Abstract
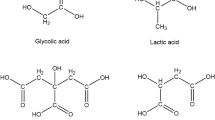
The polycarboxylate siderophore, rhizoferrin, and its dehydration products were separated by preparative HPLC and characterized by13C-NMR,1H-NMR, UV, circular dichroism (CD) and IR spectroscopy, and also by capillary electrophoresis. Assginment of all carbon atoms and protons by NMR spectra confirmed the structure of rhizoferrin and gave evidence for the presence of the cyclized dehydration byproducts, imidorhizoferrin and bis-imidorhizoferrin. The imido forms were also characterized by their mobility during capillary electrophoresis. UV spectra revealed a 1∶1 iron:ligand ratio above pH 3. Based on the absorption maximum of the metal ligand charge transfer hand at 335 nm a molar extinction coefficient of 2300m −1 cm−1 was calculated for ferric rhizoferrin. CD measurements revealed that the quarternary carbon atoms of the two citric acid residues possess anR,R configuration and that the iron complex of rhizoferrin adopts a A configuration around the metal center.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drechsel H, Metzger J, Freund S, Jung G, Boelaert JR, Winkelmann G. 1991 Rhizoferrin—a novel siderophore from the fungusRhizopus microsporus var.rhizopodiformis.Biol Met 4, 238–243.
Konestchny-Rapp S, Jung G, Meiwes J, Zähner H. 1990 Staphyloferrin A: a structurally new siderophore from staphylococci.Eur J Biochem 191, 65–74.
Nomoto K, Sugiura Y, Takagi S. 1987 Mugineic acids, studies on phytosiderophores. In: Winkelmann G, van der Helm D, Neilands JB, eds.Iron Transport in Microbes, Plants and Animals. Weinheim: VCH; 401–425.
Smith MJ, Shoolery NJ, Schwyn B, Holden I, Neilands JB. 1985 Rhizobactin, a structurally novel siderophore fromRhizobium meliloti.J Am Chem Soc 107, 1739–1743.
Thieken A, Winkelmann G. 1992 Rhizoferrin—a complexone type siderophore of the Mucorales and Entomophthorales (Zygomycetes).FEMS Microbiol Lett 94, 37–42.
Winkelmann G. 1991Handbook of Microbial Iron Chelates. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press
Winkelmann G. 1992 Structures and functions of fungal siderophores containing hydroxamate and complexone type iron binding ligands.Mycol Res 96, 529–534.
Wong G, Kappel M, Raymond KN, Matzanke B, Winkelmann G. 1983 Coordination of microbiol iron transport compounds 24. Characterization of coprogen and ferricrocin, two ferric hydroxamate siderophores.J Am Chem Soc 105, 810–815.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drechsel, H., Jung, G. & Winkelmann, G. Stereochemical characterization of rhizoferrin and identification of its dehydration products. Biometals 5, 141–148 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061320
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061320