Summary
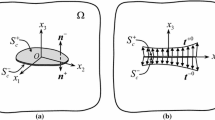
A closed-form solution for plates containing surface cracks is obtained by using an equivalent through-crack model, which reduces the three-dimensional problem of the surface cracked plates to a two-dimensional Hilbert problem. The effect of surface crack is replaced by a continuous distribution of forcesN(x, 0) and momentsM(x, 0) applied along the crack face of the equivalent through-crack model. A convenient form of expressing these forces and moments is by using power polynomials. Then the singular integral equation, expressing the solution of the Hilbert problem can be readily integrated.
According to this model we assumed that the crack depth at extremities, where the crack intersects the free surface of the plate, is not zero. This assumption, corroborated by experimental evidence, means that a singularity exists at the extremities of the crack. The experimental evidence was achieved by using the method of caustics and photoelasticity. The results of the evaluation of the stress intensity factor for elliptical cracks were compared well with the solutions of the respective 3-D problem solved by applying the finite-element method, the line-spring model based on the Reissner plate theory, the finite-element alternating method and the benchmark estimate. The distribution of the stress intensity factor along the crack lips, as calculated in this paper, was dropping off rapidly in the surface layer and it was very close to the results given by the approximate 3-D theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newman, J. C. Jr.: A review and assessment of stress intensity factors for surface crack. NASA TM 78 805 (1978).
Shah, R. C., Kobayashi, A. S.: On the surface flaw problem, in: The surface crack: physical problems and computational solutions (Swedlow, J. L., ed.), p. 79, 1972.
Smith, F. W., Sorensen, D. R.: The semi-elliptical surface crack — A solution by the alternating method. Int. J. Fract. Mech.12, 47 (1976).
Raju, I. S., Newman, J. C. Jr.: Stress intensity factor for a wide range semi-elliptical surface crack in finite-thickness plate. Engng. Fract. Mech.11, 917 (1979).
Newman, J. C. Jr., Raju, I. S.: Analysis of surface cracks in finite plates under tension or bending loads. NASA TP 1578 (1979).
Alturi, S. N., Kathiresan, K.: Stress intensity factor solutions for arbitrarily shaped surface flaws in reactor pressure vessel nozzle corners. Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping8, 313 (1980).
Heliot, J., Labbens, R., Pellissier-Tanon, A.: Benchmark problem no. 1-semi-elliptical surface crack-results of computation. Int. J. Fract.15, R 197 (1979).
Delale, F., Erdogan, F.: Line-spring model for surface cracks in a Reissner plate. Int. J. Engng. Sci.19, 1331 (1981).
Nishioka, T., Atluri, N.: Analytical solution for embedded elliptical cracks, and finite element alternating method for elliptical surface cracks, subjected to arbitrary loadings. Engng. Fract. Mech.17, 247 (1983).
Hartranft, R. J., Sih, G. C.: An approximate three dimensional theory of plate with application to crack problem. Int. J. Engng. Sci.8, 711 (1970).
Sih, G. C.: A review of the three-dimensional stress problem for a cracked plate. Int. J. Fract. Mech.7, 39 (1971).
Theocaris, P. S.: The method of caustics applied to elasticity problems, in: Development in stress analysis-I (Holister, G. S., ed.), p. 27, 1979.
Theocaris, P. S., Wu, D. L.: The equivalent through-crack model for the surface part-through crack. Published in Athens. The National Technical University of Athens, May 1983.
Rice, J. R., Levy, N.: The part-through surface crack in an elastic plate. J. Appl. Mech.39, 185 (1972).
Smith, C. W., Peters, W. H., Kirby, G. C., Andonian, A.: Stress intensity distributions for natural flaw shapes approximating ‘benchmark’ geometries. Fracture Mechanics13, ASTM-STP 743, 422 (1981).
Smith, C. W., Peters, W. H. III, Kirby, G. C.: Crack-tip measurements in photoelastic models. Exp. Mech.22, 448 (1982).
Tada, H., Paris, P. C., Irwin, G. R.: The stress analysis of cracks. Handbook, Del Res. Corp., Hellertown, Pennsylvania 1973.
Kaya, A. C., Erdogan, F.: Stress intensity factors and COD in an orthotropic strip. Int. J. Fract.16, 171 (1980).
Muskhelishvili, N. I.: Some basic problems of the mathematical theory of elasticity. Groningen: Noordhoff 1953.
McGowan, J. J. (ed.): A critical evaluation of numerical solutions to the ‘benchmark’ surface-flaw problem. Exp. Mech.20, 253 (1980).
Raju, I. S., Newman, J. C. Jr.: Three-dimensional finite element analysis of finite-thickness fracture specimens. NASA TN D-8414 (1977).
Benthem, J. P.: State of stress at the vertex of a quarter-infinite crack in a half-space. Intern. Jnl. Sol. Struct.13, 479 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 7 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Theocaris, P.S., Wu, D.L. A closed-form solution to the equivalent through-crack model for surface cracks. Acta Mechanica 58, 153–173 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01176597
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01176597