Abstract
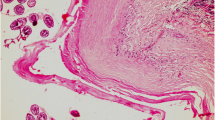
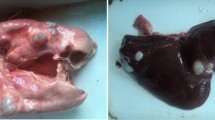
Protoscolices ofEchinococcus granulosus isolated from hydatid cysts of sheep and donkeys in Jordan were cultured in vitro using a modified diphasic culture system. Protoscolices from these two sources manifested differences in the mode of development, evagination and growth rates. Protoscolices isolated from sheep cysts grew in vitro in the polyzoic direction up to the three- to four-segmented mature worms, reaching a length of 2.9 mm. In contrast, donkey protoscolices failed to develop beyond the early stages, even after 67 days of culturing. On prolonged culturing, few worms of donkey origin reached the banding and segmentation stages, attaining a maximal length of 1.6 mm at periods ranging between 81 and 114 days of culturing. None of these segmented worms showed genital differentiation or analgen. The evagination and growth rates of protoscolices isolated from donkey liver cysts were compared with those obtained from sheep liver or lung cysts. The most significant difference in these rates occurred at the commencement of the segmentation stage. Differences in the development, growth and evagination rates observed between the donkey and sheep forms may reflect the strain variation ofE. granulosus in this country.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Hafez SK, Al-Yaman FM, Said IM (1986a) Further studies on prevalence of hydatidosis in slaughtered animals from North Jordan. Z Parasitenkd 72:89–96
Abdel-Hafez SK, Said IA, Al-Yaman FM (1986b) Comparative aspects on the fertility and viability of hydatid cysts in sheep from North Jordan. Jpn J Parasitol 35:490–496
Al-Yaman FM, Assaf L, Hailat N, Abdel-Hafez SK (1985) Prevalence of hydatidosis in slaughtered animals from North Jordan. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 79:501–506
Dailey MD, Sweatman GK (1965) The taxonomy ofEchinococcus in the donkey and dromedary in Lebanon and Syria. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 59:463–477
Macpherson CNL, Smyth JD (1985) In vitro culture of theEchinococcus granulosus from protoscolices of human, camel, sheep and goat origin from Kenya and buffalo origin from India. Int J Parasitol 15:137–140
McManus DP (1981) Biochemical study of adult and cystic stage ofEchinococcus granulosus of human and animal origin from Kenya. J Helminthol 55:21–27
McManus DP, Macpherson CNL (1984) Strain characterization in the hydatid organismEchinococcus granulosus: current status and new prospectives. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 78:193–198
McManus DP, Smyth JD (1982) Intermediary carbohydrate metabolism in protoscolices ofEchinococcus granulosus (horse and sheep strain) andE. multilocularis. Parasitology 84:351–366
Meyer MC, Olsen OW (1980) Essentials of parasitology. M.W.C. Brown, pp 236–241. Published in USA (dubuque, Iowa)
Said IM (1987) Antigenic characterization of hydatid cyst components and comparative morphology of protoscolices extracted from various intermediate hosts in Jordan. MSc Thesis, Department of Biological Sciences, Yarmouk University, Irbid, Jordan
Said IM, Abdel-Hafez SK, Al-Yaman FM (1988) Morphological variation ofEchinococcus granulosus protoscolices of hydatod cysts of human and various domestic animals in Jordan. Int J Parasitol 18:1111–1114
Shennak MM, Tarawneh MS, Amr SS, Al-Sheikh TM, Abu-Rajab MT, Gree SS (1985) Patterns of hepatomegaly in Jordanians: a prospective study of 800 cases. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 79:443–448
Smyth JD (1967) Studies on tapeworm physiology: XI. In vitro cultivation ofEchinococcus granulosus from protoscolex to the strobilar stage. Parasitology 57:111–133
Smyth JD (1979)Echinococcus granulosus andE. multilocularis: in vitro culture of the strobilar stage from protoscolices. Angew Parasitol 20:137–147
Smyth JD (1985) In vitro culture ofEchinococcus. Proceedings of the 13th International Congress of Hydatidology, Madrid, 24–27 April, pp 84–89
Smyth JD, Davies Z (1974a) In vitro culture of the strobilar stage ofEchinococcus granulosus (sheep strain): a review of the basic problems and results. Int J Parasitol 4:631–644
Smyth JD, Davies Z (1974b) Occurrence of physiological strains ofEchinococcus granulosus by in vitro culture of protoscolices from sheep and horse hydatid cysts. Int J Parasitol 4:4443–4445
Smyth JD, McManus D, Barrett NJ, Bryceson A, Cowie AGA (1980) In vitro culture of human hydatid material. The Lancet p 442
Thompson RCA (1977) Hydatidosis in Great Britain. Helminthol Abstr Ser A 46:10
Thompson RCA, Kumaratilake LM (1985) Comparative development of Australian strains ofEchinococcus granulosus in dingoes and domestic dogs with further evidence for the origin of the Australian sylvatic strain. Int J Parasitol 15:535–542
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work received financial support from U.S. AID (grant 6.132) and the Yarmouk University Research Council
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hijjawi, N.S., Abdel-Hafez, S.K. & Al-Yaman, F.M. In vitro culture of the strobilar stage ofEchinococcus granulosus of sheep and donkey origin from Jordan. Parasitol Res 78, 607–616 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936460
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936460