Abstract
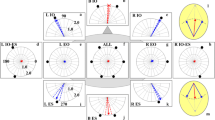
Postural responses to vibrostimulation (50–100 Hz, 0.5 mm, 4–8 sec) of muscles of the back surface of the neck were studied in healthy subjects. In the sitting position, vibrostimulation evoked local displacements (backward head deflection), but global postural responses (forward inclination of the whole body) developed in the standing position. The amplitude of the evoked body inclination was dependent upon the site of the vibrostimuli application along the vertebral column. Asymmetrical application of vibrostimuli to the muscles of the right or left neck side was accompanied by development of a lateral component in the postural response. Changes in the spatial orientation of the head led to the changes in postural response direction: head turning to the right resulted in right-side body deviation during vibration, and vice versa. Illusions of head bend caused by habituation to its static turning were accompanied by precisely the same changes in the direction of body deviation. It is assumed that “neck-evoked” motor events are mediated via central mechanisms that are involved in perception of the head and body position in space.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Magnus,Body Positioning [in Russian], USSR Acad. Sci. Publ. House, Moscow (1962).
G. G. J. Rademaker,Gleichgewichtsreaktionen und Muskeltonus unter besonderer Berucksichtigung ihres Verhaltnis bei Kleinhirosen Springer, Berlin (1981).
T. D. Roberts,Neurophysiology of Postural Mechanisms, Butterworths (1978).
F. J. R. Richmond and U. C. Abrahams, “Morphology and distribution of muscle spindles in dorsal muscles of the cat neck,”J. Neurophysiol. 28, No. 6, 1322–1339 (1975).
F. J. R. Richmond and U. C. Abrahams, “Physiological properties of muscle spindles in dorsal neck muscles in the cat,” ibid.,42, No. 3, 604–617 (1979).
F. J. R. Richmond and D. A. Barker, “Anatomical organization and sensory receptor content of soft tissues surrounding upper cervical vertebrae in cat,” ibid.,48, No. 1, 49–61. (1982).
P. K. Rose and S. A. Keirstead, “Cervical motoneurons,” in:Control of Head Movement B. Peterson, F. Richmond (eds.), Oxford University Press, New York (1988), pp. 37–48.
U. J. Wilson, K. Ezure, and S. I. B. Timerick, “Tonic neck reflex of the decerebrate cat: response of spinal interneurons to natural stimulation of neck and vestibular receptors,”J. Neurophysiol. 51, No. 3, 567–577 (1984).
D. A. Barker and U. C. A. Abrahams, “Central projection from neck afferent systems,” in:Control of Head Movement B. Peterson, F. Richmond (eds.), Oxford University Press, New York (1988), pp. 63–75.
J. Kasper, R. H. Schor, B. J. Yates, and U. L. Wilson, “Three-dimensional sensitivity and caudal projection of neck spindle afferents,”J. Neurophysiol. 59, No. 5, 1497–1509 (1988).
N. Hirai, “Cerebellar pathways contribution to head movement,” in:Control of Head Movement B. Peterson, F. Richmond (eds.), Oxford University Press, New York (1988), pp. 187–195.
O. Pompeiano, “The tonic neck reflex: supraspinal control,” in:Control of Head Movement B. Peterson, F. Richmond (eds.), Oxford University Press, New York (1988), pp. 108–119.
G. G. Berntson and M. W. Torrelo, “Expression of Magnus tonic neck reflexes in distal muscles of prehension in normal adults,”Physiol. Behav. 19, No. 4, 585–587 (1977).
T. Fukuda,Statokinetic Reflexes in Equilibrium and Movement Tokyo University Press, Tokyo (1981).
V. S. Gurfinkel, Yu. S. Levik, and M. A. Lebedev, “Postural automatisms developed by an increase in tonic background,”USSR Acad. Sci. Rep. 305, No. 5, 1266–1269 (1989).
A. Gessel, “The tonic neck reflex in human infant,”J. Pediatr. 13, No. 3, 455–459 (1938).
M. Gregoric, T. Takeya, J. B. Baron, and J. C. Bessineton, “Influence of vibration of neck muscles on balance control in man,”Agressology 19, 37–38 (1978).
G. Eklund, “General features of vibration-induced effects on balance,”Uppsala J. Med. Sci. 77, No. 1, 112–124 (1972).
C. Quoniam, J. P. Roll, A. Deat, and J. Massion, “Proprioceptive induced interactions between segmental and whole body posture,” in:Disorders of Posture and Gait Th. Brandt, W. Paulus, et al. (eds.), Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart, New York (1990), pp. 194–197.
C. M. Oman, “Motion sickness: a synthesis and evaluation of the sensory conflict theory,”Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 68, No. 2, 294–303 (1990).
R. Bianconi and J. R. Van der Meulen, “The response to vibration of the end organ of mammalian muscle spindles,”J. Neurophysiol. 26, No. 1, 177–190 (1963).
J. W. Lance, P. DeGail, and P. D. Neilson, “Tonic and phasic spinal cord mechanisms in man,”J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 29, No. 3, 535–544 (1966).
G. M. Goodwin, D. I. McCloskey, and P. B. C. Matthews, “The contribution of muscle afferents to kinaesthesia shown by vibration induced illusions of movement and by effects of paralyzing joint afferents,”Brain 95, No. 4, 705–748 (1972).
R. Lackner and M. S. Levine, “Changes in apparent body orientation and sensory localization induced by vibration of postural muscles: vibratory myesthetic illusions,”Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 50, No. 4, 346–354 (1979).
B. Biguer, M. L. Donaldson, A. Hein, and M. Jannerod, “Neck muscle vibration modifies representation of visual motion and direction in man,”Brain 111, 1405–1424 (1988).
V. S. Gurfinkel, K. Ye. Popov, B. N. Smetanin, and V. Yu. Shlykov, “Changes of vestibulomotor response directions during habituation for long-lasting static bend of the head in man,”Neirofiziologiya 21, No. 6, 210–217 (1989).
K. Ye. Popov, B. N. Smetanin, V. S. Gurfinkel, et al., “Spatial perception and vestibulomotor responses in man,” ibid.,18, No. 6, 779–787 (1986).
F. J. R. Richmond and P. P. Uidal, “The motor system: Joint and muscle of the neck,” in:Control of Head Movement B. W. Peterson, F. J. R. Richmond (eds.), Oxford University Press, New York (1988), pp. 1–21.
V. S. Gurfinkel, K. Ye. Popov, and M. U. Lypshiz, “Testing of the vertical posture regulation system by vibrational stimulation of muscle spindles,”Fiziol. Cheloveka 3, No. 3, 635–643 (1977).
J. P. Roll and R. Roll, “Kinaesthetic and motor effects of extraocular muscle vibration in man,” in:Eye Movements K. O'Regan, A. Levy-Schoen (eds.), Elsevier, Amsterdam (North-Holland), (1987), pp. 57–68.
V. S. Gurfinkel, Ye. Ye. Debreva, and Yu. S. Levik, “Role of the internal model in the perception of the position of movements,”Fiziol. Cheloveka 12, No. 4, 769–776 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 101–108, March–April, 1993.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smetanin, B.N., Popov, K.Y. & Shlykov, V.Y. Postural responses to vibrostimulation of the neck muscle proprioceptors in man. Neurophysiology 25, 86–92 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01054155
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01054155