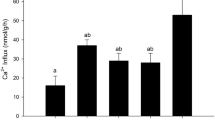
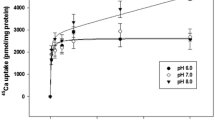
Summary
-
1.
Na and Cl efflux and gill potential were recorded simultaneously in sea water (SW)-adapted mullet.
-
2.
After transfer of the fish to freshwater (FW), an instantaneous decline of the Na efflux was observed, explained by the reversal of the gill potential which occurred simultaneously.
-
3.
Addition of increasing amounts of K or Na sulphate to FW was followed by a progressive depolarization or even a reversal of the gill potential and by a progressive increase of the Na efflux. K was far more efficient than Na in producing these effects.
-
4.
The change in gill potential was not of sufficient magnitude to explain the observed increase of Na efflux.
-
5.
Transfer from SW to FW also produced a decline of the Cl efflux. Addition of K to FW enhanced not only the Na but also the Cl efflux.
-
6.
Injection of SCN was followed in SW-adapted fish by an increase in plasma Na and Cl and the Cl efflux was depressed by about 50% while the Na efflux remained unchanged.
-
7.
After transfer of the fish to FW, the K dependent Na and Cl effluxes were depressed by SCN, while the depolarizing effect of K remained unchanged.
-
8.
The SCN efflux across the gill represented only 0.1% of the Cl efflux. SCN does not substitute for Cl in the Cl extrusion pump.
-
9.
These results suggest that the branchial Cl pump is associated with Cl exchange diffusion mechanism and with a Na/K exchange carrier insensitive to potential changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burg, M. B., Green, N.: Function of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am. J. Physiol.224, 659–668 (1973)
De Renzis, G.: Mécanisme de l'action inhibitrice du thiocyanate sur la pompe à chlore branchiale du poisson rouge. J. Physiol. (Paris)69, 290A (1974)
De Renzis, G.: The branchial chloride pump in the goldfishCarassius auratus: relationship between Cl-/HCO3- and Cl-/Cl- exchanges and the effect of thiocyanate. J. exp. Biol., in press (1975)
Epstein, F. H., Maetz, J., De Renzis, G.: Active transport of chloride by the teleost gill: inhibition by thiocyanate. Am. J. Physiol.224, 1295–1299 (1973)
Evans, D. H., Mallery, C. H., Kravitz, L.: Sodium extrusion by a fish acclimated to sea water: physiological and biochemical description of a Na-for-K exchange system. J. exp. Biol.58, 627–636 (1973)
Evans, D. H., Carrier, J. C., Bogan, M. B.: The effect of external potassium ions on the electrical potential measured across the gills of the teleostDormitator maculatus. J. exp. Biol.61, 277–283 (1974)
Garcia-Romeu, F., Motais, R.: Mise en évidence d'échanges Na+/NH +4 chez l'anguille d'eau douce. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.17, 1201–1204 (1966)
Goldin, S. M., Tong, S. W.: Reconstitution of active transport catalyzed by the purified sodium and potassium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from canine renal medulla. J. Biol. Chem.249, 5907–5915 (1974)
Goldman, D. E.: Potential, impedance and rectification in membranes. J. gen. Physiol.27, 36–60 (1943)
Greenwald, L., Kirschner, L. B., Sanders, M.: Sodium efflux and potential difference across the irrigated gill of sea water adapted rainbow troutSalmo gairdneri. J. gen. Physiol.64, 135–147 (1974)
Hodgkin, A. L., Katz, B.: The effect of sodium ions on the electric activity of the giant axon of the squid. J. Physiol. (Lond.)108, 37–77 (1949)
House, C. R., Maetz, J.: On the electrical gradient across the gill of the sea water adapted eel. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.47A, 917–924 (1974)
Kerstetter, T. H., Kirschner, L. B.: HCO −3 -dependent ATPase activity in the gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.48B, 581–589 (1974)
Kirschner, L. B.: The study of NaCl transport in aquatic animals. Am. Zool.10, 365–376 (1970)
Kirschner, L. B., Greenwald, L., Sanders, M.: On the mechanism of sodium extrusion across the irrigated gill of sea water-adapted rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. gen. Physiol.64, 148–165 (1974)
Maetz, J.: Sea water teleosts: evidence for a sodium-potassium exchange in the branchial sodium-excreting pump. Science166, 613–615 (1969)
Maetz, J.: Transport mechanisms in sea-water adapted fish gills. In: Alfred Benzon Symposium V “Transport mechanisms in epithelia” (eds. Ussing, H. H., Thorn, N. A.), pp. 427–441. Copenhagen: Munsgaard 1973
Maetz, J.: Origine de la différence de potentiel électrique transbranchiale chez le poisson rougeCarassius auratus. C. R. Acad. Sci.279D, 1277–1280 (1974)
Maetz, J., Bornancin, M.: Biochemical and biophysical aspects of salt secretion by chloride cells in teleosts. Fortschr. Zool.23, 322–362 (1975)
Motais, R.: Les mécanismes d'échanges ioniques branchiaux chez les Téléostéens. Annales Inst. Océanogr. Monaco45, 1–48 (1967)
Motais, R., Isaia, J.: Evidence for an effect of ouabain on the branchial sodium-excreting pump of marine teleosts: interaction between the inhibitor and external Na and K. J. exp. Biol.57, 391–422 (1972)
Motais, R., Garcia-Romeu, F., Maetz, J.: Exchange-diffusion effect and euryhalinity in Teleosts. J. gen. Physiol.50, 391–422 (1966)
Pic, P., Maetz, J.: Differences de potentiel transbranchial et flux ioniques chezMugil capito adapté à l'eau de mer. Importance de l'ion Ca++. C. R. Acad. Sci.280D, 983–986 (1975)
Pic, P., Mayer-Gostan, N., Maetz, J.: Branchial effects of epinephrine in the sea-water adapted mullet: II. Na+ and Cl− extrusion. Am. J. Physiol.228, 441–447 (1975)
Potts, W. T. W., Eddy, F. B.: Gill potentials and sodium fluxes in the flounderPlatichthys flesus. J. comp. Physiol.87, 29–48 (1973)
Rocha, A. S., Kokko, J. P.: Sodium chloride and water transport in the medullary thick ascending limb of Henle. J. Clin. Invest.52, 612–623 (1973)
Shuttleworth, T. J., Potts, W. T. W., Harris, J. N.: Bioelectric potentials in the gills of the flounderPlatichthys flesus. J. comp. Physiol.94, 321–329 (1974)
Smith, P. G.: The ionic relations ofArtemia salina (L.): II. Sodium, chloride and water fluxes. J. exp. Biol.51, 739–757 (1969)
Smith, P. G.: Dependence of ion flux across a membrane on ionic concentration. J. theor. Biol.41, 269–286 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maetz, J., Pic, P. New evidence for a Na/K and Na/Na exchange carrier linked with the Cl− pump in the gill ofMugil capito in sea water. J Comp Physiol B 102, 85–100 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691295
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691295