Abstract
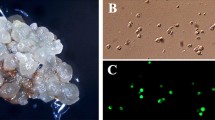
Isolated somatic embryos from petiole-derived callus cultures ofVitis rupestris Scheele have been employed in experiments on genetic transformation. Co-cultivation of somatic embryos during embryogenesis induction withAgrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA4404, which contains the plasmid pBI121 carrying the neomycin phosphotranspherase and theβ-glucuronidase genes, produced transformed cellular lines capable of recurrent somatic embryogenesis. Precocious selection for high levels of kanamycin (100 mgl-1) was an important part of our transformation protocol. Transformed lines still have strongβ-glucuronidase expression as well as stable insertion of the marker genes after 3 years of in-vitro culture, during which they have maintained their capacity to organize secondary embryos and to regenerate transgenic plants with an agreeable efficiency (13%).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baribault TJ, Skene KGM, Steele Scott N (1989) Genetic transformation of grapevine cells. Plant Cell Rep 8:137–140
Baribault TJ, Skene KGM, Cain PA, Steele Scott N (1990) Transgenic grapevines: regeneration of shoots expressingβ-glucuronidase. J Exp Bot 41:1045–1049
Barlass M, Skene KGM (1979) In-vitro propagation of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) from fragmented shoot apex. Vitis 17:335–340
Barlass M, Skene KGM (1980) Studies on the fragmented shoot apex of grapevine. II. Factors affecting growth and differentiation in-vitro. J Exp Bot 31:489–495
Berres R, Tinland B, Malgarini-Clog E, Walter B (1992) Transformation ofVitis tissue by different strains ofAgrobacterium tumefaciens containing the T-6b gene. Plant Cell Rep 11:192–195
Bevan M (1984) BinaryAgrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 12:8711–8721
Bouquet A, Piganeau B, Lamaison M (1982) Influence du génotype sur la production de cals, d'embryoides et de plantes entières par culture d'anthères in-vitro dans le genreVitis. Compt Rend Acad Sci Paris 295:569–574
Cheng ZM, Reisch BL (1989) Shoot regeneration from petioles and leaves ofVitisxlabruscana “Catawba”. Plant Cell Rep 8:403–406
Clog E, Bass P, Walter B (1990) plant regeneration by organogenesis inVitis rootstock species. Plant Cell Rep 8:726–728
Colby S, Meredith CP (1990) Kanamycin sensitivity of cultured tissues ofVitis. Plant Cell Rep 9:237–240
Colby S, Juncosa A, Meredith CP (1991) Cellular differences inAgrobacterium susceptibility and regenerative capacity restrict the development of transgenic grapevines. J Am Soc Hort Sci 116:356–361
Gray DJ (1989) Effects of dehydration and exogenous growth regulators on dormancy, quiescence and germination of grape somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 25:1173–1178
Gribaudo I, Schubert A (1990) Grapevine root transformation withAgrobacterium rhizogenes. Vitis, special issue: 412–418
Guellac V, David C, Branchard M, Tempé J (1990)Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated transformation of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 20:211–215
Hébert D, Kikkert JR, Smith FD, Reisch B (1993) Optimization of biolistic transformation of embryogenic grape cell suspensions. Plant Cell Rep 12:585–589
Hemstad PR, Reisch BI (1985) In vitro production of galls induced byAgrobacterium tumefaciens andAgrobacterium rhizogenes onVitis andRubus. J Plant Physiol 120:9–17
Hirabayashi T, Kozaki I, Akihama T. (1976) In-vitro differentiation of shoots from anther callus inVitis. Hort Sci 11:511–512
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan M (1987) GUS fusions:β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Krul WR, Worley JF (1977) Formation of adventitious embryos in callus cultures of “Seyval”, a french hybrid grape. J Am Soc Hort Sci 102:360–363
Lippincott BB, Lippincott JA (1969) Bacterial attachment to a specific wound site as an essential stage in tumour initiation byAgrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 97:620–628
Martinelli L, Bragagna P, Poletti V, Scienza A (1993) Somatic embryogenesis from leaf- and petiole-derived callus ofVitis rupestris. Plant Cell Rep 12:207–210
Matsuta N, Hirabayashi T (1989) Embryogenic cell lines from somatic embryos of grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Cell Rep 7:684–687
Mauro MCl, Nef C, Fallot J (1986) Stimulation of somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from anther culture ofVitis vinifera cv Cabernet Sauvignon. Plant Cell Rep 5:377–380
Mooney PA, Goodwin PB (1991) Adherence ofAgrobacterium tumefaciens to the cells of wheat embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 25:199–208
Monnier M, Faure O, Sigogneau A (1990) Somatic embryogenesis inVitis. Bull Soc Bot Fr 137, Actual Bot 3/4:35–44
Mullins MG, Srinivasan C (1976) Somatic embryos and plantlets from an ancient clone of the grapevine (cv. Cabernet Sauvignon) by apomixis in-vitro. J Exp Bot 27:1022–1030
Mullins MG, Tang AFC, Facciotti D (1990)Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of grapevines: transgenic plants ofVitis rupestris Scheele and buds ofVitis vinifera L. Bio/Technol 8:1041–1045
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nitsch JP, Nitsch C (1969) Haploid plants from pollen grains. Science 163:85–87
Rajasekaran K, Mullins MG (1979) Embryo and plantlets from cultured anthers of hybrid grapevines. J Exp Bot 30:399–407
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1985) Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol 5:69–76
Stamp JA, Meredith CP (1988 a) Proliferative somatic embryogenesis from zygotic embryos of grapevine. J Am Soc Hort Sci 113:941–945
Stamp JA, Meredith CP (1988 b) Somatic embryogenesis from leaves and anthers of grapevine. Sci Hort 35:235–250
Stamp JA, Colby M, Meredith CP (1990) Improved shoot organogenesis from leaves of grape. J Am Soc Hort Sci 115:1038–1042
Vilaplana M, Mullins M (1989) Regeneration of grapevines (Vitis spp.) in-vitro: formation of adventitious buds on hypocotyls and cotyledons of somatic embryos. J Plant Physiol 134:413–419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinelli, L., Mandolino, G. Genetic transformation and regeneration of transgenic plants in grapevine (Vitis rupestris S.). Theoret. Appl. Genetics 88, 621–628 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01253963
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01253963