Summary
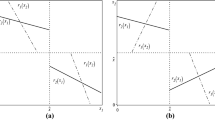
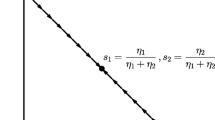
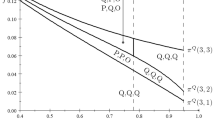
This paper analyzes how learning behaviors can substantially modify the outcome of competition in an oligopolistic industry facing demand uncertainty. We consider the case of a symmetric duopoly game where firms have imperfect information about market demand and learn through observing the volume of their sales. The main body of the paper consists in showing how market experimentation can explain the existence ofprice-dispersion in an oligopolistic industry. We study this phenomenon and its dynamic evolution in the context of an Hotelling duopoly model; we then extend the analysis to general demand functions and toN-firm oligopolies. We discuss some implications of the public good aspect of information about market demand. We then conclude with a few comments on what happens when the value of information in the oligopolistic industry is negative.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghion, P., Bolton, P., Harris, C., Jullien, B.: Optimal learning by experimentation. Rev. Econ. Stud.58, 621–654 (1991)
Aghion, P., Espinosa, M. P., Jullien, B.: Dynamic duopoly with learning through market experimentation. CREST working paper 9202, 1991
Burdett, K., Judd, K. L.: Equilibrium price-dispersion. Econometrica51, 955–969 (1983)
Buttters, G.: Equilibrium distributions of sales and advertising prices. Rev. Econ. Stud.XLIV, 465–491 (1972)
Clower, R. W.: Some theory of an ignorant monopoly. Econ. J.69, 705–716 (1959)
Cyert, R., De Groot, M.: Interim learning and the kinked demand curve. J. Econ. TheoryIII, 272–287 (1971)
Dixit, A. K., Stiglitz, J.: Monopolistic competition and optimum product diversity. Amer. Econ. Rev.67, 297–308 (1977)
Easley, D., Kiefer, N.: Controlling a stochastic process with unknown parameters. Econ.56, 1045–1064 (1988)
Grossman, S., Khilstrom, R., Mirman, L.: A Bayesian approach to the production of information and learning by doing. Rev. Econ. Stud.44, 533–547 (1977)
Kirman, A.: On mistaken beliefs and resultant equilibria. In: Individual forecasting and aggregate outcomes, pp. 147–168. Phelps, E. (eds.). Cambridge University Press 1985
McLennan, A.: Price dispersion and incomplete learning in the long run. J. Econ. Dynam. Control7, 331–347 (1984)
Mirman, L., Samuelson, L., Urbano, A.: Monopoly experimentation. Working Paper, University of Virginia 1989a
Mirman, L., Samuelson, L., Urbano, A.: Experimentation and signal jamming. Working Paper, University of Virginia 1989b
Reinganum, J.: A simple model of equilibrium price dispersion. J. Polit. Econ.XXCVII, 851–858 (1975)
Riordan, M.: Imperfect information and dynamic conjectural variations. Rand J. Econ.XVI, 41–50 (1985)
Rob, R.: Learning and capacity expansion in new market under demand uncertainty. Rev. Econ. Stud.58, 655–675 (1991)
Rothschild, M.: A two-armed bandit theory of market pricing. J. Econ. Theory9, 185–202 (1974)
Salop, S., Stiglitz, J.: Bargains and ripoffs: a model of monopolistically competitive price dispersion. Rev. Econ. Stud.XXIV 493–510 (1977)
Salop, S.: Monopolistic competition with outside goods. Bell J. Econ.10, 141–146 (1975)
Slade, M. E.: Conjecture, firm characteristics, and market structure: an empirical assessment. Int. J. Ind. Organiz.4, 347–369 (1986)
Slade, M. E.: Learning through price wars: an exercise in uncovering supergame strategies. Mimeo, University of British Columbia 1989
Wilde, L., Schwartz, A.: Equilibrium comparison shopping. Rev. Econ. Stud.46, 543–553 (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We are very grateful to Patrick Bolton for his helpful advice. We also wish to thank Richard Caves, Anthony Creane, Jean-Jacques Laffont, Andreu Mas-Colell, Eric Maskin, Jean-Charles Rochet, Margaret Slade, John Sutton, Jean Tirole, Mike Whinston and an anonymous referee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghion, P., Espinosa, M.P. & Jullien, B. Dynamic duopoly with learning through market experimentation. Econ Theory 3, 517–539 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209700
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209700