Abstract
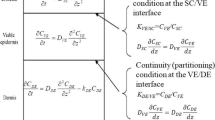
Several theories describing percutaneous drug absorption have been proposed, incorporating the mathematical solutions of differential equations describing percutaneous drug absorption processes where the vehicle and skin are regarded as simple diffusion membranes. By a solution derived from Laplace transforms, the mean residence time MRTand the variance of the residence time VRTin the vehicle are expressed as simple elementary functions of the following five pharmacokinetic parameters characterizing the percutaneous drug absorption: (1) k d, which is defined as the normalized diffusion coefficient of the skin, (2) kc, which is defined as the normalized skin-capillary boundary clearance, (3) the apparent length of diffusion of the skin ld, (4) the effective length of the vehicle lv, and (5) the diffusion coefficient of the vehicle Dv. All five parameters can be obtained by the methods proposed here. Results of numerical computation indicate that: (1) concentrationdistance curves in the vehicle and skin approximate two curves which are simply expressed using trigonometric functions when sufficient time elapses after an ointment application; (2) the most suitable condition for the assumption that the concentration of a drug in the uppermost epidermis can be considered unchanged is the case where the partition coefficient between vehicle and skin is small, and the constancy of drug concentration is even more valid when the effective length of the vehicle is large; and (3) the amount of a drug in the vehicle or skin and the flow rate of the drug from vehicle into skin or from skin into blood becomes linear on a semilogarithmic scale, and the slopes of those lines are small when Dv is small, when the partition coefficient between vehicle and skin is small, when lv is large, or when kc is small. A simple simulation method is also proposed using a biexponential for the concentration-time curve for the skin near the skin-capillary boundary, that is, the flow rate-time curve for drug passing from skin into blood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Kubota and T. Ishizaki. A theoretical consideration of percutaneous drug absorption.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 13:55–71 (1985).
K. Kubota and T. Ishizaki. A calculation of percutaneous drug absorption. I. Theoretical.Comput. Biol. Med. 16:7–19 (1986).
K. Kubota and T. Ishizaki. A calculation of percutaneous drug absorption. II. Computation results.Comput. Biol. Med. 16:21–37 (1986).
R. J. Feldman and H. I. Maibach. Absorption of some organic compounds through the skin in man.J. Invest. Dermatol. 54:399–404 (1970).
R. C. Wester, P. K. Noonan, S. Smeach, and L. Kosobud. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of intravenous and topical nitroglycerin in the rhesus monkey: Estimate of percutaneous first-pass metabolism.J. Pharm. Sci. 72:745–748 (1983).
W. I. Higuchi. Analysis of data on the medicament release from ointments.J. Pharm. Sci. 51:802–804 (1962).
R. H. Guy and J. Hadgraft. Physicochemical interpretation of the pharmacokinetics of percutaneous absorption.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 11:189–203 (1983).
R. J. Scheuplein, I. H. Blank, G. J. Brauner, and D. J. MacFarlane. Percutaneous absorption of steroids.J. Invest. Dermatol. 52:63–70 (1969).
R. J. Scheuplein. Percutaneous absorption after twenty-five years: Or “old wine in new wineskins.”J. Invest. Dermatol. 67:31–38 (1976).
R. H. Guy and H. I. Maibach. Drug delivery to local subcutaneous structures following topical administration.J. Pharm. Sci. 72:1375–1380 (1983).
K. Yamaoka, T. Nakagawa, and T. Uno. Statistical moments in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6:547–558 (1978).
B. J. Poulsen, E. Young, V. Coquilla, and M. Katz. Effect of topical vehicle composition on the invitro release of fluocinolone acetonide and its acetate ester.J. Pharm. Sci. 57:928–933 (1968).
C.-C. Hwang and A. G. Danti. Percutaneous absorption of flufenamic acid in rabbits: Effect of dimethyl sulfoxide and various nonionic surface-active agents.J. Pharm. Sci. 72:857–860 (1983).
L. Z. Benet and R. L. Galeazzi. Noncompartmental determination of the steady state volume of distribution.J. Pharm. Sci. 68:1071–1074 (1979).
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier.Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1982, p. 48.
D. Arndts and K. Arndts. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of transdermally administered clonidine.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 26:79–85 (1984).
T. R. MacGregor, K. M. Matzek, J. J. Keirns, R. G. A. van Wayjen, A. van den Ende, and R. G. L. van Tol. Pharmacokinetics of transdermally delivered clonidine.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 38:278–284 (1985).
J. E. Shaw. Pharmacokinetics of nitroglycerin and clonidine delivered by the transdermal route.Am. Heart J. 108:217–223 (1984).
J. E. Shaw and S. K. Chandrasekaran. Controlled topical delivery of drugs for systemic action.Drug Metab. Rev. 8:223–233 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubota, K., Ishizaki, T. A diffusion-diffusion model for percutaneous drug absorption. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 14, 409–439 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01059200
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01059200