PR, Mann AS, Ardito T, Kashgarian M, Morrow JS (1996) Identification of a small cytoplasmic ankyrin (AnkG119) in the kidney and muscle that binds βI σ-spectrin and associates with the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol 133: 819–830
— —, De Matteis MA, Morrow JS (1997) Na+/K+-ATPase transport from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi requires the Golgi spectrinankyrin G119 skeleton in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 10711–10716
de Zeeuw CI, Hoogenraad CC, Goedknegt E, Hertzberg E, Neubauer A, Grosveld F, Galjart N (1997) CLIP-115, a novel brain-specific cytoplasmic linker protein, mediates the localization of dendritic lamellar bodies. Neuron 19: 1187–1199
Dubyak GS, El-Moatassim C (1993) Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am J Physiol 265: C577-C606
Echeverri CJ, Paschal BM, Vaughan KT, Vallee RB (1996) Molecular characterization of the 50 kD-subunit of dynactin reveals function for the complex in chromosome alignment and spindle organization during mitosis. J Cell Biol 132: 617–633
Eichholtz T, Jalink K, Fahrenfort I, Moolenaar WH (1993) The bioactive phospholipid lysophosphatidic acid is released from activated platelets. Biochem J 291: 677–680
Elgersma Y., Kwast L, van den Berg M, Snyder WB, Distel B, Subramani S, Tabak HF (1997) Overexpression of Pex15p, a phosphorylated peroxisomal integral membrane protein required for peroxisome assembly inS. cerevisiae, causes proliferation of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. EMBO J 16: 7326–7341
Felder CC, Dieter P, Kinsella J, Tamura K, Kanterman RY, Axelrod J (1990) A transfected m5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor stimulates phospholipase A2 by inducing both calcium influx and activation of protein kinase C. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255: 1140–1147
—, Williams HL, Axelrod J (1991) A transduction pathway associated with receptors coupled to the inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein Gi that amplifies ATP-mediated arachidonic acid release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 6477–6480
Forman DS, Lynch KJ, Smith RS (1987) Organelle dynamics in lobster axons: anterograde, retrograde and stationary mitochondria. Brain Res 412: 96–106
Freund S, Ungerer M, Lohse MJ (1994) A1 adenosine receptors expressed in CHO cells couple to adenylyl cyclase and to phospholipase C. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 350: 49–56
Fukuda K, Kato S, Morikawa H, Shoda T, Mori K (1996) Functional coupling of the δ-, μ- and κ-opioid receptors to mitogen-activated protein kinase and arachidonate release in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Neurochem 67: 1309–1316
Giles H, Lansdell SJ, Bolofo ML, Wilson HL, Martin GR (1996) Characterization of a 5-HT1b receptor on CHO cells: functional responses in the absence of radioligand binding. Br J Pharmacol 117: 1119–1126
Gorgas K (1984) Peroxisomes in sebaceous glands V: complex peroxisomes in the mouse preputial gland: serial sectioning and three-dimensional reconstruction studies. Anat Embryol (Berl) 169: 261–270
Gudermann T, Kalkbrenner F, Schultz G (1996) Diversity and selectivity of receptor-G protein interaction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 36: 429–459
Hanke JH, Gardner JP, Dow RL, Changelian PS, Brissette WH, Weringer EJ, Pollok BA, Connelly PA (1996) Discovery of a novel, potent, and Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor: study of Lck- and FynT-dependent T cell activation. J Biol Chem 271: 695–701
Hardingham GE, Cruzalegui FH, Chawla S, Bading H (1998) Mechanisms controlling gene expression by nuclear calcium signals. Cell Calcium 23: 131–134
Haupt W, Scheuerlein R (1990) Chloroplast movement. Plant Cell Environ 13: 595–614
Hawes BE, van Biesen T, Koch WJ, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ (1995) Distinct pathways of Gi and Gq-mediated mitogenactivated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem 270: 17148–17153
Holleran EA, Tokito MK, Karki S, Holzbaur EL (1996) Centractin (ARP1) associates with spectrin revealing a potential mechanism to link dynactin to intracellular organelles. J Cell Biol 135: 1815–1829
Huber CM, Saffrich R, Anton M, Paßreiter M, Ansorge W, Gorgas K, Just WW (1997) A heterotrimeric G protein-phospholipase A2 signaling cascade is involved in the regulation of peroxisomal motility in CHO cells. J Cell Sci 110: 2955–2968
Iredale PA, Hill SJ (1993) Increases in intracellular calcium via activation of an endogenous P2-purinoceptor in cultured CHO-K1 cells. Br J Pharmacol 110: 1305–1310
Jalink K, Hordijk PL, Moolenaar WH (1994) Growth factor-like effects of lysophosphatidic acid, a novel lipid mediator. Biochim Biophys Acta 1198: 185–196
—, Hengeveld T, Mulder S, Postma FR, Simon MF, Chap H, van der Marel GA, van Boom JH, van Blitterswijk WJ, Moolenaar WH (1995) Lysophosphatidic acid-induced Ca2+ mobilization in human A431 cells: structure-activity analysis. Biochem J 307: 609–616
Jedlitschky G, Huber M, Völkl A, Müller M, Leier I, Müller J, Lehmann WD, Fahimi HD, Keppler D (1991) Peroxisomal degradation of leukotrienes by beta-oxidation from the omega-end. J Biol Chem 266: 24763–24772
Kelleher JF, Titus MA (1998) Intracellular motility: how can we all work together? Curr Biol 8: R394-R397
Kotz KJ, McNiven MA (1994) Intracellular calcium and cAMP regulate directional pigment movements in teleost erythrophores. J Cell Biol 124: 463–474
Lerner MR (1994) Tools for investigating functional interactions between ligands and G protein-coupled receptors. Trends Neurosci 17: 142–146
Lin LL, Lin AY, Knopf JL (1992) Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is coupled to hormonally regulated release of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 6147–6151
—, Wartmann M, Lin AY, Knopf JL, Seth A, Davis RJ (1993) cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell 72: 269–278
Lin SHX, Collins CA (1993) Regulation of the intracellular distribution of cytoplasmic dynein by serum factors and calcium. J Cell Sci 105: 579–588
Matthies HJ, Miller RJ, Palfrey HC (1993) Calmodulin binding to and cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of kinesin light chains modulate kinesin ATPase activity. J Biol Chem 1993: 11176–11187
McIntosh JR, Koonce MP (1989) Mitosis. Science 246: 622–628
Minin AA (1997) Dispersal of Golgi apparatus in nocodazoletreated fibroblasts is a kinesin-driven process. J Cell Sci 110: 2495–2505
Moolenaar WH, Kranenburg O, Postma FR, Zondag GCM (1997) Lysophosphatidic acid: G-protein signalling and cellular responses. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9: 168–173
Morris RL, Hollenbeck PJ (1993) The regulation of bidirectional mitochondrial transport is coordinated with axonal outgrowth. J Cell Sci 104: 917–927
Murphy C, Saffrich R, Grummt M, Gournier H, Rybin V, Rubino M, Auvinen P, Lütcke A, Parton RG, Zerial M (1996) Endosome dynamics regulated by a rho protein. Nature 384: 427–432
Musch A, Cohen D, Rodriguez-Boulan E (1997) Myosin II is involved in the production of constitutive transport vesicles from the TGN. J Cell Biol 138: 291–306
Nemenoff RA, Winitz S, Qian NX, van Putten V, Johnson GL, Heasley LE (1993) Phosphorylation and activation of a high molecular weight form of phospholipase A2 by p42 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 268: 1960–1964
Nicotera P, Orrenius S (1998) The role of calcium in apoptosis. Cell Calcium 23: 173–180
Nilsson H, Wallin M (1997) Evidence for several roles of dynein in pigment transport in melanophores. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 38: 397–09
Pierre P, Scheel J, Rickard JE, Kreis TE (1992) CLIP-170 links endocytic vesicles to microtubules. Cell 70: 887–900
Presley JF, Cole NB, Schroer TA, Hirschberg K, Zaal KJ, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1997) ER-to-Golgi transport visualized in living cells. Nature 389: 81–85
Rapp S, Saffrich R, Anton M, Jäkle U, Ansorge W, Gorgas K, Just WW (1996) Microtubule-based peroxisomal movement. J Cell Sci 109: 837–849
Reilein AS, Tint IS, Peunova NI, Enikolopov GN, Gelfand VI (1998) Regulation of organelle movement in melanophores by a protein kinase A (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC), and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). J Cell Biol 142: 803–813
Rhodin J (1954) Correlation of ultrastructural organization and function in normal and experimentally changed proximal convoluted tubule cells of the mouse kidney. PhD thesis, Karolinska Institute Aktiebolaget Godvil, Stockholm
Rodionov VI, Hops AJ, Svitkina TM, Borisy GG (1998) Functional coordination of rnicrotubule and actin based motility in melanophores. Curr Biol 8: 165–168
Scales SJ, Pepperkok R, Kreis TE (1997) Visualization of ER-to-Golgi transport in living cells reveals a sequential mode of action for COP II and COP I. Cell 90: 1137–1148
Schaap D, van der Wal J, Howe LR, Marshall CJ, van Blitterswijk WJ (1993) A dominant-negative mutant of raf blocks mitogenactivated protein kinase activation by growth factors and oncogenic p21ras. J Biol Chem 268: 20232–20236
Schievella A, Regier MK, Smith WL, Lin LL (1995) Calcium-mediated translocation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 270: 30749–30754
Sciaky N, Presley J, Smith C, Zaal KJ, Cole N, Moreira JE, Terasaki M, Siggia E, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1997) Golgi tubule traffic and the effects of brefeldin A visualized in living cells. J Cell Biol 139: 1137–1155
Sheetz MP (1996) Microtubule motor complexes moving membraneous organelles. Cell Struct Funct 21: 369–373
Simon VR, Pon LA (1996) Actin-based organelle movement. Experientia 52: 1117–1122
Soto U, Pepperkok R, Ansorge W, Just WW (1993) Import of firefly luciferase into mammalian peroxisomes in vivo requires nucleoside triphosphates. Exp Cell Res 205: 66–75
Sozeri O, Vollmer K, Liyanage M, Frith D, Kour G, Mark GE, Stabel S (1992) Activation of the c-raf protein kinase by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Oncogene 7: 2259–2262
Thaler CD, Haimo LT (1996) Microtubules and rnicrotubule motors: mechanisms of regulation. Int Rev Cytol 164: 269–327
Titorenko VI, Rachubinski RA (1998) Mutants of the yeastYarrowia lipolytica defective in protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum are also defective in peroxisome biogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 18: 2789–2803
Traiffort E, Ruat M, Arrang J, Leurs R, Piomelli D, Schwartz J (1992) Expression of a cloned rat histamine H2 receptor mediating inhibition of arachidonic acid release and activation of cAMP accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 2649–2653
Ueda Y, Hirai S, Osada S, Suzuki A, Mizuno K, Ohno S (1996) Protein kinase C activates the MEK-ERK pathway in a manner independent of ras and dependent on raf. J Biol Chem 271: 23512–23519
van Biesen T, Hawes B, Raymond JR, Luttrell LM, Koch WJ, Lefkowitz RL (1996) Go-protein α subunits activate mitogenactivated protein kinase via a novel protein kinase C-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 271: 1266–1269
Vaisberg EA, Grissom PM, McIntosh JR (1996) Mammalian cells express three distinct dynein heavy chains that are localized to different cytoplasmic organelles. J Cell Biol 133: 831–842
Wacker I, Kaether C, Krömer A, Migala A, Almers W, Gerdes HH (1997) Microtubule-dependent transport of secretory vesicles visualized in real time with a GFP-tagged secretory protein. J Cell Sci 110: 1453–1463
Waterman-Storer CM, Karki SB, Kuznetsov SA, Tabb JS, Weiss DG, Langford GM, Holzbaur EL (1997) The interaction between cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin is required for fast axonal transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 12180–12185
Wiemer EAC, Wenzel T, Deerinck TJ, Ellisman MH, Subramani S (1997) Visualization of the peroxisomal compartment in living mammalian cells: dynamic behaviour and association with microtubules. J Cell Biol 136: 71–80
Winitz S, Gupta SK, Quian NX, Heasley LE, Nemenoff RA, Johnson GL (1994) Expression of a mutant Gi2 α subunit inhibits ATP and thrombin stimulation of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2-mediated arachidonic acid release independent of Ca2+ and mitogenactivated protein kinase regulation. J Biol Chem 269: 1889–1896
Wu SH, Lagarias JC (1997) The phytochrome photoreceptor in the green algaMesotaenium caldariorium: implication for a conserved mechanism of phytochrome action. Plant Cell Environ 20: 691–699
Yamaguchi K, Ogita K, Nakamura S, Nishizuka Y (1995) The protein kinase C isoforms leading to MAP-kinase activation in CHO cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 210: 639–647
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huber, C.M., Saffrich, R., Gorgas, K. et al. Organelle motility regulated by the cell's environment: dissection of signaling pathways regulating movements of peroxisomes. Protoplasma 213, 18–27 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01280501
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01280501