Abstract
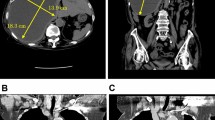
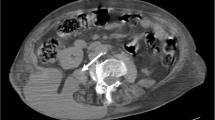
We report the case of a 61-year-old woman with cryptogenic liver abscesses who had been profoundly ill with severe upper abdominal pain, impaired consciousness, prostration, continuous high fever secondary to sepsis, and thrombocytopenia (platelets, 1–5 × 104/mm3) since admission. Ultrasonograms and computed tomograms revealed two separate multiloculated lesions in the right lobe of the liver, consistent with the liver abscesses. Immediately after diagnosis, percutaneous abscess drainage was performed under ultrasonographic guidance; however, only a small amount of pus was drained, prompting continuous irrigation of the abscess cavity. Four days later, transcatheter hepatic arterial infusion of antibiotics was attempted. However, the abscesses had enlarged and her general condition had worsened. On hospital day 8, she underwent right hepatectomy because the multiloculated lesions were refractory to drainage. The operation was successful in terms of hepatectomy, although she continued to suffer from sepsis, secondary right subphrenic abscess formation, and prolonged thrombocytopenia with associated coagulation disorders for two months. Examination of multiple cross sections of the resected specimen disclosed that the lesions consisted of aggregations of multiple small locules. There was no communication between the locules and there were true septations, rather than multiloculated lesions with pseudoseptations. The patient has been well for 2 years without recurrent abscess of the liver or any infectious disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herbert DA, Fogel DA, Simons F, et al. Medical management of pyogenic liver abscesses. Lancet 1985;I:1384.
Perera MR, Kirk A, Noone P. Presentation, diagnosis and management of liver abscess. Lancet 1980;II:629–632.
Komatsu E, Isobe Y, Imaizumi T, et al. A clinical study of therapeutic method for pyogenic liver abscesses (in Japanese with English abstract). Nippon Shokakigeka Gakkai Zasshi (Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg) 1995;28:1013–1019.
Gerzof SG, Johnson WC, Robbins AH, et al. Intrahepatic pyogenic abscesses: Treatment by percutaneous drainage. Am J Surg 1985;149:487–494.
Bertel CK, Heerden JA, Sheedy PF. Treatment of pyogenic hepatic abscesses; surgical vs percutaneous drainage. Arch Surg 1986;121:554–558.
Bissada AA, Bateman J. Pyogenic liver abscess: A 7-year experience in a large community hospital. Hepato-Gastroenterol 1991;38:317–320.
Rubin RH, Swartz MN, Malt R. Hepatic abscess: Changes in clinical bacteriologie and therapeutic aspects. Am J Med 1974;57:601–610.
Miedema BW, Dineen P. The diagnosis and treatment of pyogenic liver abscesses. Ann Surg 1984;200:328–335.
Klatchko BA, Schwarz SI. Diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to pyogenic abscess of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1989; 168:332–336.
Branum GD, Tyson GS, Branum MA, et al. Hepatic abscess; changes in etiology, diagnosis, and management. Ann Surg 1990;212:655–662.
Knoop M, Kling N, Langrehr JM, et al. Gibt es noch eine Indikation zur Leberresktion bei Leberabszessen? Zentralbl Chir 1995;120:461–466.
Hansen N, Vargish T. Pyogenic hepatic abscess: A case for open drainage. Am Surg 1993;59:219–222.
Gyoffy EJ, Frey CF, Silva J, et al. Pyogenic liver abscess; diagnosis and therapeutic strategies. Ann Surg 1987;206:699–705.
Johnson RD, Mueller PR, Ferrucci JT, et al. Percutaneous drainage of pyogenic liver abscess. Am J Roentogenol 1985;144:463–467.
Van Waes P, Feldberg M, Mali W, et al. Management of loculated abscesses that are difficult to drain: A new approach. Radiology 1983;147:57–63.
Bernardino M, Berkman W, Plemmons M, et al. Percutaneous drainage of multiseptated hepatic abscess. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1984;8:38–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurosaki, I., Takagi, K., Hatakeyama, S. et al. Right hepatectomy for pyogenic liver abscesses with true multiloculation. J Gastroenterol 32, 105–109 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213305
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213305