Abstract
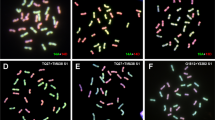
Allium ampeloprasum cultivated in Kashmir is a tetraploid. The somatic complement of the cultivar consists of 32 median or submedian chromosomes, of which 8 have secondary constrictions. The tetraploid karyotype exhibits a great deal of heterozygosity which is taken as an evidence in support of the allopolyploid nature of the species. The tetraploid form is represented by the genomic formula AAA′A″. The three genomes show a great deal of similarity and are therefore taken to represent three varieties which have given rise to this cultivar through hybridity. — Despite this, no multivalents are formed by the species during meiosis. The shift from multivalent to bivalent type of pairing is attributed to the localization of chiasmata around the centromere. This type of chiasmata localization is a means adopted by some polyploid species to stabilize as diploids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darlington, C. D., Janaki-Ammal, E. K.: Chromosome atlas of cultivated plants. London: Alien and Unwin 1945.
—, Wylie, A. P.: Chromosome atlas of flowering plants. London: Alien and Unwin 1956.
Jones, H. A., Mann, L. K.: Onions and their allies. New York: Interscience Publ. 1963.
Kadry, A. E. R., Kamel, S. A.: Cytological studies in the two tetraploid speciesA. kurrat Schweinf. andA. porrum and their hybrid. Svensk Bot. Tidskr.49, 314–324 (1955).
Khoshoo, T. N., Atal, C. K., Sharma, V. B.: Cytotaxonomical and chemical investigations on the North-west Indian garlics. Res. Bull. Panj. Univ.2, 37–47 (1960).
Koul, A. K., Gohil, R. N.: Breeding system and occasional vivipary inAllium ampeloprasum. Sci and Cult. (in press).
Levan, A.: Cytological studies inAllium. A preliminary note. Hereditas (Lund)15, 347–356 (1931).
—: Zytologische studies enAllium schoenoprasum. Hereditas (Lund)22, 1–128 (1936).
—: Meiosis inAllium porrum, a tetraploid species with chiasma localization. Hereditas (Lund)26, 454–462 (1940).
Murín, A.: Chromosome study inAllium porrum L. Caryologia (Firenze)17, 575–578 (1964).
Stebbins, G. L., Jr.: Types of polyploids. Their classification and significance. Advanc. Genet.1, 403–429 (1947).
- Variation and evolution in plants. New York 1950.
Täckholm, V., Drar, M.: Flora of Egypt. Bull Fac. Sci. Egypt Univ.3, xii + 644 pp (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koul, A.K., Gohil, R.N. Cytology of the tetraploidAllium ampeloprasum with chiasma localization. Chromosoma 29, 12–19 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01183658
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01183658