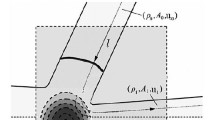
Abstract
A model is presented describing the sequence of events leading up to linear shapedcharge (LSC) liner collapse and jet/slug formation. Metallographie techniques were utilized to determine the relative efficiency of various liner configurations, i.e. the volume percentage of metal participating in jet formation. The microstructures of selected LSC fragments and some of the more interesting structural details and their implications are discussed. Timing screens and flash X-ray techniques were employed to provide data concerning the velocity of LSC jet and slug fragments and their relationship to liner configuration and material properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. H. Goodenow,Trans. Q. ASM 59 (1966) 804.
C. M. Fowler, F. S. Minshall andE. G. Zukas, “Response of Metals to High Velocity Deformation” (Interscience, New York, 1961) p. 275.
H. F. Kaiser andH. F. Taylor,Trans. AIME 27 (1939) 227.
Naval Weapons Center, “Warhead Department-Linear Shaped Charge Ejecta”, China Lake, California, March 1968 (NWC TP 4100-9, Part 3).
G. Birkhoff, D. P. Macdougall, E. M. Pugh andSir G. Taylor,J. Appl. Phys. 19 (1948) 563.
R. S. Eichelberger andE. M. Pugh,ibid. 23 (1952) 537.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayes, G.A. Linear shaped-charge (LSC) collapse model. J Mater Sci 19, 3049–3058 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01026984
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01026984