Abstract
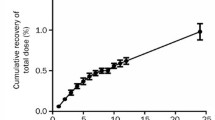
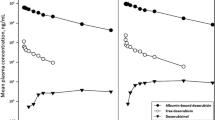
The pharmacokinetics of methotrexate (MTX) and 7-hydroxy-methotrexate (7-OH-MTX), a major metabolite, were investigated in rabbits after intravenous bolus injection and infusion using a specific HPLC assay. The arterial sampling (from the carotid artery) was used in all the studies since peculiar and significant arterial-venous differences in the plasma concentration of MTX and 7-OH-MTX were found following bolus administration of the drug. The disposition kinetics of MTX appeared polyexponential with a small terminal phase having a half-life of 10.2–27.5 hr. Extensive formation of 7-OH-MTX occurred at the two dose levels (15 and 50 mg/kg). Nonlinear disposition of MTX was reflected in several aspects of data analysis. A disproportionate increase in the AUC with dose was observed. An increase in dose not only reduced the mean total body clearance (7.49 vs. 4.26 ml/min/kg) and renal clearance (4.89 vs. 2.76 ml/min/kg), but also prolonged the mean residence time (26.2 vs. 43.3 min). The steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) of MTX was estimated to range from 0.16 to 0.25 L/kg. More than 90% of the dose was excreted as MTX and 7-OH-MTX within 8 hr after dosing. Renal clearances decreased with the increasing plasma levels, suggesting active tubular secretion as one of the excretion mechanisms. A similar pattern for renal clearance of 7-OH-MTX was obtained. Infusion studies of 7-OH-MTX revealed that this metabolite had a longer residence time and a larger Vss as compared with MTX, which were in accordance with its physicochemical properties. Essentially complete doses of 7-OH-MTX could be recovered in the rabbit urine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Farber, L. K. Diamond, R. D. Mercer, R. F. Sylvester, and J. A. Wolff. Temporary remissions in acute leukemia in children produced by folic acid antagonist, 4-aminopteroylglutamic acid (aminopterin).N. Engl. J. Med. 238:787–793 (1948).
B. A. Chabner, C. E. Myers, C. N. Coleman, and D. G. Johns. The clinical pharmacology of antineoplastic agents.N. Engl. J. Med. 292:1107–1113 (1975).
W. A. Bleyer. The clinical pharmacology of methotrexate.Cancer 41:36–51 (1978).
M. Levitt, M. B. Mosher, R. C. Deconti, L. R. Farber, R. T. Skeel, J. C. Marsh, M. S. Mitchell, R. J. Papac, E. D. Thomas, and J. R. Bertino. Improved therapeutic index of methotrexate with “leucovorin rescue.”Cancer Res. 33:1729–1734 (1973).
D. D. Shen and D. L. Azarnoff. Clinical pharamacokinetics of methotrexate.Clin. Pharmacokin. 3: 1–13 (1978).
R. G. Buice, W. E. Evans, C. A. Nicholas, P. Sidhu, A. B. Straughn, M. C. Meyer, and W. R. Crom. Radioassay, and radioimmunoassay of serum methotrexate, as compared with liquid chromatography.Clin. Chem. 26:1902–1904 (1980).
S. K. Howell, Y. Wang, R. Hosoya, and W. W. Sutow. Plasma methotrexate as determined by liquid chromatography, enzyme-inhibition assay, and radioimmunoassay after high-dose infusion.Clin. Chem. 26:734–737 (1980).
J. L. Cohen, G. H. Hisayasu, A. R. Barrientos, M. S. B. Nayar, and K. K. Chan. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid Chromatographic analysis of methotrexate and 7-hydroxymethotrexate in serum.J. Chromatogr. 181:478–483 (1980).
S. A. Jacobs, R. G. Stoller, B. A. Chabner, and D. G. Johns. 7-Hydroxymethotrexate in human subjects and rhesus monkeys receiving high dose methotrexate.J. Clin. Invest. 57:534–538 (1976).
R. E. Kates and T. N. Tozer. Separation of methotrexate and nonmethotrexate components in rat plasma.J. Pharm. Sci. 62:2056–2057 (1973).
H. M. Redetzki, J. E. Redetzki, and A. L. Elias. Resistance of the rabbit to methotrexate: isolation of a drug metabolite with decreased cytotoxicity.Biochem. Pharmacol. 15:425–433 (1966).
D. M. Valerino, D. G. Johns, D. S. Zahavko, and V. T. Oliverio. Studies of metabolism of methotrexate by intestinal flora.I. Biochem. Pharmacol. 21:821–831 (1972).
S. A. Jacobs, R. G. Stoller, B. A. Chabner, and D. G. Johns. Dose-dependent metabolism of methotrexate in man and rhesus monkeys.Cancer Treat. Rep. 61:651–656 (1977).
J. L. Wisnicki, W. P. Tong, and D. B. Ludlum. Analysis of methotrexate and 7-hydroxy-methotrexate by high pressure liquid chromatography.Cancer Treat. Rep. 62:529–532 (1978).
K. K. Chan, M. S. B. Nayar, and J. L. Cohen. Metabolism of methotrexate in man after high and conventional doses.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 28:551–561 (1980).
W. E. Evans, C. F. Stewart, P. R. Hutson, D. A. Cairnes, W. P. Bowman, G. C. Yee, and W. R. Crom. Disposition of intermediate-dose methotrexate in children with acute lymphocytic leukemia.Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 16:839–842 (1982).
M. L. Chen, W. P. McGuire, T. E. Lad, and W. L. Chiou. Pharmacokinetics of methotrexate and 7-hydroxymethotrexate in patients using a specific HPLC assay.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol., in press.
J. Lankelma and E. V. D. Klein. The role of 7-hydroxymethotrexate during methotrexate anti-cancer therapy.Cancer Lett. 9:133–142 (1980).
M. L. Chen and W. L. Chiou. Sensitive and rapid high-performance liquid Chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of methotrexate and its metabolites in plasma, saliva, and urine.J. Chromatogr. 226:125–134 (1981).
W. L. Chiou, G. Lam, M. L. Chen, and M. G. Lee. Arterial-venous plasma concentration differences of six drugs in the dog and rabbit after intravenous administration.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 32:27–39 (1981).
W. L. Chiou and G. Lam. The significance of arterial-venous plasma concentration difference in clearance studies.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 20:197–203 (1982).
S. Bojholm, O. B. Paulson, and H. Falchs. Arterial and venous concentrations of phenobar-bital, phenytoin, clonazepam, and diazepam after rapid intravenous injections.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 32:478–483 (1982).
J. D. Best and J. B. Halter. Release and clearance rates of epinephrine in man: importance of arterial measurements.J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 55:263–268 (1982).
G. Lam and W. L. Chiou. Determination of renal clearances using arterial and venous plasma: procainamide in rabbits.J. Pharm. Sci. 70:1373–1375 (1981).
G. Lam and W. L. Chiou. Determination of the steady-state volume of distribution using arterial and venous plasma data from constant infusion studies with procainamide.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 34:132–134 (1982).
W. L. Chiou, G. Lam, M. L. Chen, and M. G. Lee. Effect of arterial-venous plasma concentration difference on the determination of mean residence time of drugs in the body.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 35:17–26 (1982).
W. L. Chiou. The physiological significance of the apparent volume of distribution Vd,area or Vd,β, in pharmacokinetic studies.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 33:499–508 (1981).
W. L. Chiou. New physiologically-based methods for the calculation of the apparent steady-state volume of distribution in pharmacokinetic studies.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 20:255–258 (1982).
G. Lam and W. L. Chiou. Arterial and venous blood sampling in pharmacokinetic studies: propranolol in rabbits and dogs.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 33:33–48 (1981).
M. L. Chen, G. Lam, M. G. Lee, and W. L. Chiou. Arterial and venous blood sampling in pharmacokinetic studies: griseofulvin.J. Pharm. Sci. 71:1386–1389 (1982).
E. Watson, J. L. Cohen, and K. K. Chan. High-pressure liquid Chromatographic determination of methotrexate and its major metabolite, 7-hydroxymethotrexate, in human plasma.Cancer Treat. Rep. 62:381–387 (1978).
M. G. Lee, M. L. Chen, and W. L. Chiou. Pharmacokinetics of drugs in blood. II. Unusual distribution and storage effect of furosemide.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 34:17–28 (1981).
W. L. Chiou. Critical evaluation of potential error in pharmacokinetic studies of using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level-time curve.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6:539–546 (1978).
W. L. Chiou. New calculation method for mean apparent drug volume of distribution and application to rational dosage regimens.J. Pharm. Sci. 68:1067–1069 (1979).
W. L. Chiou. New calculation method of mean total body clearance of drugs and its application to dosage regimens.J. Pharm. Sci. 69:90–91 (1980).
S. M. Huang and W. L. Chiou. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of chlorpheniramine in rabbits after intravenous administration.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 9:711–723 (1981).
M. L. Chen and W. L. Chiou. Tissue metabolism and distribution of methotrexate in rabbits.Drug Metab. Disp. 10:706–707 (1982).
M. L. Chen and W. L. Chiou. Clearance studies of methotrexate and 7-hydroxymethotrexate in rabbits after multiple-dose infusion.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 11:515–527 (1983).
A. J. Patterson, W. A. Ritschel, D. Zelliner, and S. H. Kim. Methotrexate serum and saliva concentrations in patients.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 19:381–385 (1981).
K. Yamaoka, Y. Tanigawara, T. Nakagawa, and T. Uno. Capacity-limited elimination of cefmetazole in rat.Int. J. Pharm. 10:291–300 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was in part supported by a grant from the National Cancer Institute, PHS CA 29754.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, ML., Chiou, W.L. Pharmacokinetics of methotrexate and 7-hydroxy-methotrexate in rabbits after intravenous administration. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 11, 499–513 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062208
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062208