Summary
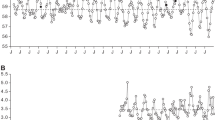
Exercise metabolic rate was established by indirect calorimetry in 18 healthy subjects. Each subject was tested every month for 1 year. Four variables demonstrated a circannual rhythm and its acrophases occured in the following months:RQ in October; exercise metabolic rate in April; acceleration of heart rate during exercise in February; percentage of body fat in August.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brennan PJ, Greenberg G, Miali WE, Thompson SG (1982) Seasonal variation in arterial blood pressure. Br Med J 285: 919–923
Burton AC (1935) Human calorimetry. II. The average temperature of the tissues of the body. J Nutr 9: 261–280
Cornélissen G, Halberg F, Stebbings J, Halberg E, Carandente F, Hsi B (1980) Chronobiometry with pocket calculators and computer systems. Ric Clin Lab 10: 333–285
Durnin JVG, Rahaman MM (1967) The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurements of skinfold thickness. Br J Nutr 21: 681–689
Erikssen J, Rodahl K (1979) Seasonal variation in work performance and heart rate response to exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 42: 133–140
Flatt JP (1979) Interactions between energy and protein metabolism in man. Z ErnÄhrungswiss [Suppl] 23: 58–71
Halberg F, Tong YL, Johnson EA (1967) Circadian system phase, an aspect of temporal morphology; procedures and illustrative examples. In: Mayersbach HV (ed) The cellular aspects of biorhythms. Symposium on Biorhythms. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 20–48
Ingemann-Hansen T, Halkjaer-Kristensen J (1982) Seasonal variation of maximal oxygen consumption rate in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 49: 151–157
Ohno T, Kuroshima A (1973) Seasonal variation of basal metabolism with special reference to its relation to the age. Jpn J Biometeor 9: 12–13
Sasaki T, Halberg F (1979) Reproducibility during decades and individualization of circannually rhythmic metabolic rate in Japanese men and women. In: Advances in the biosciences, vol 19. Chronopharmacology. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 247–254
Statistical Bulletin (1966) Metrop Life Insurance Comp 47: 1–3
Zahorska-Markiewicz B (1980) Weight reduction and seasonal variation. Int J Obesity 4: 139–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the National Institute of Food and Nutrition
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahorska-Markiewicz, B., Markiewicz, A. Circannual rhythm of exercise metabolic rate in humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 52, 328–330 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01015221
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01015221